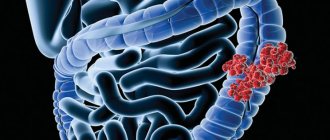
Sigmoid colon cancer often does not manifest clinical symptoms for a long time. For this reason, the diagnosis is often made at a late stage of the tumor process. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital recommend that even with minor manifestations of intestinal discomfort, immediately seek help.
At the Yusupov Hospital, oncologists use the latest methods for diagnosing diseases of the sigmoid colon. Patients are examined using the latest equipment from leading global manufacturers. Laboratory technicians examine blood, feces and other biological materials using high-quality reagents, which allows you to obtain accurate test results.
Surgeons at the Oncology Clinic masterfully perform traditional and innovative surgical interventions. Chemotherapists prescribe patients the most effective antitumor drugs that have minimal side effects. Radiologists conduct radiation therapy with modern devices that allow them to target the pathological focus without damaging the tissue surrounding the tumor.
What is colon cancer?
This is a malignant tumor that is one of the top three among other cancers in terms of incidence and mortality throughout the world.
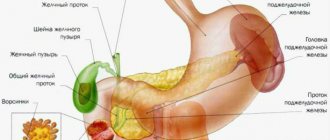
Colon cancer originates from the mucous membrane of the colon and can spread to all layers of the intestinal wall and affect nearby organs and structures. Colon cancer affects men more often.
Most often, this disease is diagnosed between the ages of 50 and 75 years, but recently it has been detected more often than before in young patients.
Indications
There are a number of pathologies for the treatment of which there is a need for this surgical intervention:
- traumatic injuries (in this case, emergency surgery is necessary);
- benign neoplasms that lead to partial or complete obstruction of the intestinal lumen or there is a high risk of malignant degeneration of the tumor;
- malignant neoplasms (if there is cancer, the operation is performed with regional lymphadenectomy to prevent relapse);
- complicated diverticulitis (diverticula are pouch-like protrusions of the intestinal wall that can appear in any part of the gastrointestinal tract, but most often occur in the large intestine);
- volvulus of the sigmoid colon, leading to intestinal obstruction;
- ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane, which leads to severe discomfort for the patient (pain, constipation, frequent bleeding) and cannot be treated with medication.
Causes and risk factors for development
Among the risk factors for developing colon cancer are: a diet high in fat, red meat and low fiber, alcohol consumption, smoking, low physical activity, diabetes, chronic inflammatory diseases of the colon (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), presence of a family history of colorectal cancer.
In 3-5% of patients, colon cancer is associated with the presence of hereditary syndromes (familial adenomatosis of the colon and MUTYH-associated polyposis, Lynch syndrome).
2. Reasons
The etiopathogenesis of cancer, that is, the appearance and non-stop division of immature cells with the development of a tumor from them, growing into neighboring structures, forming its own blood supply network and capable of metastasizing to other parts of the body, is beyond the scope of this article. Let us only note that this mechanism, common to any oncological pathology, still remains the subject of intense research; this, of course, does not mean that it is completely unknown, however, the immediate causes of the fatal “breakdown” of the immune system (one of the tasks of which is the identification and destruction of immature cells) have yet to be established and clarified, which will ultimately make it possible to develop means of reliable prevention and treatment.
Risk factors that contribute to the initiation of the cancer process in the sigmoid colon are well known:
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of “cooked red meat” (WHO wording), fats, sugar and all those food additives, most of which are clear and aggressive carcinogens; insufficient consumption of plant foods and fluids;
- physical inactivity, excess body weight;
- alcohol consumption and smoking (these factors are not included for propaganda purposes: it has long been reliably proven, for example, that in relation to colon cancer, smoking is not only a pathogenetic factor, but also doubles mortality despite therapy);
- mature and old age, especially in the presence of the above risk factors;
- inflammatory and/or ulcerative processes in the intestines;
- tendency to constipation due to hypotension and weakened peristalsis;
- hereditary predisposition;
- the presence of asymptomatic polyps and papillomas in the intestines (some genetically determined forms of polyposis practically guarantee malignancy, i.e. malignant degeneration of intestinal polyps).
Visit our Oncology page
Colon cancer. Symptoms
Early forms of colon cancer do not cause any symptoms for a long time; in most cases, they are detected during colonoscopy in patients without any complaints. As the tumor grows, the patient develops and develops dyspeptic symptoms (decreased appetite, belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, bloating or flatulence, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region), stool disorders, mucus and blood appear in the stool. In patients with damage to the left side of the intestine, intestinal obstruction often occurs. Patients also complain of constant weakness and increased fatigue, causeless weight loss, and progressive iron deficiency anemia is characteristic.
Often, patients consult a doctor only after the appearance of severe symptoms: traces of blood and mucus in the stool, prolonged constipation, changes in the appearance of stool, pain and a significant deterioration in the general condition.
Classification
Taking into account the characteristics of tumor growth, oncologists distinguish two types of sigmoid colon cancer: exophytic and endophytic. Exophytic tumors grow into the intestinal lumen. They are protruding nodes on a thick stalk. As the pathological process progresses, sigmoid colon cancer often ulcerates. Bleeding and infection occurs.
Endophytic cancer of the sigmoid colon grows predominantly deep into the intestine. The tumor spreads along the intestinal wall and can cover the intestine circularly. In its center, areas of ulceration appear. Due to the circular growth of sigmoid colon cancer, the intestinal lumen narrows and the movement of feces becomes difficult. This type of growth is most characteristic of sigmoid colon cancer.
Histologists distinguish three types of sigmoid colon cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma originates from glandular epithelial cells. It can be highly differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated;
- Mucous (mucosal) adenocarcinoma is a type of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma, represented by mucinous cells that secrete large amounts of mucus. The tumor grows quickly and metastasizes early;
- Signet ring cell carcinoma of the sigmoid colon is represented by atypical signet ring-shaped cells, which are formed as a result of intracellular accumulation of mucin, pushing the cell nuclei to the periphery. The tumor is aggressive and has an unfavorable course.
Cancer of the recto-sigmoid colon is represented by two forms: scirrhus and adenocarcinoma.
Diagnosis of colon cancer
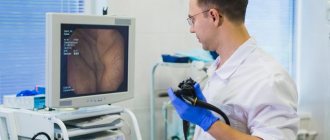
The gold standard for diagnosing colon diseases is colonoscopy. The study allows not only to visualize the tumor, determine the location and size, macroscopic type, assess the risk of complications (perforation, bleeding), but also obtain tissue samples for histological examination.
If colon cancer is detected at colonoscopy, a CT scan of the chest and abdomen with contrast is prescribed to exclude the presence of tumor metastases.
As additional research methods, the following can be performed: MRI of the abdominal cavity and pelvis using contrast; in difficult cases, PET-CT - positron emission tomography - is used.
Stages and methods of treatment of colon cancer
Treatment options for colon cancer depend on the stage of the process. Thus, at stages 0 and 1, it is possible to perform a minimally invasive endoscopic operation during colonoscopy.
Stage 2-3 requires removal of the section of intestine with the tumor and all regional lymph nodes. The method of performing such an operation is determined by the doctor. An open, laparoscopic or robotic method can be used. To improve long-term treatment results, preoperative chemotherapy is sometimes used.
If a patient is diagnosed with stage 3 colon cancer, then after surgery such a patient is prescribed adjuvant chemotherapy - it reduces the risk of tumor recurrence.
In the case of stage 4, the treatment strategy is developed at a multidisciplinary council, taking into account the localization and spread of the primary tumor, metastases, and concomitant diseases. Both chemotherapy and surgery, or a combination of both, can be used.
Forecast
The survival prognosis of patients with sigmoid colon cancer depends on the histological type of the tumor, the level of cell differentiation, the prevalence of the malignant process, the presence of concomitant diseases and the age of the patient.
The average five-year survival rate is 65.2%. A more optimistic prognosis after surgery for adenocarcinoma of the sigmoid colon, since the tumor grows slowly and practically does not metastasize. When sigmoid colon cancer of the first stage is detected, 93.2% of patients overcome the five-year mark, the second - 82.5%, the third - 59.5%. 8.1% of patients with stage 4 sigmoid colon cancer survive up to five years. Therefore, consult a doctor when the first signs of intestinal dysfunction appear.
To establish an accurate diagnosis in the early stages of sigmoid colon cancer, when the first signs of intestinal disorders appear, call the Yusupov Hospital. After a comprehensive examination, if the diagnosis is confirmed, oncologists will provide adequate therapy. After treatment, doctors at the oncology clinic conduct clinical observation, the purpose of which is the timely detection and treatment of early metastases. This makes it possible to improve the quality and increase the life expectancy of patients diagnosed with sigmoid colon cancer.
Make an appointment
Operations performed for colon cancer
Right hemicolectomy – used for tumors of the ascending colon and cecum, hepatic flexure of the colon. The surgeon removes the final portion of the small intestine and the right half of the colon.
Left-sided hemicolectomy - required when the left parts of the colon are affected by tumors.
Resection of the transverse colon is rarely performed when the tumor is located in the middle third of the transverse colon. Most often in such situations they resort to extended right-sided hemicolectomy or extended left-sided hemicolectomy.
Resection of the sigmoid colon - removal of the sigmoid colon with a tumor.
If it is impossible to radically remove the tumor, then to prevent the development of complications, a palliative or symptomatic operation is performed (formation of a bypass intestinal stoma, colon stenting, formation of a bypass anastomosis, etc.), which helps improve the patient’s condition and makes it possible to safely begin chemotherapy.
Symptoms
The insidiousness of malignant tumors of the sigmoid colon is that in the initial stages there are no signs of the disease. The clinical picture unfolds when the process enters stages 3-4.
In this case, general and local symptoms are distinguished. Common symptoms include weight loss, chronic fatigue, increased fatigue, pallor and pasty skin (against the background of chronic iron deficiency anemia).
Local symptoms include:
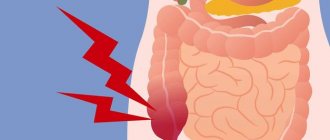
- Abdominal pain. Pain can have various causes, from impaired intestinal motility to tumor growth into adjacent tissues and organs.
- Impaired stool regularity. Patients are bothered by chronic constipation, which is replaced by foul-smelling diarrhea. This occurs due to the fact that feces accumulate above the tumor site, which, in turn, leads to increased fermentation and putrefaction processes, the intestinal contents liquefy, and constipation is replaced by diarrhea. Due to inflammation of the intestinal wall and injury to the tumor, there may be streaks of blood in the stool. When the intestinal lumen is obstructed (blocked) by a tumor, intestinal obstruction develops, which is accompanied by cramping pain, bloating, increased symptoms of intoxication, nausea and vomiting. This condition requires emergency hospitalization in a surgical hospital for immediate medical care.
In addition, signs of sigmoid colon cancer may include:
- Increased gas formation.
- Nausea and bloating.
- Discharge of mucus, blood or pus from the anus.
Therapeutic measures after surgery
After the operation, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where doctors monitor vital functions (blood pressure, oxygen saturation, kidney function), and also provide the necessary therapy. If the postoperative period is favorable, the patient is transferred to a hospital ward, where he receives further treatment. The doctor selects the diet for the patient in the postoperative period individually, depending on the volume and nature of the intervention. The main task after surgery is early rehabilitation of the patient. Subsequent treatment tactics after discharge are determined based on the results of histological examination at the oncology consultation
Possible complications
Possible complications:
- bleeding due to inadequate hemostasis;
- failure of postoperative wound sutures or anastomosis;
- infectious complications (life-threatening conditions such as peritonitis and sepsis may develop);
- dynamic intestinal obstruction (intestinal paresis);
- adhesive disease;
- postoperative hernia.
A sigmoidectomy is a major surgical procedure. However, if the operation is performed correctly by qualified surgeons and the patient follows all recommendations, it is possible to achieve a good quality of life for the patient after resection.
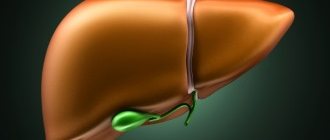
Colon cancer metastases
Metastases can be regional - to the lymph nodes that collect lymph from the intestine, and distant. The most common sites of distant metastases in colon cancer are the liver and lungs. Less commonly, metastases can affect the spleen, adrenal glands, bones, and retroperitoneal lymph nodes. The most difficult to treat are peritoneal metastases - peritoneal carcinomatosis.
It is important to remember that stage 4 is not a death sentence! Correctly developed treatment tactics can achieve 15-year survival in 11% of patients.
Stages
Oncologists distinguish 4 stages of sigmoid colon cancer:
In the first stage of the tumor, the size of the tumor does not exceed two centimeters. The tumor is located within the submucosal layer or mucosa. Regional lymph nodes are not affected by atypical cells.
In the case of the second A stage of cancer, the tumor occupies less than half the circumference of the intestine and does not grow into the wall. There are no metastases in the lymph nodes and internal organs. A cancerous tumor at stage 2B is located in the intestinal wall, but does not extend beyond its boundaries. Oncologists detect metastases in the lymph nodes. There are no distant metastases.
With stage 3A sigmoid colon cancer, the size of the tumor exceeds half the circumference of the intestine. There are no atypical cells in the regional lymph nodes. In stage 3B tumors, regional lymph nodes are affected by metastases.
The tumor in stage 4 cancer blocks the lumen of the sigmoid colon. Hematogenous metastases are detected in other organs. In stage 4 sigmoid colon cancer, nearby organs are affected, and enterovesical fistulas and conglomerates are formed.
Recovery after surgery
The Ilyinskaya Hospital has implemented the concept of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS).
This set of measures is aimed at the fastest possible physical and psychological rehabilitation of the patient after even extensive surgical interventions, as well as social adaptation. The ideology is based on the results of many years of international clinical research, recognized and implemented in all developed countries. It includes: preoperative preparation - prehabilitation, a special technique for administering anesthesia during surgery in combination with minimally invasive operating techniques, early mobilization of the patient (you can sit up in bed, do breathing exercises, get to your feet soon after transfer to the ward), early alimony ( You can start eating and drinking soon after surgery). This helps to quickly restore intestinal function and avoid the development of complications from the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
All patients who have undergone surgery for colon cancer remain under the supervision of an oncologist and regularly undergo scheduled examinations to timely detect the progression of the disease and adjust the individual treatment plan.
Advantages of going to Ilyinskaya Hospital
The treatment strategy for patients with colon cancer at the Ilyinskaya Hospital is based on the concept of a multidisciplinary combined and integrated approach, combining the use of modern surgical technologies with the achievements of radiation, drug and immunotherapy. Each clinical case is reviewed at an oncology council (Tumor-board), which includes: a chemotherapist, an oncologist surgeon, a radiologist, a radiologist, an oncopsychologist, and a rehabilitation physician. This approach allows us to develop the most effective personalized treatment tactics for the patient, take into account all individual nuances and achieve maximum efficiency.