Causes of development of hypothalamic syndrome
The hypothalamus is a section of the brain that is responsible for regulating humoral and nervous functions. This department also regulates metabolism, blood vessel activity, mental functions, thermoregulation, sexual and eating behavior. A variety of reasons can cause disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamus:
- malignant tumors in the brain;
- neurointoxication caused by exposure to alcohol, toxic substances, and drugs;
- traumatic brain injuries of varying severity that damaged the hypothalamus;
- pathological processes that are found in the vascular system and lead to stroke or osteochondrosis in the cervical spine;
- chronic diseases, hypertension, bronchial asthma, gastric ulcer;
- pregnancy, as well as the hormonal changes it causes in a woman’s body;
- mental or psychological tension, stress or shock;
- infections such as rheumatism, influenza, malaria, chronic tonsillitis;
- A high level of vascular permeability in the hypothalamic region plays an important role in the development of pathology, since this is what affects the penetration of toxins and viruses into this area of the brain.
Classification of hypothalamic syndrome
In endocrinology, a lot of attention is paid to the study of hypothalamic syndrome. As a result of long-term research, a classification of the disease was developed, according to which many of its forms are distinguished.
Based on etiology, several types of the disease are distinguished, which were caused by various reasons: neuroinfection, traumatic brain injury, constitutional exogenous obesity, neuroendocrine restructuring of the body during puberty.
According to clinical manifestations, the syndrome is classified depending on the predominant symptom in the clinical picture, which may be obesity, germinal disorder, hypercortisolism, neurocirculatory disorder.
According to the course of the disease, the following forms are distinguished: progressive, stable, regressive, recurrent. As for the forms of hypothalamic syndrome, these include the following:
- Vegetative-vascular form. The most common form of the disease, occurring in the form of crises. It is characterized by clinical manifestations such as heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia, blood pressure fluctuations, and respiratory dysfunction.
- Violation of thermoregulation. Since the hypothalamus plays a very important role in the process of regulating body temperature, patients experience an increase in body temperature. In addition, symptoms of this form of the syndrome include attacks of hunger, thirst, and obesity. Often, a violation of thermoregulation is accompanied by chills.
- Hypothalamic (diencephalic) epilepsy. This form is characterized by pain in the stomach and heart, tremors, general weakness, breathing disorders, causeless fear, and rapid heartbeat. Over time, complications such as convulsions, disturbances of consciousness, and a series of epileptic seizures appear.
- Neurotrophic form. Patients experience trophic disorders: obesity or, on the contrary, sudden weight loss, swelling, headaches. During exacerbations or after them, a rash may appear, which is accompanied by severe itching.
- Neuromuscular form. The main manifestation of this form is physical asthenia. During it, patients complain of numbness and stiffness of the limbs. In addition, attacks occur from time to time during which patients are unable to walk or stand for some time.
- Sleep and wakefulness disorders.
- Pseudoneurasthenic and psychopathological form. Patients who have been diagnosed with this form of the disease complain of anxiety, heart palpitations, unreasonable fear, a feeling of lack of air, severe headache, chills, ringing in the ears and even sound hallucinations.
As for the frequency of diagnosing different forms of the syndrome, the first place is occupied by the vegetative-vascular form (32%), the second is the metabolic-endocrine form (27%), and the third is the neuromuscular syndrome (10%).
Sympathoadrenal crisis
Sympathoadrenal crisis in hypothalamic syndrome is manifested by severe headache, pain in the heart, palpitations, a feeling of fear, palpitations, a feeling of fear, difficulty breathing, numbness of the extremities. During a crisis, the skin is pale, dry, blood pressure (BP) is elevated, there may be slight hyperthermia (37.0; 37.1; 37.2; 37.3; 37.4; 37.5; 37.6; 37.8 ; 37.9 degrees Celsius), dilated pupils, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (reaction) (ESR, ROE), hyperglycemia (increased blood glucose levels). The attack often ends with chills, frequent urination (pollakiuria) or a single copious discharge of urine (polyuria).
Symptoms of hypothalamic syndrome
The clinical picture of symptoms of hypothalamic syndrome is very diverse and polymorphic; it can manifest itself in a large number of permanent or transient disorders. First of all, it is worth noting metabolic disorders, which can manifest themselves in diseases such as:
- diabetes insipidus (dry mouth, polyuria, general weakness);
- adiposogenital dystrophy (increased appetite, weakness, nutritional obesity);
- frontal hyperostasis;
- juvenile basophilism (obesity, arterial hypertension, stretch marks and stretch marks on the skin);
- pituitary cachexia;
- premature puberty or, conversely, its delay;
- gigantism;
- dwarfism
Patients also experience psychovegetative symptoms of the syndrome, including increased fatigue, severe headaches, insomnia, drowsiness, decreased or, conversely, increased sexual desire, sudden mood swings and depression.
There is also a disruption in the functioning of the cardiovascular system: vascular spasms appear, physical endurance decreases, unstable blood pressure is observed, and during stress or physical activity the heartbeat increases.
Patients often experience vasoinsular and sympathoadrenal crises. As for vasoinsular crises, their characteristic symptoms are fever, dizziness, suffocation, nausea, cardiac arrest, general weakness and sweating. Patients also complain of frequent urge to go to the toilet, as well as increased urination. In turn, sympathetic-adrenal crises are usually accompanied by symptoms such as agitation, panic attack, and anxiety.
The duration of such crises can range from 15 minutes to 3 hours. General weakness and fear of a relapse of the crisis persists for quite a long time. Such crises often occur due to emotional stress, pain, changes in meteorological conditions and other reasons. Mostly crises occur in the evening, and are preceded by symptoms such as lethargy, sudden changes in mood, headache and tingling in the heart area.
Complications of hypothalamic syndrome
Treatment of hypothalamic syndrome must be comprehensive and timely, since otherwise various complications may arise. Namely, such complications primarily include:
- gynecomastia (pathology of the mammary glands in men, which is characterized by their significant increase due to tissue hypertrophy);
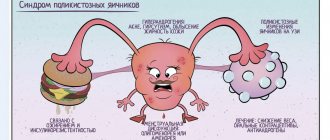
- polycystic ovarian changes;
- menstrual irregularities (oligo- and amenorrhea, uterine bleeding);
- myocardial dystrophy (secondary myocardial damage, which is caused by various metabolic disorders and is accompanied by tachycardia, shortness of breath, and interruptions in heart rhythm);
- hirsutism (hair growth on the face and body in women of an androgenic nature);
- insulin resistance;
- severe form of gestosis (a pathology in which a pregnant woman experiences swelling, increased blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine).
Neurotrophic form
The neurotrophic form includes various trophic disorders due to damage to the hypothalamus: trophic ulcers, focal or diffuse edema of different parts of the body (especially in combination with vegetative-vascular crises), brittle nails, osteoporosis, osteodystrophy, some types of alopecia /hair loss/. In its pure form, the neurotrophic form is rare, and trophic disorders are included in the structure of other forms of hypothalamic syndrome, more often in the neuroendocrine-metabolic form.
Diagnosis of hypothalamic syndrome
The diagnosis is based on a carefully collected medical history, the results of endocrinological and neurological examinations, as well as biochemical and electrophysiological studies. Before prescribing a diagnosis, the doctor must exclude diseases of the endocrine glands, internal organs, and adnexal cavities. Diagnosing hypothalamic syndrome can be accompanied by some difficulties, since its symptoms are similar to the clinical manifestations of endocrine diseases. Therefore, before making a diagnosis, the patient must undergo examination by an endocrinologist and neurologist.
For a thorough diagnosis of hypothalamic syndrome, specific tests such as a sugar curve, EEG of the brain, three-point thermometry, and three-day Zimnitsky tests are used. An important place among diagnostic methods is occupied by blood sugar testing. The study should be carried out on an empty stomach with a load of 100 g of sugar. During a blood test, the doctor can record the following variants of the curve:
- hyperglycemic (blood sugar is significantly increased);
- hypoglycemic (sugar below normal);
- double-humped (a sharp decrease in blood sugar levels is replaced by an increase);
- torpid (a slight increase in glucose occurs at one point).
For hypothalamic syndrome, thermometry is indicated, which is carried out at three points: the rectum and the armpits. During the examination, the doctor records such disorders as isothermia, hypo- and hypertemia, and thermal inversion. To diagnose underlying disorders in the brain, the doctor uses electroencephalography. The three-day test according to Zimnitsky is designed, in turn, to record changes in the fluid consumed and excreted by the patient.
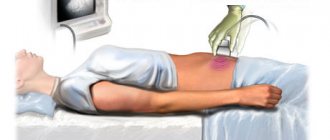
To identify tumors, injuries, the consequences of hypoxia, and increased intracranial pressure, MRI of the brain is prescribed. When diagnosing a disease, it is extremely important to conduct a study of hormones and biochemical parameters. The data obtained will help identify metabolic disorders. In addition to the listed diagnostic techniques, ultrasound of the adrenal glands, internal organs, and thyroid gland is also used to obtain a more detailed clinical picture of the diagnosis.
Treatment of hypothalamic syndrome
Since hypothalamic syndrome is a very complex disease that can manifest itself in different forms, its treatment should be under the supervision of an endocrinologist and neurologist. Consultation with other specialists may also be required.
Drug treatment of hypothalamic syndrome includes the following measures:
- prescribing medications that affect the state of parasympathetic and sympathetic tone (Belloid), beta-blockers (Obsidan), anticholinergics (Platifillin), adrenolytics (Pirroxan), ganglion blockers;
- taking psychotropic drugs - anxiolytics (clonazepam, Xanax) and antidepressants (amitriptyline, lerivon, Prozac);
- general strengthening drugs - vitamin C, as well as B vitamins;
- medications for the treatment of the underlying disease, as well as medications for detoxification therapy.
The main goal of treatment of hypothalamic syndrome is the correction of dysfunction of the hypothalamus. Of course, treatment must be comprehensive. Namely, at the first stage of treatment, the causes that caused the development of the disease are eliminated. For example, this could be the treatment of injuries and tumors, the rehabilitation of infectious foci. If intoxication with drugs, alcohol, or pesticides has been diagnosed, detoxification therapy is prescribed.
Crises bring the greatest discomfort to patients with hypothalamic syndrome. To prevent them, the doctor may prescribe the following medications: pyrroxan, eglonil, bellataminal, antidepressants and grandaxin. To eliminate metabolic disorders, methods such as vitamin therapy and diet therapy are suitable.
It is also extremely important to eliminate various neuroendocrine disorders with the help of replacement therapy, diet, and drugs that regulate neurotransmitter metabolism. To treat the disease, doctors also often prescribe medications that improve cerebral circulation, calcium, and B vitamins.
It is also worth noting that, in fact, hypothalamic syndrome is a whole system of diseases and individual symptoms. Therefore, it is extremely important to identify the leading syndrome during diagnosis, since the effectiveness of treatment will depend on this. In addition, hypothalamic syndrome can manifest itself in different forms.
Therefore, when treating the disease, it is necessary to proceed from the characteristics of each individual case. Namely, acute and chronic infections require urgent absorbable and anti-inflammatory therapy. In turn, post-traumatic syndrome should be treated with cerebrospinal puncture and dehydration. To recover from carbohydrate imbalance, diet and vitamin therapy are prescribed. Additional treatment methods that have shown to be effective include acupuncture, therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy.
Prognosis of hypothalamic syndrome
Since hypothalamic syndrome is considered a very serious and complex disease, timely diagnosis and treatment are extremely important. In case of delayed diagnosis of the disease, complications for the patient’s body are possible. First of all, these include the appearance of arterial hypertension. In addition, diabetes mellitus and myocardial dystrophy may develop against the background of the syndrome.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the patient’s ability to work, which is determined depending on the symptoms and severity of the disease. In any case, during treatment it is necessary to limit physical and mental stress as much as possible, and also avoid working at night. There is a real possibility of complete loss of ability to work. However, it occurs exclusively in the case of frequent crises, as well as as a result of severe and complicated endocrine diseases. By the way, in such cases, depending on their profession, patients may be assigned disability group III or II.
When does it occur and how long does it last?
It is an officially recognized fact that in some cases a person who has recovered from a coronavirus infection suffers from its consequences for a long time, and the severity of the post-Covid syndrome does not depend on the severity of the disease, age, health status and other factors. It is customary to refer to post-Covid syndrome as symptoms that last more than 12 weeks, are changeable, characterized by a wave-like course, and cannot be explained by any other reasons. The syndrome can occur immediately after suffering from Covid or after some time.
Prevention of hypothalamic syndrome
Unfortunately, it is impossible to name any specific preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of hypothalamic syndrome. All prevention of this disease essentially comes down to a correct lifestyle. Firstly, it is necessary to adhere to the principles of a healthy, nutritious diet, which include limiting the consumption of animal fats, as well as introducing fruits and vegetables into the diet. Secondly, it is worth limiting emotional and physical stress. In addition, it is advisable to include foods containing large amounts of iodine in your diet.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist with ultrasound examination (primary) | 4 200 |
| Endoscopic ovarian resection | 95 000 — 125 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions