What is cetrotide used for?
GnRH is synthesized by the hypothalamus. By acting on the pituitary gland, the hormone stimulates the production of follitropin and luteotropin. These pathways influence ovarian function by regulating the menstrual cycle. When stimulated, the patient is first given medications containing FSH and LH to enhance follicle maturation. Cetrotide is then given to avoid the release of gametes and maintain the follicles at the desired size until a certain period.
Cetrotide, as a GnRH antagonist, allows you to suppress the secretion of endogenous gonadotropic hormones (LH, FSH) to prevent premature ovulation. Thus, spontaneous release of the egg from the ovary is impossible. This allows for the formation of a large number of follicles in the gonads. This increases the chances of successful IVF, since more mature eggs are obtained during puncture.
With natural cycles, one, maximum two oocytes are released monthly. But not all women ovulate every month. There are anovulatory cycles. Inhibition of gonadotropins by Cetrotide is completely reversible.
Indications
Cetrotide is necessary to control hormonal stimulation of the gonads during in vitro fertilization for infertility. It is used to block the release of luteotropin into the bloodstream and prevent the highest level of LH, which is achieved before ovulation. This allows the germ cells to be completely preserved before puncture of the dominant follicle.
The drug can be used only as prescribed by a doctor and under medical supervision. The gynecologist individually selects the dose, regimen, and timing. Treatment cannot be adjusted without the doctor’s knowledge. GnRH antagonists can reduce the duration of therapy and also reduce the risk of gonadal hyperstimulation.
Cetrotide is usually used 5-6 days after the start of hormone stimulation. Treatment is adjusted by the attending physician taking into account many factors.
Cetrotid®
Cetrotide can only be prescribed by a gynecologist. To achieve maximum effectiveness of treatment with Cetrotide, you should carefully read these recommendations.
After the first injection, the patient should be under the supervision of a physician for 30 minutes to ensure that there is no allergic or pseudo-allergic reaction to the administration of the drug. All tools and drugs to stop such a reaction must be available.
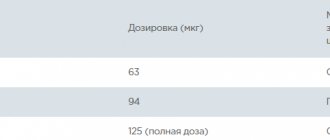
Cetrotide 0.25 mg
The contents of 1 bottle (0.25 mg of cetrorelix) should be administered once a day every 24 hours in the morning or evening.
Administration of the drug in the morning: Treatment with Cetrotide should begin on the 5th or 6th day of ovarian stimulation (approximately 96-120 hours after the start of stimulation) with a gonadotropin preparation, recombinant or isolated from urine, and continue throughout the entire period of gonadotropin stimulation, including the day of administration of the ovulatory dose of human chorionic gonadotropin (CG).
Administration in the evening: Treatment with Cetrotide should begin on day 5 of ovarian stimulation (approximately 96-108 hours after the start of stimulation) with a gonadotropin preparation, recombinant or isolated from urine, and continue throughout the period of gonadotropin stimulation, including the evening preceding the day of administration of the ovulatory dose. HG.
Cetrotide 3.0 mg
The contents of 1 bottle (3.0 mg of cetrorelix) should be administered on the 7th day of ovarian stimulation (approximately 132-144 hours after the start of stimulation) with a gonadotropin preparation, recombinant or isolated from urine.
After a single administration of 3.0 mg of cetrorelix, the effect of the drug continues for at least 4 days. If on the 5th day after administration of Cetrotide 3.0 mg the size of the follicles does not allow ovulation induction to be prescribed, an additional 0.25 mg of Cetrorelix (Cetrotide 0.25 mg) should be administered once a day, starting 96 hours after administration of the drug Cetrotide 3.0 mg and including the day of administration of the ovulatory dose of hCG.
Recommendations for self-administration of the drug Cetrotide 0.25 mg and 3.0 mg (information for the patient).
The first injection must be given by a medical specialist. After receiving appropriate instructions from the doctor about the symptoms that may indicate an allergic reaction, the consequences of such a reaction and the need for its treatment, the patient can self-administer Cetrotide.
Cetrotide is injected subcutaneously into the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall, preferably in the area around the navel. To avoid local irritation upon repeated administration of the drug, the injection site should be changed daily.
Cetrotide should only be diluted in the supplied diluent. During dissolution, the bottle should be gently rocked. To avoid the formation of bubbles, do not vigorously shake to speed up dissolution. Do not use the solution if it is opaque or contains undissolved particles.
From the bottle, draw all its contents into the syringe. This will allow you to administer a dose of cetrorelix of at least 0.23 mg when using Cetrotide 0.25 mg and at least 2.82 mg when using Cetrotide 3.0 mg. The solution should be administered immediately after its preparation.
When self-administering Cetrotide, you must perform the following steps:
1. Wash your hands. It is very important that your hands and all equipment needed for injection are clean.
2. On a clean surface, place everything you need for the injection (one bottle, one syringe with solvent, one yellow-marked needle, one gray-marked needle and two alcohol-soaked swabs).
3. Open the snap cap on the bottle. Wipe the aluminum ring and rubber plug with one swab of alcohol.
4. Take the needle with the yellow marking and remove the wrapper from it. Remove the syringe with solvent from the package. Place the needle on the syringe with solvent and remove the protective cap.
5. Insert the needle into the center of the rubber stopper of the bottle. Inject the solution from the syringe into the vial by slowly pressing the plunger.
6. Without removing the needle from the bottle, gently rock the bottle until the powder is completely dissolved. Avoid vigorous shaking to prevent bubbles from forming during dissolution.
7. Draw the entire contents of the bottle into the syringe. If there is any solution left in the bottle, turn the bottle over and pull out the needle so that its hole is just under the stopper. If you look from the outside at the inside of the stopper, you can control the movement of the needle and liquid. It is very important to draw the entire contents of the bottle into the syringe.
8. Remove the needle from the syringe and put the syringe down. Take the gray marked needle and remove the wrapper from it. Place the needle on the syringe and remove the protective cap.
9. Turn the syringe over with the needle up and press the plunger until all air bubbles come out of the syringe. Do not touch the needle or let it come into contact with any surface.
10. Select the injection site in the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall, preferably in the area around the navel. Take a second swab soaked in alcohol and wipe the skin at the intended injection site. Hold the syringe in one hand. With your other hand, gently squeeze the skin surrounding the injection site and secure it firmly between your fingers.
11. Hold the syringe as you would normally hold a pencil, and at a 45-degree angle, insert the needle completely into the skin.
12. Once the needle is fully inserted, stop squeezing the skin.
13. Carefully pull the syringe plunger back. If blood appears in the syringe, proceed as stated in paragraph 14. If there is no blood, slowly inject the solution by pressing the plunger. After injecting the entire solution, slowly remove the needle and gently press a swab soaked in alcohol onto the skin at the injection site. The needle should be removed from the skin at the same angle at which it was inserted.
14. If blood appears in the syringe, remove the needle from the skin and lightly press it with a tampon at the injection site. This solution cannot be used for repeated injection; pour the contents of the syringe into the sink. Start over from step 1.
15. The syringe and needles can only be used once. Throw them away immediately after use (to avoid injury, put protective caps on the needles).
Preparation of solution for injection
- treat your hands with a disinfectant solution or use medical gloves;
- remove the plastic cap from the glass bottle with powder;
- wipe the cork with alcohol;
- release the yellow mixing needle from the wrapper and place it on the syringe with the solvent;
- Insert a needle into the rubber stopper of the bottle and press the syringe plunger, releasing liquid from it;
- lightly rotate the bottle in your hand until the powder is completely dissolved. Do not shake to avoid the formation of bubbles;
- fill the syringe with the resulting clear solution;
- cover the needle with a cap and unscrew it from the syringe;
- replace the yellow needle with a gray one;
- release air from the syringe;
- wipe the injection area with alcohol;
- pinch the fold on the abdomen, insert the needle and release the medicine, slowly pressing on the piston;
- Press the puncture site with a swab soaked in alcohol. Do not rub.
If an injection is missed, a double dose is not administered. The next injection is given on time. If more than 6 hours have passed, you should notify the doctor.
Preparation of solution for injection
Mode of application
The drug is available in the form of a lyophilisate (powder containing the drug), and a syringe with water for injection is included with it. The product must be used only with the included solvent.
The solvent contained in the syringe must be introduced into the bottle with the drug. During administration, the bottle should be slightly shaken to better dissolve the powder. Vigorous shaking of the bottle should be avoided. After dissolving the drug, it is necessary to draw the entire contents of the bottle into a syringe. The drug must be used immediately after its preparation.
Cetrotide is administered subcutaneously. The most optimal place for injection is the lower abdomen - the area around the navel. After treating the skin with an alcohol wipe, you must insert the needle into the skin fold perpendicularly and press the piston all the way. To avoid redness, the injection site should be changed daily.
Introduction rules
- the solution is injected under the skin of the abdomen. Each time you need to change the injection site;
- use immediately after preparation. The finished product should not be stored;
- give injections at the same time;
- do not use the medicine if the liquid is cloudy or contains foreign particles;
- do not mix with other medications in the same syringe;
- Dispose of the syringe after the injection.
Home self-injections can be done after consulting a doctor, receiving instructions, and studying the instructions in detail.
Introduction rules
Contraindications
Cetrotide is not prescribed if absolute contraindications are identified:
- hypersensitivity to cetrorerix or excipients;
- allergic reactions to GnRH or any similar hormone;
- severe renal and liver failure;
- pregnancy, suspicion of it;
- lactation;
- postmenopause.
With relative restrictions, the gynecologist determines the advisability of individual use of the drug.
Cetrotide Liof for sub solution 250 mg N7
ATX Code:
C07AB07 (Bisoprolol)
Active substance:
bisoprolol
Release form, packaging and composition of the drug
Yellow film-coated tablets, round, biconvex; at the break there is a white or almost white core.
| 1 tab. | |
| bisoprolol fumarate | 5 mg |
Excipients: magnesium stearate - 1.2 mg, colloidal silicon dioxide - 1.2 mg, crospovidone - 1.2 mg, corn starch - 15.6 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - up to 120 mg.
pharmachologic effect
A selective beta1-blocker without internal sympathomimetic activity and does not have membrane stabilizing activity. Reduces plasma renin activity, reduces myocardial oxygen demand, reduces heart rate (at rest and during exercise) and cardiac output, while stroke volume does not decrease significantly. Inhibits AV conduction. Has antianginal and hypotensive effects. In high doses (200 mg or more) it can cause blockade of β2-adrenergic receptors, mainly in the bronchi and vascular smooth muscles.
The hypotensive effect is associated with a decrease in minute blood volume, sympathetic stimulation of peripheral vessels, a decrease in the activity of the renin-angiotensin system (of greater importance for patients with initial hypersecretion of renin), restoration of sensitivity in response to a decrease in blood pressure and an effect on the central nervous system.
The antianginal effect is due to a decrease in myocardial oxygen demand as a result of a decrease in heart rate and decreased contractility, prolongation of diastole, and improved myocardial perfusion.
The antiarrhythmic effect is due to the elimination of arrhythmogenic factors (tachycardia, increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system, increased cAMP content, arterial hypertension), a decrease in the rate of spontaneous excitation of sinus and ectopic pacemakers and a slowdown in AV conduction (mainly in the antegrade and, to a lesser extent, in the retrograde directions via the AV node) and along additional paths.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption - 80-90%, food intake does not affect absorption.
Cmax in blood plasma is achieved after 2-4 hours. Plasma protein binding is 26-33%. Bisoprolol penetrates to a small extent through the BBB and the placental barrier; excreted in breast milk.
Metabolized in the liver.
T1/2 - 9-12 hours. Excreted by the kidneys - 50% unchanged, less than 2% - with bile.
Indications of the active substances of the drug
Arterial hypertension, prevention of angina attacks, chronic heart failure.
Dosage regimen
The method of administration and dosage regimen of a particular drug depend on its release form and other factors. The optimal dosage regimen is determined by the doctor. The compliance of the dosage form of a particular drug with the indications for use and dosage regimen should be strictly observed.
Individual. For oral administration, the daily dose is 2.5-10 mg, the frequency of administration is 1 time / day. The maximum daily dose is 10 mg.
Contraindications for use
Acute heart failure, chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation, cardiogenic shock, collapse, AV block of II and III degrees (without a pacemaker), SSSU; sinoatrial blockade, severe bradycardia (heart rate <50 beats/min), Prinzmetal's angina, marked decrease in blood pressure (systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg), history of severe forms of bronchial asthma and COPD, late stages of peripheral circulatory disorders, Raynaud's disease , pheochromocytoma (without simultaneous use of alpha-blockers), metabolic acidosis, simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors (except for MAO type B inhibitors), children and adolescents under 18 years of age, hypersensitivity to bisoprolol and other beta-blockers.