Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
Whooping cough is an infectious disease characterized by a specific paroxysmal spasmodic cough. It is transmitted by airborne droplets, and the main feature of the disease is the complete absence of innate immunity. Despite the fact that whooping cough affects children in the vast majority of cases, the disease can also occur in adults.
Diphtheria is also an infectious disease that affects the oropharynx area. It can spread to the bronchi, skin, larynx, etc. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as by household contact under certain temperature conditions. The severity and seriousness of this disease is determined by the toxin that the diphtheria bacillus secretes. It can affect the nervous system, heart, blood vessels, kidneys and poses a real threat to health.
Tetanus is a disease caused by a toxic bacterium, the tetanus bacillus. The incidence of death with this disease is very high, especially in children and the elderly. Bacteria enter the body through a cut, wound, or burn. Even a small scratch on the skin can be enough for the development of the disease. It is characterized by muscle spasms up to complete stiffness, convulsions.
These dangerous diseases posed a real threat to life before the advent of vaccines. They mainly affect children, but the vaccination schedule also includes adults. This must be done every 10 years in adulthood, but this issue can be resolved individually, taking into account the patient’s health condition and the opinion of the general practitioner. Multicomponent vaccination allows you to prevent three infections at once in children and adults.
general description
Gardasil is a vaccine, given as an injection (shot), to protect girls and young women, boys and young men from disease caused by the human papillomavirus.
Gardasil for girls and women aged 9 to 26 years protects against female diseases caused by this virus:
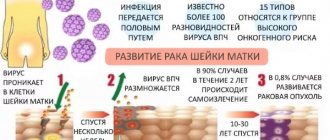
- Cervical cancer;
- Genital warts;
- Cancer of the vulva and vagina;
- Anal cancer;
- Precancerous lesions of the genital area.
At the same age, the vaccine is also given to boys and young men. It protects against dangerous diseases caused by the human papillomavirus.
- Genital warts;
- Anal cancer;
- Precancerous lesions of the anus.
Gardasil only provides protection against disease caused by a specific type of this virus, it targets virus types 6, 11, 16, 18. Most cases of the diseases listed above are caused by these 4 types of HPV. The vaccine does not protect against all other viruses and bacteria, and other types of HPV. It is not intended to treat HPV infection. Use is indicated for protection and prevention against infection.
Adasel
home
Vaccination
Adasel
ADASEL
Vaccine for the prevention of diphtheria (with reduced antigen content), tetanus and whooping cough (acellular), combined, adsorbed for revaccination of children over 6 years of age
(Manufacturer Sanofi Pasteur Limited, Canada).
Whooping cough
- one of the most common childhood infections, an acute infectious disease characterized by a peculiar convulsive cough.
Whooping cough is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis
, which is transmitted by airborne transmission from an infected person.
The peculiarity of whooping cough is the complete absence
is innate immunity
to it
a newborn
can get this disease .
And, in the absence of immunity, the probability of getting sick after close contact with a sick person reaches 100%. Patients may experience prolonged paroxysmal spasmodic coughing for 1-2 weeks. Coughing, especially severe at night, is often accompanied by vomiting. In early infants, whooping cough may be accompanied by apnea ( respiratory arrest
) and
cyanosis
without cough, and in adolescents and adults, the only manifestation of the disease may be a persistent cough, which is uncharacteristic of whooping cough.
The disease can last up to several months. First of all, you should be wary of complications of whooping cough
:
pneumonia
,
convulsions
(in 3% of infants), brain damage (
encephalopathy)
,
respiratory arrest
,
emphysema
, penetration of air into the subcutaneous fatty tissue,
hemorrhage in the brain
or
in the membranes of the eye
, in young children Due to strong tension,
a hernia can form and the rectum may fall out.
The main purpose of vaccination against whooping cough is to reduce the risk of acute whooping cough in infancy.
It is important to note that children in the age group
from 7 to 14 years
occupy a leading place in the structure of cases due to
the weakening of post-vaccination immunity just by the age of 6–7 years.
It is
school-age children
, as well as
parents
, who are one of
the main sources of infection for unvaccinated children in the first months of life
;
whooping cough is especially severe in them.
Diphtheria
- an infectious disease caused by the bacterium
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
(Loeffler's bacillus).
Diphtheria most often affects the oropharynx
, but often affects
the larynx, bronchi, skin and other organs
.
The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets
from a sick person to a healthy person.
If diphtheria affects the oropharynx, then in addition to severe intoxication, the development of croup is possible - suffocation
, which develops when
the airways are obstructed due to developing edema and mechanical obstruction (blockage) with diphtheria film
.
Unfortunately, even now in the 21st century, in countries with low vaccination coverage, diphtheria is still a significant health problem for children. Complications
are dangerous :
infectious-toxic shock: paralysis of the soft palate and vocal cords, neck muscles, respiratory tract and limbs;
nasal voice; choking while eating; pouring liquid food through the nose; motionless hanging of the velum; possible strabismus, ptosis, facial paralysis. Tetanus
an
infectious disease caused by toxic strains
of the rod-shaped bacterium Clostridium tetani
, often
fatal .
The pathogen enters the body through a wound or cut
; infection often occurs through
burns and frostbite
.
Bacteria can enter the body even through minor scratches
(but deep puncture wounds and skin breaks are especially dangerous).
80% of cases of tetanus occur in newborns (when infected through the umbilical cord), as well as in boys under 15 years of age due to their increased trauma. Tetanus
begins suddenly -
with spasms
and
difficulty opening the mouth (trismus)
, which is associated with tonic tension of the masticatory muscles.
Next, the process quickly affects the muscles of the back, abdomen, and limbs. Painful cramps
occur , which appear spontaneously or with minor irritations (touch, light, voice).
The prognosis for the disease is unfavorable
bronchitis, pneumonia, myocardial infarction, sepsis, auto-fractures of bones and spine, dislocations, ruptures of muscles and tendons, separation of muscles from bones, venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary edema
may occur In a later period,
weakness, tachycardia, spinal deformity, contractures of muscles and joints, and temporary paralysis of the cranial nerves occur.
The effectiveness of vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus has been documented. In most clinical trials, effectiveness ranged from 80% to 100%.
Possible reactions:
Painful sensations, compaction at the injection site. Local reaction usually goes away on its own within 2-3 days. General reactions can be in the form of increased fatigue in children and headache in adolescents, an increase in body temperature above 38 °C. It is recommended to reduce pain and in case of hyperthermia, give the child orally paracetamol or ibuprofen in an age-appropriate dosage in the form of syrup, suspension or tablets (for older children). Children with a tendency to allergic reactions are recommended to take antihistamines.
More detailed information on the vaccine can be found at the following link:
https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=79f8061f-3416-4eea-831c-9685a5a552de&t=
Pentaxim and Adasel. What is the difference? What's the best thing to do?
In this video, the head of the BPH prevention department of 143 branch No. 4, Agieva Milana Bashirovna, will tell you more about these two vaccinations.
In 2021, a new vaccine appeared in Russia - “Adasel” - against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough.⠀
One dose of the vaccine contains: ⠀
- tetanus toxoid 5 Lf (more than 20 IU); ⠀
— diphtheria toxoid 2 Lf (more than 2 IU); ⠀
- five acellular components of whooping cough - pertussis toxoid, hemagglutinin, fimbriae agglutinogens, pertactin.
The Adasel vaccine also includes excipients - aluminum phosphate, 2-phenoxyethanol, water for injection. The main difference between this vaccine and other vaccines containing acellular pertussis component is the reduced amount of pertussis antigens to 2.5 mcg.
According to laboratory studies, such a low number allows one to achieve a good level of protection against infection and reduce the possibility of unwanted reactions to vaccination⠀
"Adasel" is a suspension for intramuscular administration. In appearance, it is a cloudy, whitish homogeneous liquid, packaged in 2 ml bottles containing 0.5 ml of vaccine. They are packed in a cardboard box of 1 or 5 units.
At what age is Adasel used? ⠀
Children are vaccinated after 4 years of age. Adults are vaccinated until age 64. The drug is used only for repeated revaccination, that is, before this, the person must be vaccinated with other vaccines containing antigens of whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus.
Primary vaccination "Adasel" is carried out within the time limits established by the national vaccination calendar. For children this is the age of 6–7 years. Adults are vaccinated once every ten years.
Using Adasel for the second and subsequent revaccinations every ten years allows you to create immunity against whooping cough in adolescents and adults. This is important if the family plans to have an infant.
The strategy of vaccinating the entire environment of the child provides protection to children from birth until the development of their own immunity in response to the introduction of DPT at 3–4 and 5–6 months.
In the Children's State Hospital, 143 children attending kindergartens and schools at the age of 6-7 years can receive a second revaccination against diphtheria, whooping cough and tetanus with the Adasel vaccine.
In this video, Alla Vadimovna Malysheva will talk about vaccines for the prevention of Whooping cough, Diphtheria, Tetanus
Description
Gardasil is an injection usually given into a muscle in the arm. The vaccinated person will need to go through 3 stages indicated in the vaccine administration schedule:
- Dose 1 is taken on the day of the first vaccination;
- Dose 2 is administered 2 months after the first injection;
- Dose 3 is required 6 months after the first dose.
Make sure all 3 doses are received on time to get the best protection. If you miss one dose, do not ignore this issue, talk to your doctor.
How effective is the Gardasil vaccine?
It is 100% effective in preventing diseases caused by the four types of HPV included in it, if the woman has not yet been infected with them. For women who have already been infected, the effectiveness is somewhat less.
It is important that pre-existing HPV infections cannot be cured by vaccination. More importantly, approximately 30% of cervical cancers are caused by rarer types of HPV and therefore cannot be prevented by vaccination. Therefore, vaccinated girls and women should, nevertheless, regularly conduct a PAP test.
Contraindications
You should not take Gardasil if you have or experience:
- Allergic reactions after the last use of Gardasil;
- Severe allergic reaction to yeast, amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate, polysorbate 80.
Before taking Gardasil, you must tell your doctor:
- If you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant, the vaccine is not recommended for this category of women;
- About problems with immunity, the presence of HIV infection, cancer, or taking medications that affect the body’s immune system;
- Temperature elevated to more than 37.8°C;
- About the occurrence of an allergic reaction after the next dose of Gardasil;
- About taking any medications sold without a prescription.
Your doctor will help you decide whether you can get vaccinated now.
Also tell your doctor if you have any of the following problems after the vaccine:
- With swollen glands in the neck, armpits, groin;
- Chills and general malaise;
- Joint pain;
- tiredness, unusual weakness, confusion;
- Pain in legs, muscles, chest, abdomen;
- Shortness of breath, bleeding, skin infection and other symptoms.
Should boys be vaccinated?
The vaccine is also effective for boys, but experts debate whether widespread vaccination is justified, weighing the cost of the vaccine against the incidence of penile and anal cancer. In 2012-2014 studies in the United States, HPV vaccination was also offered to boys. We recommend, if possible, that boys be vaccinated against HPV, as the prevalence of anal cancer is growing, and genital warts are also not harmless and can lead to delayed and painful urination.
Side effects
After taking Gardasil, a person may faint. In this case, he may get injured and get hurt. Therefore, it is necessary to remain under the medical supervision of your doctor for at least 15 minutes after receiving the vaccine. Some people may tremble and become stiff when they lose consciousness. This may require treatment and a course of therapy from your doctor.
Side effects of Gardasil include:
- Headache and dizziness, fainting;
- Swelling, redness, bruising, pain and itching at the injection site;
- Nausea, vomiting, fever.
Tell your doctor if you experience signs of an allergic reaction. It can be:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Bronchospasm, wheezing;
- Rash, hives.