Ampicillin
Ampicillin is an “old man” in the series of semi-synthetic penicillins, the effectiveness of which in relation to objects of the mycoworld allows it to be actively used today. This is a broad-spectrum antibiotic with a bactericidal effect, i.e. it does not inhibit the growth and development of bacteria, as bacteriostatic drugs do, but completely destroys them. The mechanism of action of ampicillin is as follows: it inhibits transpeptidase (an enzyme involved in protein synthesis), prevents the formation of peptide bonds and interferes with the final stage of peptidoglycan synthesis in the cell membrane of a dividing bacterium, causing its death.
The list of objects of ampicillin's close attention will be quite voluminous. The drug is active against the widest range of gram-positive (Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., Enterococcus faecalis, Listeria spp.) and gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Yersinia multocida, Haemophilus influenzae, Shigella spp. ., Proteus mirabilis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis,) bacteria. It is also worth mentioning microorganisms against which ampicillin is powerless: these are all strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, penicillinase-forming strains of Staphylococcus spp., most strains of Proteus vulgaris, Enterobacter spp.
, Klebsiella spp.
The release forms of ampicillin include both oral and parenteral administration. In the first case, these are tablets and capsules, in the second, powder for preparing a solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration. The injectable form of ampicillin is used primarily for severe or moderate infections. So, for meningitis, 14 g of the drug is administered daily in 6-8 intramuscular injections, for gonococcal urethritis - 0.5 g twice during one day. The solution itself is prepared using pharmaceutical water for injection (a solution for intravenous administration can be prepared using saline). The duration of treatment is determined by the severity and nature of the disease and can vary from 5 days to several months. The standard dose of ampicillin for internal use is 0.25 g 4 times a day, taken half an hour to an hour before meals. The maximum daily dose is 3 g. During a course (not one-time) use of the drug, it is recommended to monitor the condition of the liver, kidneys and hematopoietic organs. For chronic infections, it is necessary to periodically change the antibacterial agent to avoid the development of superinfection due to the growth of microorganisms insensitive to ampicillin.
Ampicillin for injection 500 mg bottle No. 1
Dosage forms
powder for the preparation of an infusion solution 500 mg, powder for the preparation of an injection solution, powder for the preparation of an injection solution 0.5 g, powder for the preparation of an injection solution 500 mg, powder for the preparation of a solution for intravenous administration 500 mg, powder for the preparation of a solution for intramuscular administration 500 mg
Manufacturers
ICN Polypharm (Russia), Biosynthesis (Russia), Biochemist (Russia), Borisov Medical Preparations Plant (Belarus), Bryntsalov (Russia), Vaccines and Serums Research Institute (Russia), Kievmedpreparat (Ukraine), Kraspharma (Russia), Moskhimfarmpreparaty them. ON THE. Semashko (Russia), Sintez AKO, Kurgan (Russia), Ferein (Russia)
PharmGroup
Antibiotics of the penicillin group
International nonproprietary name
Ampicillin
Leave procedure
Available with prescription
Compound
The active substance is ampicillin.
pharmachologic effect
Antibacterial, bactericidal. Active against a wide range of gram-positive (alpha- and beta-hemolytic streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., most enterococci) and gram-negative (Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Proteus mirabilis, many species of salmonella, shigella, Escherichia coli) microorganisms. Destroyed by penicillinase, acid-resistant (per os use possible). Food reduces absorption. Poorly penetrates the BBB. Practically does not undergo biotransformation. It is excreted mainly by the kidneys, partially excreted in bile, and in nursing mothers - in milk. Does not accumulate.
Indications for use
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract (pneumonia, lung abscess, bronchitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis), otitis media, peritonitis, sepsis, endocarditis, kidney and urinary tract infections, cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, gonorrhea, biliary system infections, whooping cough, listeriosis, abdominal typhus and paratyphoid, skin and soft tissue infections, musculoskeletal infections, meningitis.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems), severe liver dysfunction, breastfeeding (must be suspended during treatment).
Side effect
Dyspeptic symptoms, dysbacteriosis, superinfections caused by resistant strains; allergic reactions.
Directions for use and dosage
They are set individually depending on the severity and location of the infection and the sensitivity of the pathogen. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of therapy.
special instructions
With long-term treatment with ampicillin in weakened patients, superinfection caused by drug-resistant microorganisms (yeast-like fungi, gram-negative microorganisms) may develop. It is advisable for these patients to simultaneously prescribe B vitamins and vitamin C, and, if necessary, nystatin or levorin.
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 degrees. List B.
Literature
Encyclopedia of Medicines 2003. Medicines M.D. Mashkovsky 14th edition.
Interaction
Reduces the effect of oral contraceptives, increases - anticoagulants, aminoglycoside antibiotics. Allopurinol increases the appearance of skin rashes.
Overdose
It has a toxic effect on the central nervous system (especially in patients with renal failure). Treatment: symptomatic.
Synonyms
Ampiside, Ampic, Ampirex, Ampicillin, Ampicillin Innotek, Ampicillin trihydrate, Ampicillin-AKOS, Ampicillin-Teva, Ampicillin sodium salt sterile, Ampicillin trihydrate, Amplital, Apo-Ampi, Decapen, Zetsil, Campicillin, Mescillin, Penodil, Pentarcin, Pentrexil, Roscillin, Standacillin, Upsampi, Helm-Ampicillin, Helm-Ampicillin, Epicocillin
AMPICILLIN+SULBACTAM por. d/prig. injection 1000+500 mg vial. No. 1 with water solution d/in.
Directions for use and doses
Intravenously (stream and drip), intramuscularly.
The route of administration depends on the severity of the infection and the dose chosen. The following are the total doses of ampicillin and sulbactam (in a 2:1 ratio). In adults and children over 12 years of age and weighing more than 40 kg
for the treatment of moderate infections, 1.5 g is administered intramuscularly or intravenously every 6 hours.
For severe infections - 3 g every 6 hours. The maximum daily dose of sulbactam should not exceed 4 g, which corresponds to a daily dose of the drug equal to 12 g.
Treatment should be continued for at least another 2-3 days after the clinical symptoms of the disease disappear. The duration of treatment is 5-14 days, but in more severe cases it can be increased or additional ampicillin can be prescribed.
For uncomplicated gonorrhea - 1.5 g once.
To prevent postoperative infection - 1.5-3 g during anesthesia, then for 24 hours after surgery at the same dose every 6-8 hours.
In children over 1 month and under 12 years of age (or weighing less than 40 kg)
the drug is administered at a dose of 150 mg/kg per day, which is divided into 3-4 injections. In case of severe infection, the dose can be increased to 300 mg/kg/day. The duration of the course of therapy should not exceed 14 days.
In premature newborns and children in the first week of life, the daily dose of the drug is 75 mg/kg, which is divided into two injections.
In children aged 7 days to 28 days, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 150 mg/kg per day, divided into 3 intravenous administrations.
In patients with impaired renal function, the dosage regimen is adjusted depending on the values of creatinine clearance (CC).
| Creatinine clearance, ml/min | T 1/2, h | Recommended administration mode |
| 30 | 1 | 1.5-3 g every 6-8 hours |
| 15-29 | 5 | 1.5-3 g every 12 hours |
| 5-14 | 9 | 1.5-3 g every 24 hours |
In children with renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), the drug is administered in usual single doses (50-75 mg/kg), increasing the intervals between doses, as indicated in adults.
Preparation of solutions
:
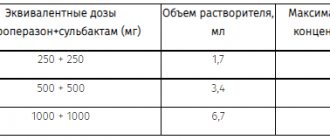
To prepare a solution for intramuscular administration, sterile water for injection, 0.5% procaine solution, and 0.5% lidocaine solution are used as a solvent. Add 4 ml of solvent to a bottle containing 1.5 g of the drug.
To prepare a solution for intravenous jet administration, add 12 ml of water for injection and 0.9% sodium chloride solution to a bottle containing 1.5 g of the drug. Inject slowly over 3-5 minutes.
To prepare a solution for intravenous drip administration, 1.5-3 g of the drug is dissolved in 15 ml of water for injection, then the resulting solution is added to 150-200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution and injected at a speed of 60 -80 drops per minute.
Ampicillin tablets 250 mg No. 20
Ampicillin tablets 250mg No. 20
Ampicillin trihydrate Buy Ampicillin trihydrate in pharmacies
DOSAGE FORMS tablets tablets 250mg
MANUFACTURERS ICN Tomskkhimpharm (Russia) Akrikhin KhFK (Russia) Belgorod "Vremya" (Russia) Belmedpreparaty (Belarus) Biosynthesis OJSC (Russia) Biopharm Pravo-Alfa (Russia) Biokhimik OJSC (Russia) Borisov Medical Preparations Plant (Belarus) Bryntsalov- A (Russia) Veropharm Belgorod branch (Russia) Vilar (Russia) Wicher-Pharm (Russia) Voronezh-Vremya Pharm Production Company (Russia) Voronezhkhimpharm (Russia) Vostok (Russia) Dalkhimpharm (Russia) Darnitsa Pharmaceutical company (Ukraine) Health pharmaceutical company (Ukraine) Irbitsky Chemical-Pharmaceutical Plant (Russia) Kievmedpreparat (Ukraine) Kiev Vitamin Plant (Ukraine) Medisorb (Russia) Moskhimfarmpreparaty im. ON THE. Semashko (Russia) Novosibirsk Plant of Medical Preparations (Russia) Update of PFC (Russia) Organics OJSC (Russia) Pokrovsky Plant of Biological Preparations (Russia) Synthesis AKO Kurgan (Russia) Tatkhimfarmpreparaty (Russia) Tyumen Chemical-Pharmaceutical Plant (Russia) Uralbiopharm (Russia) Usolye -Siberian Chemical Pharmaceutical Plant (Russia)
GROUP Antibiotics of the penicillin group
COMPOSITION Active substance - ampicillin.
INTERNATIONAL NON-PROPENTED NAME Ampicillin
SYNONYMS Ampirex, Ampicillin, Ampicillin trihydrate, Ampicillin-AKOS, Ampicillin-Teva, Ampicillin sodium salt, Ampicillin sodium salt sterile, Amplital, Decapen, Standacillin
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION Antibacterial, bactericidal. Active against a wide range of gram-positive (alpha- and beta-hemolytic streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., most enterococci) and gram-negative (Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Proteus mirabilis, many species of salmonella, shigella, Escherichia coli) microorganisms. Destroyed by penicillinase, acid-resistant (per os use possible). Food reduces absorption. Poorly penetrates the BBB. Practically does not undergo biotransformation. It is excreted mainly by the kidneys, partially excreted in bile, and in nursing mothers - in milk. Does not accumulate.
INDICATIONS FOR USE Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract (pneumonia, lung abscess, bronchitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis), otitis media, peritonitis, sepsis, endocarditis, kidney and urinary tract infections, cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, gonorrhea, biliary system infections, whooping cough, listeriosis, typhoid and paratyphoid fever, skin and soft tissue infections, musculoskeletal infections, meningitis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity (including to other penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems), severe liver dysfunction, breastfeeding (must be suspended during treatment).
SIDE EFFECTS: Dyspeptic symptoms, dysbacteriosis, superinfections caused by resistant strains; allergic reactions.
INTERACTION Reduces the effect of oral contraceptives, increases the effect of anticoagulants, aminoglycoside antibiotics. Allopurinol increases the appearance of skin rashes.
METHOD OF APPLICATION AND DOSAGE Set individually depending on the severity and localization of the infection, the sensitivity of the pathogen. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of therapy.
OVERDOSE Manifests itself as a toxic effect on the central nervous system (especially in patients with renal failure). Treatment: symptomatic.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS With long-term treatment with ampicillin in weakened patients, the development of superinfection caused by drug-resistant microorganisms (yeast-like fungi, gram-negative microorganisms) is possible. It is advisable for these patients to simultaneously prescribe B vitamins and vitamin C, and, if necessary, nystatin or levorin.
STORAGE CONDITIONS: In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 degrees. List B.