What is colon cancer?
Colon cancer is formed from the mucous membrane and is malignant in nature. Adenocarcinoma is more common, squamous cell carcinoma is less common.
In most cases, a malignant neoplasm is formed as a result of the transformation of polyps that have arisen in the colon. Thus, timely removal of polyps reduces the likelihood of developing cancer and is a surgical prevention of cancer.
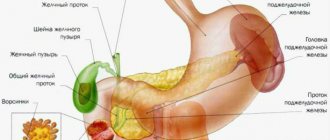
A colon tumor forms in one of its sections:
- Cecum
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
- Descending colon
- Sigmoid colon
Despite the possibility of cancer forming in any part of the colon, the incidence of lesions in each area varies significantly. Thus, in 50% of cases, the tumor affects the sigmoid colon, more than 20% occurs in the cecum, 10% in the transverse colon, and about 15% in areas of the physiological bends of the intestine. And only in 2% of cases, cancer initially affects several parts of the colon.
The rehabilitation period after removal of polyps in the rectum
During the recovery period, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations so that healing and recovery occur as quickly as possible.
It is important to follow a special diet. After about twelve hours or a day, you are allowed to drink pure water or tea without adding sugar or other sweeteners. In the first seven days after surgery, it is allowed to eat only liquid and well-ground foods, which will be easily absorbed by the intestines and will not create additional stress on it.
After about a month, if there are no complications, you can also slowly return to your usual diet. However, fatty and fried foods, alcoholic drinks, spicy and smoked foods remain prohibited.
Additionally, you can do therapeutic exercises. But this should be decided and exercises selected by a specialized doctor.
To undergo diagnosis and treatment of submucosal formation of the intestine, seek help from a private medical specialist. To find out the doctors' work schedule and make an appointment, call the phone number.
Back to list
From the practice of doctors in the endoscopy department. Removal of a large villous tumor of the sigmoid colon
A 67-year-old patient was admitted to City Clinical Hospital No. 52 with complaints of dark blood in the stool and constipation. The woman was sent for a colonoscopy, which revealed a gigantic formation in the sigmoid colon, 7*5*6 cm, with a lobular structure, spreading along the walls of the intestine and almost completely blocking its lumen. It should be noted that 3 months before hospitalization, the patient went to the clinic, where, during colonoscopy, a polyp measuring 3 * 3 m on a wide base was first discovered - a biopsy was taken: villous adenoma. Blood tests show signs of anemia (HB 96 g/l).
The tactics for colon polyps are usually straightforward - removal followed by histological examination.
The patient is being monitored at her place of residence, constipation has resolved, and her blood count has returned to normal. At control colonoscopy after 3 months. - linear scar that does not deform the wall.
| During the process of applying ligatures | Control after 3 months |
Classification of colon cancer
There are several clinical manifestations of the tumor process and their signs:
- obstructive: the main manifestation is intestinal obstruction of varying severity, so when the intestinal lumen is partially closed, the patient experiences a feeling of fullness, bloating, cramping abdominal pain, constipation and poor discharge of gases; in case of acute intestinal obstruction, immediate surgical intervention is required; more common in tumors of the left half of the colon.
- toxic-anemic form: expressed in anemia, weakness, lethargy, increased fatigue. More often found in tumors of the right half of the colon.
- dyspeptic: characteristic symptoms are nausea leading to vomiting, lack of appetite, aversion to food, pain in the epigastric region along with bloating and a feeling of heaviness;
- enterocolitic type of tumor: accompanied by disorders of the functioning of the intestinal tract, manifested by diarrhea or constipation, bloating, rumbling and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, blood and mucous discharge with feces;
- pseudo-inflammatory: the patient experiences an increase in temperature, pain in the abdomen, and intestinal disorders; during laboratory tests - leukocytosis and increased ESR;
Innovative diagnostic methods used in clinics in Belgium
Virtual colonoscopy (CT colonography) is a method of non-invasive visualization of the mucous membrane of the large intestine by constructing a three-dimensional computer model. Its diagnostic value approaches that of conventional colonoscopy, without causing any discomfort to the patient.
PET-MRI is a hybrid of magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography. The method allows you to obtain a detailed image of the intestine with visualization of areas of abnormally increased metabolism (cancer tumor).
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
The first symptoms of the pathological process are practically absent, but there is a slight deterioration in general well-being, a decrease in activity and appetite. In the early stages of the disease, a person begins to gain weight.
Symptoms of colon cancer completely depend on the location of the tumor, size, extent of spread, the presence of other gastrointestinal diseases and complications that arise.
The clinical complex is manifested by a feeling of pain and discomfort, constipation or diarrhea, blood and mucous discharge during bowel movements, and deterioration of well-being.
A more detailed description of the symptoms that appear:
- abdominal pain of varying intensity occurs in 85% of people with a colon tumor;
- a state of discomfort in the intestines is accompanied by a lack of appetite, a feeling of nausea and heaviness in the upper abdomen; disorders of the normal functioning of the intestine are associated with narrowing of the lumen and impaired motility as a result of inflammation of its walls; manifestations of these changes are diarrhea, constipation, rumbling and flatulence; constipation may be replaced by diarrhea; a sharp narrowing of the intestinal lumen leads to complete or partial obstruction;
- an impurity in the feces of a pathological nature is observed in almost half of the patients and consists of purulent discharge, blood and mucous;
- changes in the general well-being of patients occur as a result of the intoxication process: a person feels general malaise, high fatigue, lethargy, weight loss, fever, anemia; more pronounced symptoms of intoxication appear when the tumor is localized in the right half of the colon;
Diet
Nutrition for colorectal cancer should be balanced. The cooks at the Yusupov Hospital include foods high in plant fiber in the patient’s diet. This measure is aimed at preventing constipation and removing toxins. The therapeutic diet for rectal cancer is an addition to the main therapy.
General dietary recommendations for colon cancer:
- Small meals 5-6 times a day;
- Use of fresh products when preparing food;
- Eating boiled or steamed food;
- Refusal of fatty meats, smoked and pickled foods;
- Exclusion from the diet of carbonated drinks and foods that increase gas formation.
The diet for radiation therapy of the rectum requires the exclusion of coarse, salty foods, which irritate the oral mucosa. Nutrition for colon cancer for patients at the Yusupov Hospital is developed by a nutritionist taking into account individual preferences. The diet includes fresh foods
Diagnosis of colon cancer
Diagnosis of colon cancer consists of a set of measures:
- clinical examination methods: collecting anamnesis, presenting complaints, palpation and examination of the patient;
- X-ray examinations: radiography of the abdominal organs, irrigoscopy, virtual colonoscopy.
- endoscopic examinations: fibrocolonoscopy (during a biopsy), if necessary, sigmoidoscopy;
- radionuclide scan of the liver: to detect metastasis of the cancer process;
- ultrasound and CT scan of the abdominal cavity.
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
Recovery after surgery
The Ilyinskaya Hospital has implemented the concept of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS).
This set of measures is aimed at the fastest possible physical and psychological rehabilitation of the patient after even extensive surgical interventions, as well as social adaptation. The ideology is based on the results of many years of international clinical research, recognized and implemented in all developed countries. It includes: preoperative preparation - prehabilitation, a special technique for administering anesthesia during surgery in combination with minimally invasive operating techniques, early mobilization of the patient (you can sit up in bed, do breathing exercises, get to your feet soon after transfer to the ward), early alimony ( You can start eating and drinking soon after surgery). This helps to quickly restore intestinal function and avoid the development of complications from the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
All patients who have undergone surgery for colon cancer remain under the supervision of an oncologist and regularly undergo scheduled examinations to timely detect the progression of the disease and adjust the individual treatment plan.
Treatment methods for colon cancer
The main method of treatment for colon cancer is surgery, sometimes with chemotherapy in the postoperative period.
The method of surgical treatment is determined after carrying out appropriate diagnostic measures to determine the extent of spread of the tumor process:
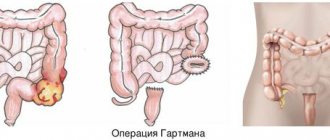
- radical surgery: right or left hemicolectomy, which consists of removing the affected part of the intestine with the further formation of an anastomosis between the two remaining sections; multi-stage interventions involve colostomy with further resection of the affected area.
- palliative operations: performed in the presence of distant metastases and may involve removing part of the intestine or forming bypass anastomoses.
After the operation, it is forbidden to eat food for the first 24 hours; during this time, anti-shock therapy is carried out, as well as measures to eliminate intoxication and dehydration of the body.
Starting from the second day, the patient is allowed to take liquid, semi-soft food and drink warm drinks. Over time, the daily diet includes dishes such as low-fat broths, pureed porridges, pureed vegetables, steamed omelets, herbal teas, various juices and compotes from fresh or frozen fruits and berries.
Therapeutic measures after surgery
After the operation, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where doctors monitor vital functions (blood pressure, oxygen saturation, kidney function), and also provide the necessary therapy. If the postoperative period is favorable, the patient is transferred to a hospital ward, where he receives further treatment. The doctor selects the diet for the patient in the postoperative period individually, depending on the volume and nature of the intervention. The main task after surgery is early rehabilitation of the patient. Subsequent treatment tactics after discharge are determined based on the results of histological examination at the oncology consultation
Survival prognosis
The prognosis for colon tumors largely depends on the stage of the pathological process, the spread of atypical cells to nearby organs, tissues and lymph nodes, as well as on the histological structure of the malignant neoplasm.
The presence of metastases in regional lymph nodes plays a major role in the duration and quality of life after surgery. Thus, among patients with lymph node involvement within 5 years, survival rate was observed in only 40% -50%, and in cases without lymph node involvement, the survival rate was more than 80% of patients.
Establishing diagnosis
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Physical examination, assessment of the general condition of the patient.
- Palpation (in some cases you can detect the tumor with your hands).
- Irrigoscopy (X-ray contrast examination of the colon).
- Endoscopic methods (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy).
- Laboratory diagnostics (blood tests, stool tests, tumor markers).
When a patient first contacts the patient and has characteristic complaints, the doctor will first order tests to confirm or rule out oncology. If the diagnosis is confirmed, additional examinations are prescribed to identify the shape, location and size of the tumor.