Furazolidone belongs to the group of drugs - nitrofurans. It is available with a prescription and has an affordable price. A characteristic feature is a pronounced effect on gram-negative aerobic microorganisms that disrupt the functioning of the digestive system. Gram-positive aerobic microorganisms are less sensitive to the drug. The product is effective against fungi of the genus Candida.
The release form of furazolidone is flat-cylindrical tablets with a chamfer. They may have a yellow or slightly greenish shell. One contour package contains 10 tablets. They are sold in cardboard boxes with instructions.
The strength of the drug depends on the dosage. A characteristic feature of the drug is also its mild immunostimulating effect. Furazolidone also reduces the production of toxins by pathogenic microorganisms, which improves the general condition of a person in the treatment of certain pathologies. It is very important that the resistance of harmful microorganisms to the drug furazolidone, the instructions for use indicate this, develops slowly.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Furazolidone is an antimicrobial agent derived from nitrofuran . Salmonella , Shigella , Campylobacter , as well as protozoa ( Giardia , Trichomonas ) and Vibrio cholerae are highly sensitive to it . Depending on the concentration, it has a bactericidal or bacteriostatic effect.
The mechanism of action is the blockade of many enzyme systems of the microorganism. Nitrofurans disrupt cellular respiration, suppress the Krebs cycle and block the biosynthesis of nucleic acids. As a result, the shell of microorganisms or their cytoplasmic membrane is destroyed. When the drug acts, destroyed microbial cells release less toxins. Unlike other antimicrobial agents, they activate the immune system.
Acts on strains resistant to some antibiotics. Does not affect anaerobes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Resistance of microorganisms to the drug occurs rarely.
What is Furazolidone used for? Since it is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and high concentrations are created in the intestine, it is used for intestinal infections of bacterial and protozoal etiology. Unlike Furadonin, it is characterized by low toxicity.
Pharmacokinetics
Well absorbed when taken orally. Distributed in tissues and liquids. In the cerebrospinal fluid during meningitis , the same concentrations are created as in the plasma; therapeutic concentrations are also achieved in the intestinal lumen. Intensively metabolized in the liver to an inactive metabolite. Excreted by the kidneys (up to 65%), small amounts are determined in feces,
Indications
Indications for the use of the drug furazolidone, the instructions focus on this, are associated with its antiprotozoal, bactericidal, bacteriostatic and antimicrobial properties. The medicine is effective in the fight against various pathogenic microorganisms, in particular:
- Salmonella.
- Trichomonas.
- Giardia.
To understand what furazolidone helps with, you need to know how the active substance affects harmful microorganisms. It blocks the enzyme systems of harmful bacteria cells. As a result, they are gradually destroyed. During exposure to furazolin, bacterial cells produce fewer toxins.
Most often, furazolidone in adults, the instructions for use indicate this, is prescribed for the treatment of the following diseases:
- Food poisoning.
- Cystitis.
- Dysentery.
- Typhoid fever.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Cholera.
- Giardiasis.
The drug is quickly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. After this, it enters all tissues and fluids through the bloodstream, providing systemic treatment.
Side effects
- skin rash, skin itching, Quincke's edema ;
- decreased appetite;
- pulmonary edema , bronchospasm (with long-term use);
- nausea, vomiting;
- hepatotoxic effect;
- neuritis (with long-term use).
The risk of peripheral neuropathy increases with diabetes mellitus , hypovitaminosis B and C , and anemia .
Furazolidone tablets, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
The drug is taken orally, after meals, as it can cause dyspeptic disorders. The tablets should be taken with a glass of water.
With long-term use for the purpose of preventing neuritis , it is combined with taking B vitamins .
Instructions for use of Furazolidone
The dose for adults for paratyphoid fever , dysentery and food poisoning is 0.1 g per day 4 times a day for 5–10 days. Single dose - 0.2 g, daily dose - 0.8 g.
For giardiasis - 0.1 g 4 times a day for up to 7 days, after a week the same course is repeated.
For trichomonas urethritis - 0.1 g 4 times for 3 days.
For trichomonas colpitis, the dosage and frequency of administration are the same and in parallel, a powder containing furazolidone and milk sugar is injected into the vagina, and suppositories containing 4-5 mg of furazolidone are administered into the rectum.
For the treatment of burns locally in the form of bandages with a solution of the drug (1:25000).
Instructions for use for children
For children, the dose is calculated per kg of body weight. It is: one-time - 0.0025 g per kg, and daily 0.01 g per kg, distributed over 3-4 doses. The course of treatment is 5-7 days.
Application in veterinary medicine
The veterinary drug is a yellow powder, insoluble in water.
The drug is used for: salmonellosis , coccidiosis , colibacillosis , enteritis , balantidiasis in animals and birds. You can also use a pharmaceutical drug in tablets (one tablet contains 50 mg).
The dosage for these diseases is the same for chickens, turkey poults and broilers - the drug is added to the feed at the rate of 3 mg per head 2 times a day, treatment is carried out for 8 days. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated, but after a break of 10 days. As a preventative measure, young animals up to 10 days of age are given 2 mg per head once a day.
An overdose is unacceptable, since the bird becomes drowsy, lethargic and may die. How to feed to chickens? Better with food. Another option is to dissolve it in water and give it as a drink. But you need to know that the drug does not dissolve well and loses its properties when exposed to sunlight.
Furazolidone tablets 50 mg No. 10
Compound
Active ingredient: furazolidone – 50 mg; excipients: lactose monohydrate, anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide, calcium stearate, potato starch.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered parenterally, furazolidone is poorly absorbed and inactivated in the intestine. Only about 5% of the drug is excreted from the body in the urine unchanged or in the form of metabolites, causing the urine to turn brown.
Indications for use
Prescribed for the treatment of dysentery, paratyphoid, food toxic infections, giardiasis and other diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to it.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, end-stage chronic renal failure, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, pregnancy, lactation, children under 5 years of age. Do not use for urinary tract infections.
Directions for use and doses
Take orally after meals. For dysentery, paratyphoid fever, food toxic infections of a paratyphoid nature, 100 - 150 mg (2 - 3 tablets) (adults) are prescribed 4 times a day for 5 - 10 days. The drug can be prescribed to children over 5 years old at 25-50 mg (1/2 - 1 tablet) 4 times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the nature and severity of the infection. It is not recommended to use furazolidone for more than 10 days. The therapeutic effect in the treatment of diarrhea with furazolidone develops within 2 to 5 days of therapy. Sometimes patients may require longer treatment periods. If a satisfactory clinical response is not obtained within 7 days, this means that the pathogen is refractory to the action of furazolidone and the drug should be discontinued. Additional therapy with other antibacterial agents or bismuth salts is not contraindicated. (See “Drug Interactions” section). If furazolidone is prescribed in doses greater than recommended or for longer than five days, the physician should assess the risk of developing a hypertensive crisis associated with the accumulation of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. The patient should be informed about medications and foods that predispose to the development of hypertensive crises. For giardiasis, adults are prescribed 100 mg (2 tablets) 4 times a day; children - at the rate of 10 mg/kg per day. The daily dose should be given in 3 to 4 doses. Higher doses for adults orally: single 200 mg, daily 800 mg.
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light and moisture, at a temperature not exceeding 25? C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
3 years. Do not use the medicine after the expiration date.
special instructions
Prescribed with caution for chronic renal failure and diseases of the nervous system. It should be taken into account that furazolidone is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor; when using it, the same precautions should be observed as when using monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Furazolidone has the ability to sensitize the body to the effects of alcohol and is used to treat alcoholism when other drugs are insufficiently effective or there are contraindications to their use. After taking furazolidone (for 10 - 12 days), a negative conditioned reflex reaction to an alcoholic drink is usually developed. Drinking alcohol against the background of furazolidone causes a feeling of heat in the face and neck, burning throughout the body, heaviness in the occipital region, in addition, the pulse quickens and blood pressure decreases. Effect on the ability to drive a car and work with moving mechanisms: in therapeutic doses, furazolidone does not have an undesirable effect on the ability to drive a car and work with moving mechanisms. To prevent neuritis with long-term use, it is necessary to combine the intake with B vitamins.
Description
Tablets from yellow to greenish-yellow, flat-cylindrical, chamfered.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
On prescription.
Dosage form
Tablets 50 mg.
Manufacturer and organization accepting consumer complaints
Open Joint Stock Company "Borisov Medical Preparations Plant", Republic of Belarus, Minsk region, Borisov, st. Chapaeva, 64/27, tel./fax. +375(177) 735612.
Pharmacodynamics
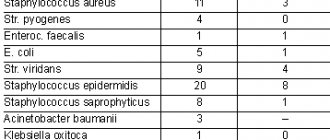
The drug belongs to antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agents. Has a bacteriostatic effect against microbes. The mechanism of action is to disrupt the activity of certain bacterial enzyme systems. Spectrum of action: gram-positive cocci (Streptococcus, Staphylococcus), gram-negative bacilli (Escherichia, Salmonella, Shigella, Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter), protozoa (Lamblia). Of the pathogens of intestinal infections, the most sensitive are the pathogens of dysentery, typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever. Resilience develops slowly.
Side effects
When taken orally, furazolidone relatively often causes nausea, vomiting, and reduces appetite. In some cases, allergic reactions (exanthema and enanthema) are possible. It is possible to develop a hypersensitivity reaction, which is manifested by a decrease in blood pressure, urticaria, fever and arthralgia. These reactions disappear after discontinuation of the drug. While taking the drug, nausea, vomiting, headache, and general malaise may occur, which decrease or disappear when the dose is reduced or the drug is discontinued. People taking furazolidone may develop a disulfiram-like reaction to alcohol: redness of the skin, a slight increase in temperature, shortness of breath, and in some cases, a feeling of tightness in the chest. To reduce adverse reactions, it is recommended to take the drug with plenty of liquid and, if necessary, reduce the dose; prescribe antihistamines, calcium chloride, B vitamins. If side effects are severe, stop further use.
Interaction
Furazolidone is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor; When using it, the same precautions should be observed as when using other monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Aminoglycosides and tetracyclines enhance the antimicrobial properties of furazolidone. Sensitizes the body to alcohol. Furazolidone increases the inhibition of hematopoiesis against the background of chloramphenicol and ristomycin.
Overdose
Symptoms: acute toxic hepatitis, hematotoxicity, neurotoxicity (polyneuritis).
Treatment: discontinuation of the drug, taking large amounts of fluid, symptomatic therapy, antihistamines, B vitamins.
Interaction
Aminoglycosides and Tetracycline enhance its antimicrobial effect.
Antidepressants, phenylephrine , ephedrine , MAO inhibitors, tyramine , amphetamine in combination with furadonine cause a significant increase in blood pressure.
Agents that alkalize urine reduce the effect of the drug.
Inhibition of hematopoiesis increases when used with chloramphenicol and Ristomycin .
Incompatible with alcohol, as this combination causes disulfiram-like reactions.
Furazolidone
Manufacturer: BIOSINTEZ JSC (Russia)
◊ tab. 50 mg: 10 or 20 pcs. Reg. No.: LS-001785
Clinical and pharmacological group:
Antibacterial drug, nitrofuran derivative
Release form, composition and packaging
| ◊ Pills | 1 tab. |
| furazolidone | 50 mg |
10 pieces. — cellless contour packages. 10 pieces. — cellless contour packages (1) — cardboard packs. 10 pieces. — cellless contour packages (2) — cardboard packs. 10 pieces. — contour cellular packaging. 10 pieces. — cellular contour packages (1) — cardboard packs. 10 pieces. — contour cell packaging (2) — cardboard packs. 20 pcs. — polymer jars (1) — cardboard packs. 20 pcs. - dark glass jars (1) - cardboard packs.
Description of the active components of the drug "Furazolidone"
pharmachologic effect
Antimicrobial agent, nitrofuran derivative. Active against gram-negative bacteria (including Shigella spp., Salmonella spp.), some gram-positive bacteria, as well as Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia lamblia.
Indications
Dysentery, paratyphoid, food poisoning, giardiasis, trichomonas urethritis.
Dosage regimen
For dysentery, paratyphoid fever, food toxic infections in adults, use 50-150 mg 4 times a day for 5-10 days. In children, doses are reduced according to age.
For giardiasis in adults - 100 mg 4 times a day; children - 10 mg/kg/day in 3-4 doses.
For trichomonas urethritis - 100 mg 4 times a day for 3 days. Maximum doses for adults: single - 200 mg, daily - 800 mg.
Side effect
Maybe:
nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, allergic reactions in the form of skin rash.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to furazolidone.
Use for renal impairment
Use with caution in patients with severe renal impairment.
Application for children
Use with caution in children under 1 month of age.
special instructions
Use with caution in patients with severe renal impairment, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, and in children under 1 month of age.
Furazolidone is a MAO inhibitor and appropriate precautions should be taken when using it.
Furazolidone has the ability to sensitize the body to the effects of ethanol and can be used to treat alcoholism.
Drug interactions
Agents that alkalize urine reduce the effect of furazolidone, while acidifying agents increase it.
The simultaneous use of aminoglycosides and tetracyclines enhances the antimicrobial properties.
Furazolidone increases the inhibition of hematopoiesis against the background of chloramphenicol and ristomycin.
Drug interactions
Agents that alkalize urine reduce the effect of furazolidone, while acidifying agents increase it.
The simultaneous use of aminoglycosides and tetracyclines enhances the antimicrobial properties.
Furazolidone increases the inhibition of hematopoiesis against the background of chloramphenicol and ristomycin.
Furazolidone for children
The instructions for children provide the following indications for use: amoebic dysentery , salmonellosis , giardiasis .
How to give Furazolidone to children?
A convenient form of release for children is in the form of granules, from which a suspension is prepared by adding 100 ml of water. When properly prepared, 1 ml of suspension will contain 0.0003 g of the drug. The suspension is used 4 times a day, measuring with a measuring cup and used until 7 years of age. A single dose is: 1-2 years, 4-5 ml, 3-4 years, 6-7 ml, 4-5 years, 7.5-8.5 ml.
From the age of 7, children can already take pills. The dosage of tablets for children is correspondingly less than for adults. At the age of 7-14 years, a single dose of 0.03-0.05 g is recommended, a daily dose of 0.12 g-0.15 g.
Reviews from parents indicate its effectiveness in intestinal infections:
- “... We took Bifiform and Enterofuril - nothing helped. I had diarrhea for a week until the doctor prescribed Furazolidone + Linex”;
- “... Smecta didn’t help, Enterofuril didn’t help either, in the end Furazolidone helped.”
Typically, no adverse reactions were observed during the 5-day period of administration.
Dosage
The tablets are taken after meals. They need to be swallowed and washed down with at least 100 g of liquid. The dosage depends on the pathology that requires treatment, as well as on the age of the patients.
The effectiveness of the drug in the treatment of dysentery and food poisoning has been proven. In this case, tablets are indicated in the following quantities depending on the age factor:
- For adults - 2-3 pieces. It is allowed to take 4 times a day, but the maximum dose should not exceed 800 mg.
- For children - the daily amount is calculated at the rate of 6-7 mg/kg body weight. Distribute it into 4 doses.
When treating giardiasis, adults usually take 2 tablets 4 times a day. Calculation of the daily amount of the drug for children is 6 mg/kg body weight. The duration of taking furazolidone for the treatment of any disease should not exceed 10 days. In most cases, a positive effect is achieved within 2-5 days. If after 7 days no improvement is observed, this indicates that the causative agent of the disease is refractory to the effects of the drug. This means that other antibacterial agents must be used for treatment.
Furazolidone for cystitis
How effective is this drug for cystitis ? Based on pharmacokinetics, its highest concentration is determined in the intestinal lumen, and it follows that the drug will be most effective against intestinal infections. Furadonin in the treatment of urinary tract infections , but it is more toxic.
If furazolidone can be used as monotherapy for cystitis, then for pyelitis and pyelonephritis it is prescribed in combination with antibiotics. Derivatives of the nitrofuran series do not create therapeutic concentrations in the kidney parenchyma, therefore they are used only for cystitis.
Furazolidone tablets for cystitis in the usual dosages, which were mentioned above, are used for uncomplicated disease. For hemorrhagic or purulent cystitis, more serious treatment is required.
Furazolidone for diarrhea
Is this drug always indicated? And is it possible to take it immediately in case of any bowel disorder?
There are clear indications - shigellosis , amoebic dysentery , salmonellosis . The drugs of choice for the treatment of salmonellosis and shigellosis are fluoroquinolone drugs and furazolidone. Sometimes, even with acute intestinal infection (AI), especially in children, treatment begins with probiotics ( Bifiform , Probifor , Enterol , Bifistim ) and enterosorbents ( Filtrum , Neosmectin , Enterosgel ). Only in severe forms or in the absence of effect from previous treatment, furazolidone anti-diarrhea tablets are prescribed for 2-3 days.
Only a doctor can prescribe how to take it for diarrhea, and if there is no positive dynamics, a switch to “reserve” antibiotics ( imipenem , Azithromycin , Amikacin , etc.) is possible. Do not forget to take a course of probiotics after treatment.
Furazolidone analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Acylact
Iodoxide
Kolposeptin
Lactonorm
Hexicon
Ecofemin
Lactozhinal
Depanthol
McMirror
Dafnedjin
There are no analogues for the active substance. Nirofuran derivatives have a similar effect:
- Nifuroxazide
- Enterofuril
- rifaximin
- imipenem
- Azithromycin
- Amikacin
- Fluoroquinolone
- Ciprofloxacin
Reviews about Furazolidone
The question is often asked about this drug: is it an antibiotic or not? This is not an antibiotic, but a synthetic antibacterial agent, which differs from true antibiotics in the mechanism of action on microorganisms and the effect on the human body.
What are Furazolidone tablets for? Is this drug prescribed only for diarrhea? Intestinal infections are the main indication for the use of the drug. In addition to Furazolidone, other intestinal antiseptics ( Nifuroxazide , rifaximin ) can be prescribed to correct microflora, followed by the use of probiotics.
Furazolidone tablets in combination with sorbents and Creon are prescribed for the treatment of giardiasis . There are reviews about this very often. In this case, reviews of Furazolidone are mostly negative, since even a 10-day course did not lead to eradication of the parasite. Metronidazole or Macmiror are more effective than Furazolidone. What else does this drug help with? For urinary system infections, it is prescribed for 7-14 days.
There are other indications for the use of Furazolidone, which the abstract does not indicate. For example, anti-Helicobacter therapy, including Furazolidone, is effective in the treatment of erosive and ulcerative diseases in adults. The same treatment regimen is used for children infected with Helicobacter pylori (HP). It includes De-Nol , Furazolidone, Amoxicillin , Ranitidine and after treatment, 100% eradication of HP is achieved.
Reviews often indicate side effects of the drug - nausea and sometimes vomiting. When taking the drug without a doctor's prescription, carefully study all contraindications and follow the recommended doses.
Furazolidone 50 mg No. 10 tablet
Instructions for the use of the drug for specialists FURAZOLIDONE (Furazolidonum) Trade name Furazolidone International nonproprietary name Furazolidone Dosage form Tablets 0.05 g Composition One tablet contains the active substance - furazolidone - 0.05 g, excipients: milk sugar, potato starch, calcium stearate , aerosil. Description Tablets from yellow to greenish-yellow, flat-cylindrical, with a chamfer Pharmacotherapeutic group Other antiseptic and antimicrobial agents for use in gynecology. ATC code G01AX06 Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics When taken orally, it is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration of furazolidone in blood plasma after taking a dose of 100 mg is 0.25-0.43 mcg/ml and is achieved after 1.85-3.0 hours. It easily penetrates the placenta and the blood-brain barrier. It is found in therapeutic concentrations in urine and feces. It undergoes biotransformation in the liver to form an amino derivative. It is excreted from the body in the urine, with the proportion of unchanged drug being 65%, as well as in feces. Pharmacodynamics Synthetic broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. It has a bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect. The mechanism of action is associated with the restoration of furazolidone in microbial cells under the influence of flavoprotein (in aerobic organisms) and ferredoxin reductase (in anaerobic organisms and parasitic protozoa) into an active intermediate that damages ribosomal proteins, disrupts the synthesis of protein, DNA, RNA. Active against gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp.; gram-negative aerobic bacteria: Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp., Helicobacter pylori, Klebsiella spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Proteus spp. Active against Enterococcus spp., fungi of the genus Candida. Active against the protozoa Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia lamblia. The most sensitive to the drug are the pathogens of dysentery, typhoid and paratyphoid (Salmonella spp., Shigella spp.). It has little effect on the pathogens of purulent and anaerobic infections Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp. Microbial resistance to the drug develops slowly. Indications for use: dysentery, paratyphoid fever, food poisoning and acute bacterial diarrhea, eradication of H. pylori in the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic gastritis (as part of a second-line treatment regimen) trichomonas colpitis, urethritis, giardiasis. Method of administration and dosage The drug is administered orally, after meals, with plenty of water. Adults: 100-150 mg 4 times a day; course of treatment – 7-10 days. It is recommended to carry out treatment in cycles of 3-6 days with an interval of 3-4 days in the same doses. Maximum dose for adults: single dose – 200 mg, daily dose – 800 mg. For children, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day in 3-4 doses. In the treatment of giardiasis, furazolidone is prescribed to adults at a dose of 100 mg 4 times a day. For trichomonas colpitis, combined treatment is carried out with furazolidone orally, 100 mg 3-4 times a day for 3-4 days, at the same time 5-6 g of powder containing furazolidone mixed with milk sugar in a ratio of 1:400-500 is administered intravaginally, suppositories with furazolidone are used rectally . Treatment is carried out daily for 7-14 days. When eradicating H. pylori in people with gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic gastritis, furazolidone is used at a dose of 400 mg/day in 4 doses in combination with amoxicillin (2000 mg/day) and H+/K+-ATPase inhibitors in standard doses. The course of treatment is 10-14 days. (Second-line regimen recommended by the III Maastricht Agreement). Side effects - nausea, vomiting, anorexia - dizziness, polyneuritis - allergic skin reactions (in the form of skin rash). Contraindications - severe renal dysfunction, renal failure, oliguria - glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; - acute porphyria - children under 2 years of age - first trimester of pregnancy - hypersensitivity to furazolidone. Drug interactions Urine alkalizing agents (sodium bicarbonate, trisamin) reduce the effect of furazolidone (by accelerating its excretion in the urine), and urine acidifying agents (amino acid solutions, ascorbic acid, methionine, potassium orotate) increase it. Aminoglycosides and tetracyclines enhance the antimicrobial effect of furazolidone. When used together with chloramphenicol and ristomycin, it enhances the hematotoxic effect (the ability to inhibit hematopoiesis) of these drugs. It has a disulfiram-like effect, sensitizing the body to the products of ethanol metabolism. During treatment with furazolidone, the use of drinks containing alcohol is contraindicated. Furazolidone inhibits MAO; when using it, fermented foods containing tyramine (red wines, smoked meat and meat products, oysters, soft cheeses, chocolate, products with soy protein) should be excluded from the diet. Acidic fruit juices enhance the effect of furazolidone, up to the possibility of developing a toxic effect. When used together with antidepressants from the group of MAO inhibitors (nialamide, tranylcypramine, moclobemide), tricyclic antidepressants (imipramine, amitriptyline), sympathomimetics (ephedrine, cocaine), there is a risk of developing a hypertensive crisis. B vitamins weaken the neurotoxic undesirable effects of furazolidone. Special instructions Caution when prescribing should be observed in persons with electrolyte disturbances, impaired renal function, deficiency of B vitamins, because the neurotoxic effect of the drug may be enhanced. Pregnancy and lactation The use of furazolidone in the second and third trimester of pregnancy is possible only after a careful assessment of the benefit/risk ratio for the mother and fetus. If it is necessary to use it during lactation, the child should be weaned from the breast for the entire period of treatment. Use in pediatrics Not recommended for use in children under 2 years of age Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery In therapeutic doses, furazolidone does not have an undesirable effect on the ability to drive a vehicle or other operator activities. Overdose When high doses are administered, neurotoxic reactions, polyneuritis, acute toxic hepatitis, and disorders of the hematopoietic system may occur. Helpful measures: discontinuation of the drug, taking large amounts of fluid to increase the excretion of the drug in the urine, hemodialysis, symptomatic therapy (antihistamines, B vitamins). There is no specific antidote. Release form and packaging 10 tablets in a contour-free packaging. Contour cellless packages, together with the appropriate number of instructions for use in the state and Russian languages, are placed in a group package. Storage conditions Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 5 to 30 ºС. Keep out of the reach of children! Shelf life: 3 years Do not use after expiration date. Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies By prescription, Republic of Belarus. Minsk region, Borisov, st. Chapaeva, 64/27
Furazolidone price, where to buy
The drug is available in all pharmacies in Moscow and other Russian cities, so you do not need a prescription in Latin to purchase the drug.
The price of Furazolidone tablets 50 mg No. 20 is about 100 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Furazolidone Renewal tab.
0.05g 20pcs ZAO PFK Renewal 121 rub.order - Furazolidone tablets 50 mg 20 pcs. LLC Avexima Siberia
122 RUR order
- Furazolidone tablets 50 mg 10 pcs. LLC Avexima Siberia
74 RUR order
- Furazolidone tab. 50 mg 20 pcs. YuzhPharm LLC
78 RUR order
- Furazolidone tablets 50 mg 10 pcs Renewal JSC "PFK Obnovleniye"
86 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Furazolidone tablets 50 No. 20 Anzhero-Sudzhensky chemical-f.z.
118 RUR order
- Furazolidone (50 mg tablet No. 20) YuzhPharm
73 rub. order
- Furazolidone (50 mg tablet No. 10) YuzhPharm
52 RUR order
- Furazolidone (50 mg tablet No. 10)Update of PFC CJSC
95 rub. order
- Furazolidone Avexima (50 mg tablet No. 20) Avexima Siberia LLC
117 RUR order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Furazolidone 50 mg No. 20 tablets PAT Monpharm, Ukraine
28 UAH.order
PaniPharmacy
- FURAZOLIDONE tablets Furazolidone tablets. 50 mg No. 20 Ukraine, Monfarm JSC
34 UAH order
show more