Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
The pharmacy is closed on Sundays and holidays.
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: delivery of medicines, medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2021 Pharmacy 84.
Fosfomycin
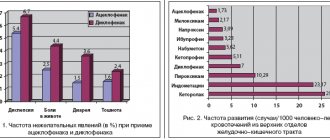
The following undesirable effects are presented by organ system in accordance with the following gradation of the frequency of their occurrence: very common - more than 10% (≥1/10), frequent - more than 1%, but less than 10% (≥1/100 to <1/10 ), uncommon - more than 0.1%, but less than 1% (≥1/1000 to <1/100), rare - more than 0.01%, but less than 0.1% (≥1/10000 to <1/1000 ), very rare - less than 0.01% (<1/10000, including individual reports), unknown (cannot be estimated based on available data).
Immune system disorders
: rarely - acute hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactic shock). If any symptoms of anaphylactic reactions develop, such as dyspnea, hypotension, cyanosis, urticarial rash, severe malaise, it is necessary to discontinue the drug and begin appropriate symptomatic therapy.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
: uncommon - rash, pruritis, urticaria, exanthema. Skin redness, erythema, frequency unknown - angioedema.
Digestive system disorders
: infrequently - diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, anorexia, change in taste, loss of appetite, rarely - stomatitis, severe colitis with blood in the stool, pseudomembranous colitis. If patients experience abdominal pain or frequent bowel movements, it is necessary to stop taking the drug and begin appropriate symptomatic therapy.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract
: often - transient increase in the activity of liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase), infrequently - increased levels of lactate dehydrogenase, bilirubin, rarely - impaired liver function, jaundice, frequency unknown - cholestatic hepatitis. In such cases, patients should be under medical supervision. If any liver dysfunction is detected, it is necessary to stop taking the drug and begin appropriate symptomatic therapy.
Nervous system disorders
: rarely - numbness, headache. Dizziness, decreased sensitivity, frequency unknown - increased fatigue, confusion, convulsions. If seizures develop, it is necessary to stop taking the drug and begin appropriate symptomatic therapy.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
: infrequently - shortness of breath, rarely - cough, acute attack of bronchial asthma, discomfort in the chest, a feeling of squeezing in the chest.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
: rarely - leukopenia, anemia, granulocytopenia, eosinophilia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis or thrombocytopenia. very rarely - aplastic anemia. Therapy must be carried out under the control of the patient's blood count. If any disorders develop, it is necessary to stop taking the drug and begin appropriate symptomatic therapy.
Cardiovascular disorders
: infrequently - thrombophlebitis, rarely - rapid heartbeat, vascular pain, hyperemia.
Renal and urinary tract disorders
: rarely - impaired renal function, edema, increased concentration of urea in the blood, proteinuria.
General and administration site disorders
: infrequently - increased body temperature, pain at the injection site, rarely - phlebitis, thirst, feeling of general malaise.
Laboratory and instrumental data
: rarely - hypernatremia, hypokalemia, electrolyte imbalance.
- Magazine archive /
- 2018 /
The effectiveness of fosfomycin trometamol in acute uncomplicated cystitis
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/urology.2018.6.70-75
A.V. Kuzmenko, V.V. Kuzmenko, T.A. Gyaurgiev
Department of Urology (Head – Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor A.V. Kuzmenko) Voronezh State Medical University named after. N. N. Burdenko”, Voronezh, Russia
Introduction. Acute cystitis is the most common manifestation of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. The choice of an antibacterial drug for the treatment of this disease is determined not only by the spectrum of antimicrobial activity against pathogens, but also by the pharmacokinetics of the drug, which would ensure its high concentrations in urine with a single or double dose, as well as a high safety profile and reasonable cost. One of the drugs whose effectiveness in the treatment of patients with UTI has been proven is fosfomycin, which has been on the pharmaceutical market for a long time and is widely used in urological practice. Given the persistent trend towards a decrease in the sensitivity of uropathogens to antibacterial drugs, there is also a risk of a decrease in the effectiveness of fosfomycin. This necessitates monitoring the resistance of the main pathogens to it. This article presents our experience of using fosfomycin in the treatment of women with acute uncomplicated cystitis. Purpose of the study: to evaluate the effectiveness of fosfomycin trometamol in the treatment of women with acute uncomplicated cystitis. Materials and methods. From September to November 2021, we examined and treated 57 women with acute uncomplicated cystitis aged 19 to 40 years. All patients were prescribed Fosfomycin Esparma (fosfomycin trometamol) once, 1 sachet after urination. Examinations were carried out on the 1st, 3rd and 7th days. Urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia, and pain intensity were assessed. A general urinalysis and bacteriological examination of urine samples with uroculture culture on solid nutrient media were also performed, establishing the type of pathogens, sensitivity to antibiotics and the degree of bacteriuria. Results. When contacted, all patients complained of pain in the projection of the bladder, frequent urination in small portions, and a feeling of discomfort in the urethra. All women were diagnosed with leukocyturia and bacteriuria. By the 3rd day after taking fosfomycin, dysuric symptoms persisted in 22.8% of patients, pain – in 17.5%. In 42% of women, slight leukocyturia remained. Bacteriological analysis of urine did not reveal the growth of pathogens. By the 7th day after the start of therapy, all observations showed normalization of all clinical and laboratory parameters. Conclusion. Considering the wide spectrum of action, low resistance of uropathogenic strains, high level of safety and compliance, based on the results of our study, we recommend the use of fosfomycin as a first-choice drug in the treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection.
Key words: lower urinary tract infections, acute cystitis, fosfomycin, dysuria
The full text of the article is available in the Doctor's Library
Literature
1. The urology. Russian clinical guidelines / pod red. Yu.G. Alyaev, PV Glybochko, DY Pushkar. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2021. 544 p. Russian (Urology. Russian clinical guidelines. Edited by Yu.G. Alyaev, P.V. Glybochko, D.Yu. Pushkar. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2018. 544 p.).
2. Pickard R., Bonkat G., Bartoletti R. et al. EAU Guidelines on urological infections. Eur Urol. 2017;67(6):1099–1109.
3. Alyaev Yu.G., Glybochko PV, Gadgieva ZK A role of determination of functional state of lower urinary tract for choosing of treatment strategy in patients with chronic cystitis and chronic unobstructed pyelonephritis. Urologiia. 2011;6:4–8. Russian (Alyaev Yu.G., Glybochko P.V., Gadzhieva Z.K. The role of determining the functional state of the lower urinary tract in the choice of treatment tactics in patients with chronic cystitis and chronic non-obstructive pyelonephritis. Urology. 2011;6:4–8) .
4. Gadgieva ZK, Kazilov YB The features of approach to prophylaxis of recurrent lower urinary tract infection. Urologiia. 2016;S3:65–76. Russian (Gadzhieva Z.K., Kazilov Yu.B. Features of the approach to the prevention of recurrent lower urinary tract infections. Urology. 2016;S3:65–76).
5. Kuz'menko AV, Kuz'menko VV, Gyaurgiev TA Chronobiologic approach to the treatment of chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in acute phase. Urologiia. 2021:2:60–65. Russian (Kuzmenko A.V., Kuzmenko V.V., Gyaurgiev T.A. Chronobiological approach to the treatment of chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in the acute stage. Urology. 2021:2:60–65).
6. Gyaurgiev TA, Kuz'menko AV, Vakhtel' VM, Luk'yanovich PA The treatment of patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in acute phase in combination with pthototherapy with use of apparatus “Svetozar”. A systematic analysis and management in biomedical systems. 2014;13(4):821–824. Russian (Gyaurgiev T.A., Kuzmenko A.V., Vakhtel V.M., Lukyanovich P.A. Treatment of patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in the acute stage in combination with phototherapy using the Svetozar apparatus. System analysis and management in biomedical systems 2014;13(4):821–824).
7. Foxman B. Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Dis. Mon. 2003;9(1):53–70.
8. Kuz'menko AV, Gyaurgiev TA, Kuz'menko VV An effectiveness of complex phytotherapy in the treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection in women. Urologiia. 2018;4:10–13. Russian (Kuzmenko A.V., Gyaurgiev T.A., Kuzmenko V.V. The effectiveness of the use of complex herbal remedies in the treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in women. Urology. 2018;4:10–13).
9. Sinyakova LA A current view on the antibacterial therapy of urinary tract infection. A management strategy of patients with recurrent cystitis. Urologiia. 2010;3:45–49. Russian (Sinyakova L.A. Modern views on antibacterial therapy of the urinary tract. Tactics for managing patients with recurrent cystitis. Urology. 2010;3:45–49).
10. Kuz'menko AV, Gyaurgiev TA, Khimicheva MN, Titov AY, Turbin AS, Diogenova VA The results of using phototherapy and chronotherapy for the treatment of women with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in acute phase. A systematic analysis and management in biomedical systems. 2016;15(4):614–619. Russian (Kuzmenko A.V., Gyaurgiev T.A., Khimicheva M.N., Titov A.Yu., Turbin A.S., Diogenova V.A. Results of the use of phototherapy and chronotherapy in the treatment of women with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in the acute stage. System analysis and control in biomedical systems. 2016;15(4):614–619).
11. Gyaurgiev TA, Kuz'menko AV, Vlasova JV, KHimicheva MN An assessment of effectiveness of chronotherapy and phototherapy in combination therapy of patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in acute phase. A systematic analysis and management in biomedical systems. 2015;14(3):422–425. Russian (Gyaurgiev T.A., Kuzmenko A.V., Vlasova Zh.V., Khimicheva M.N. Evaluation of the effectiveness of chronotherapy and phototherapy in the complex treatment of patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in the acute stage. System analysis and management in biomedical systems. 2015;14(3):422–425).
12. Gyaurgiev TA, Kuz'menko AV, Lavrenov AL A morphometric analysis of the effectiveness of chronotherapy and phototherapy in therapy of patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in acute phase. A systematic analysis and management in biomedical systems. 2015;14(3):477–481. Russian (Gyaurgiev T.A., Kuzmenko A.V., Lavrenov A.L. Morphometric analysis of the effectiveness of chronotherapy and phototherapy in the treatment of patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis in the acute stage. System analysis and management in biomedical systems. 2015;14(3) :477–481).
13. Gilbert DN, Moellering RC, Eliopoulus GM, Chambers HF, Saag MS The stanford guide to antimicrobal therapy. 2010, Antimicrobal therapy Inc. USA. 219 p.
14. Shepherd AK, Pottinger PS AK Management of Urinary Tract Infections in the Era of Increasing Antimicrobial Resistance. Med Clin N Am. 2013;97:737–757.
15. Deck D., Winston L. Beta-lactam and other cell wall- and membrane-active antibiotics. Basic and clinical pharmacology / ed. by B. Katzung,S. Masters, A. Trevor. 12th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2012.
16. Gupta K., Hooton TM, Stamm WE Increasing antimicrobial resistance and the management of uncomplicated community-acquired urinary tract infections. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001;135:41–50.
17. Palagin IS, Sukhorukova MV, Dekhnich AV, Eidel'stein MV, Shevelev AN, Gtinev AV, Perepanova TS, Kozlov RS, research group “DARMIS”. The current state of antibiotic resistance of pathogens of community- acquired infections of the urinary tract in Russia: the results of the DARMIS study” (2010–2011). Klinicheskaya mikrobiologia i antimicrobnaya himioterapiya. 2012;14(4):280–302. Russian (Palagin I.S., Sukhorukova M.V., Dekhnich A.V., Eidelshtein M.V., Shevelev A.N., Grinev A.V., Perepanova T.S., Kozlov R.S., "DARMIS" research group. Current state of antibiotic resistance of pathogens of community-acquired urinary tract infections in Russia: results of the "DARMIS" study (2010–2011). Clinical microbiology and antimicrobial chemotherapy. 2012;14(4):280–302).
18. Laurent OB et al. An effectiveness of fosfomycin trometamol for treatment of patients with chronic recurrent cystitis. Effectivnaya farmakoterapiya v urologii 2008;4:15. Russian (Laurent O.B. et al. The effectiveness of fosfomycin trometamol in the treatment of patients with chronic recurrent cystitis. Effective pharmacotherapy in urology. 2008;4:15).
19. Loran OB, Sinyakova LA, Kosova IV The mistakes in antibacterial therapy of acute pyelonephritis. Consilium medicum. 2008;9-10:37–40. Russian (Lauran O.B., Sinyakova L.A., Kosova I.V. Errors in antibacterial therapy of acute pyelonephritis. Consilium medicum. 2008;9-10:37–40).
20. Reffert JL, Smith WJ Fosfomycin for the treatment of resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Insights from the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34(8):845–857.
21. Minassian MA et al. A comparison between single-dose fosfomycin trometamol (Monuril) and a 5-day course of trimethoprim in the treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infection in women. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 1998;10(1):39–47.
22. Ceran N. et al. A randomized comparative study of single-dose fosfomycin and 5-day ciprofloxacin in female patients with uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections. J. Infect. Chemother. 2010;16(6):424–430.
23. Etienne M. et al. Antibiotic treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis based on rapid urine test and local epidemiology: lessons from a primary care series. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014;14:137.
24. Yarovoy SK A role of fosfomycin in the treatment of the diseases of urinary tract. Eksperimental'naya i klinicheskaya urologiia. 2013;4:115–120. Russian (Yarovoy S.K. The place of fosfomycin in the treatment of diseases of the urinary system. Experimental and Clinical Urology. 2013;4:115–120).
25. Frank A.J.M., Moll J.M.H., Hort J.F. A comparison of three ways measuring pain. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1982;21:200–211.
About the authors / For correspondence
AUTHORIZATION: A. V. Kuzmenko – Doctor of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, Head. Department of Urology, Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education VSMU named after. N. N. Burdenko, Voronezh, Russia; e-mail
Similar articles
- Systemic enzyme therapy in the treatment of women with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis
- Endovascular treatment of persistent dysuria and chronic pelvic pain in pelvic varicose veins in women
- The use of D-mannose in the prevention of recurrent lower urinary tract infections in women
- Reasons for late detection of bladder tuberculosis
- Are there alternative methods of antibiotic therapy and prevention of uncomplicated urinary tract infections?