General information
In order for a person to lead an active lifestyle, and for his body to function correctly, without failures, energy must flow into the cells, tissues of organs and systems. Its main source is glucose in the blood. To break it down and convert it into energy, it is necessary to have a certain hormone produced by the pancreas - insulin.
As a result of the development of any diseases of this organ, the production of the hormone decreases. The breakdown of glucose slows down. This leads to energy deficiency, which negatively affects the functioning of all human organs. At the same time, as food continues to enter the body, blood sugar levels rise, sometimes significantly exceeding normal levels. It settles in blood vessels in the form of single crystals. A person develops a dangerous, intractable disease – diabetes mellitus.
There are two types of diabetes:
- T1DM – consists of pancreatic dysfunction, insulin stops being produced completely or partially; energy does not flow to the cells;
- T2DM – characterized by cell insensitivity to insulin; Despite the fact that the gland continues to produce the hormone in sufficient quantities, the cells that have lost sensitivity do not absorb energy, and the sugar level in the blood increases.
Depending on what type of disease a person suffers from, a specific treatment method is prescribed. With T2DM, in some cases, following a special diet may be sufficient. If this method turns out to be ineffective, then over time the gland begins to produce less hormone. In this case, as with type 1 diabetes, insulin preparations are prescribed, which prevent the development of complications, expressed in disturbances in the functioning of internal organs (heart, kidneys), blood vessels, and decreased vision.
Who is insulin therapy indicated for?
Indications for prescribing insulin therapy are:
- type 1 diabetes mellitus;
- type 2 diabetes mellitus with ineffective treatment with glucose-lowering drugs
- ketoacidosis of varying severity;
- severe diabetic microangiopathy (with organ dysfunction);
- ineffectiveness of the diet and the maximum dose of oral hypoglycemic drugs (HbA1c - >7.5%, fasting glycemia - >8 mmol/l);
- comatose states (ketoacidotic, lactic acidotic, hyperosmolar);
- chronic recurrent diseases in the acute stage (tuberculosis, pancreatitis, pyelonephritis, etc.);
- pancreatectomy;
- acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA);
- severe, in particular purulent infections;
- myocardial infarction;
- surgical interventions;
- significant loss of body weight in a short period of time.
If for patients with the first type of diabetes mellitus insulin therapy is a mandatory component of treatment, then for patients with the second type it is prescribed in exceptional cases:
- during surgical interventions;
- for acute cardiovascular disorders (myocardial infarction, stroke);
- for severe infectious diseases;
- with the development of hyperosmolar and lactic acidotic coma or precoma;
- with the rapid progression of late complications of diabetes mellitus (severe diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy, a decrease in glomerular filtration rate less than 60 ml/min as part of diabetic nephropathy).
Insulin therapy is prescribed to people with diagnosed diabetes mellitus to achieve several goals:
- eliminate maximum clinical symptoms of diabetes;
- achieve optimal metabolic control of the disease for a long period of time;
- prevent acute and chronic complications of diabetes;
- to ensure the highest achievable quality of life for patients.
The use of insulin therapy alone is not capable of fully achieving the above objectives, and therefore it is strictly recommended to be combined with:
- individually designed diet;
- dosed individual physical activity;
- teaching the patient the simplest methods of treatment and ways to urgently stabilize his or her health;
- practical application of acquired knowledge, that is, the implementation of constant self-monitoring (in particular, keeping a log of actually eaten carbohydrate bread units, the amount of insulin administered, the degree of physical activity and “emergency” situations that have arisen).
Insulin tablets
Despite this, many people with diabetes are afraid to start taking insulin. The main reason for this is the need for constant administration of the drug in the form of injections. The dream of many diabetics is insulin tablets. Despite the fact that you can sometimes find media reports that scientists from America and Australia were able to invent insulin tablets, this is most likely not true.
The dream of pills for type 1 diabetes is not yet possible. At the moment, this is the only method of treating T1DM that allows not only to improve the quality of life of a sick person, but also to significantly increase its duration. At the same time, it is not necessary to use a syringe to administer insulin, which is always difficult. Today, scientists, pharmacologists, and doctors suggest using such an invention as a syringe pen. The procedure with their help is simple, and the use of special needles for insulin syringe pens allows you to administer the drug absolutely painlessly.
According to the degree of purification, medications are divided into the following:
- traditional (purified using old, ineffective methods, and therefore contains protein impurities with a highly allergenic effect);
- monopeak (the content of unnecessary impurities is one thousandth);
- monocomponent (unnecessary impurities are beyond detection limits).
Today, diabetics can choose their own insulin based on the designations indicated on the packages. Manufacturers identify the highly purified monocomponent drug with the sign “MS”, and the identical human drug with the sign “NM”. If necessary, you can always consult with an endocrinologist, who will suggest the best option.
Classification of insulin
But even if the patient decides to take insulin injections, he will not be able to purchase the drug at the pharmacy on his own. It must be selected by an endocrinologist, especially since there are a lot of types of insulin on the shelves of modern pharmacies and it is very difficult to understand their purpose without special knowledge.
All insulin preparations are classified into types according to several criteria. For example, depending on the “origin”, the following types of insulin are distinguished.
- Obtained from the pancreas of pigs or cattle. The first option is preferable, since it is closer to the human one. In the second case, an allergic reaction may occur.
- Synthesized artificially using human rDNA insulin.
- Genetically engineered, it is also obtained from pork insulin using modern innovative technologies, which makes it possible to obtain a drug almost identical to the human hormone.
The following classification method takes into account the speed of penetration of the drug into the blood and the duration of its action. On this basis, insulin is divided into the following categories:
- ultra-short;
- short;
- average;
- long.
The drugs of the last two categories are considered basic, basic. They are administered 1-2 times a day, which allows you to maintain blood sugar levels at a normal level for a long period of time. Ultra-short and short preparations are used before each meal, which helps prevent the increase in blood sugar levels caused by the intake of food into the body.
Ultra-short
When used to lower blood sugar levels, it must be remembered that the faster the effect of the drug occurs, the shorter the duration of its action. The fastest, ultra-short drugs begin to work 10 minutes after administration. These are very powerful, effective medications, the effect of which is as close as possible to the natural hormone and lasts for 3 hours. The injection is given immediately before or immediately after a meal.
Short
The effect of the drug begins after 30 minutes and lasts for 5-8 hours. Preliminary administration of the medicine allows it to begin working simultaneously with the intake of food into the body, and it is desirable that it contains predominantly slow carbohydrates. A long period of action leads to the fact that the hormone remains in the blood after all the food has been absorbed and the amount of glucose in the blood has decreased. To prevent this from leading to hypoglycemia, additional food intake (snack) is necessary.
Like other insulin preparations, short- and ultra-short-acting drugs are introduced into the body using disposable syringes or reusable insulin pens into the subcutaneous fatty tissue. This promotes a more uniform, slow penetration of the hormone into the blood. The rate of absorption depends on various factors, primarily:
- injection site, it can be the shoulder, thigh, but the drug begins to act most quickly when it is injected into the stomach;
- the dose of the administered medication, the larger it is, the more effective the effect will be;
- the thickness of the fat layer, the smaller it is, the faster the absorption will be.
The drug and its dose are selected by a specialist endocrinologist, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body, depending on the stage of development of the disease. But a person with diabetes can independently regulate the dose, depending on the number of “bread units” entering the body: 1 unit of short-acting insulin is administered per 1 unit of bread, so that no more than 1 unit per kilogram of body weight enters the body at a time.
To accurately determine the dose, doctors recommend that patients keep a “food diary”. It is necessary to record each meal, the sugar level measured after that, the dose and name of the administered drug, and the concentration of glucose in the blood after taking the drug. This “Diary” allows the treating endocrinologist to choose a more effective treatment method. In addition, in the event of an emergency (the development of ketoacidosis), an emergency doctor or an intensive care unit specialist called to the house will also be able to use the notes taken to determine which medicine should be used to provide emergency care. In this case, the injection is given intravenously.
Medium and long
These drugs are intended for basic, basic therapy. They must be used daily, regardless of the time and amount of food taken. Medium-duration medications require administration twice a day: 2/3 of the dose in the morning before breakfast and 1/3 of the dose before dinner. With medium-lasting insulin, the effect is achieved after 1-1.5 hours, and the duration is 20 hours. Long-acting (long-term) insulin can be used once a day. It starts working in 1-3 hours. The main advantage of its use: the absence of a peak of activity. The concentration of insulin in the blood remains at a constant level throughout the entire duration of action, that is, 24 hours.
Depending on the type of diabetes mellitus, the stage of development of the disease, and the characteristics of the body, the doctor will prescribe one of two insulin therapy technologies.
- Combined. It is also called traditional and is used to treat patients who cannot take care of themselves or control the dose of the administered drug: elderly people, patients with diabetes with mental disorders, and so on. It involves the simultaneous administration of two drugs using one medical syringe, one of which is basic (medium-acting or long-acting), and the second is a short-acting drug. Its main disadvantage is its low efficiency, which leads to earlier manifestation of various complications.
- Basis-bolus therapy. In this case, both short and long-acting (medium) insulin preparations are also used. But unlike the traditional method, this option does not involve “mixing” them. They are administered in different injections, which makes it possible to bring their effect closer to the physiological production of the hormone by the body itself. This method is considered the best and is used more often.
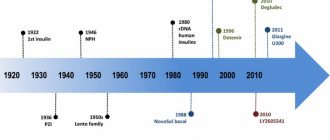
Nobel Prize
In 1923, the Nobel Committee awarded the Physiology or Medicine Prize to Banting and MacLeod, just 18 months after the drug was first reported at a meeting of the Association of American Physicians. This decision aggravated the already difficult relations between scientists, because Banting believed that MacLeod's contribution to the invention of insulin was greatly exaggerated; in Banting's opinion, the prize should have been divided between him and his assistant Best. To restore justice, Banting shared his share of the prize with Best, and McLeod with the biochemist Collip8.
The patent for the creation of insulin, owned by Banting, Best and Collip, was sold by scientists to the University of Toronto for $3. In August 1922, a cooperation agreement was concluded with the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly and Co., which helped establish the production of the drug on an industrial scale.
More than 90 years have passed since the invention of insulin. Preparations of this hormone are being improved; since 1982, patients have been receiving human insulin, and in the 90s analogues of human insulin appeared - drugs with different durations of action, but we must remember the people who were at the origins of the creation of this drug, which saves the lives of millions every day of people.
Bibliography
- IDF diabetes atlas 7th Edition. Available at: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/.
- Bliss M. The history of insulin. Diabetes Care 1993;16 Suppl 3:4-7. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8299476.
- Bliss M. The discovery of insulin: the inside story. Publ. Am. Inst. Hist. Pharm. 1997;16:93-9. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11619903.
- Karamitsos DT. The story of insulin discovery. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011;93 Suppl 1:S2-8. doi:10.1016/S0168-8227(11)70007-9.
- Banting Notebook: 1920-21. Fisher Rare Book Library, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
- Stylianou C, Kelnar C. The introduction of successful treatment of diabetes mellitus with insulin. JR Soc. Med. 2009;102(7):298-303. doi:10.1258/jrsm.2009.09k035.
- Rosenfeld L. Insulin: discovery and controversy. Clin. Chem. 2002;48(12):2270-88. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12446492.
- de Herder WW. Heroes in endocrinology: Nobel Prizes. Endocr. Connect. 2014;3(3):R94-R104. doi:10.1530/EC-14-0070.
Release form
Insulin preparations go on sale in the form of solutions or suspensions, packaged in glass hermetically sealed bottles (5-10 ml). The top of the cork is rolled with an aluminum cap. For use in conjunction with a syringe pen, medicines are packaged in special cartridges (cases, cartridges).
For use in medical institutions, the drug can be in the form of a soluble white powder. It contains at least 3.1% sulfur. To introduce it into the body, it is diluted with special water for injection with the addition of hydrochloric acid, glycerin, and a solution of phenol (tricresol).
pharmachologic effect
Insulin drugs affect all tissues and internal organs of the human body. But its “work” is most pronounced in its effect on muscle and fat tissue, the liver, metabolic processes occurring in the body, and digestion. Among the main functions of these drugs:
- regulation of carbohydrate metabolism due to stimulation of glucose penetration through the cell membrane, which promotes its conversion into glycogen and further utilization;
- increased glycogen content in muscle tissue;
- stimulation of the formation of peptides, glucosyltransferase, hexokinase enzyme, pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex;
- suppression of fat breakdown (lipolysis), which leads to a reduction in the amount of free fatty acids and reduces their entry into the systemic circulation;
- reduces the formation of glucose from fatty acids and amino acids, prevents the breakdown of glycogen (glycogenolysis);
- prevents the synthesis of ketone (acetate) bodies;
- slows down the process of converting amino acids into oxocarboxylic acids and so on.
The effectiveness of the drug depends on the characteristics of the body, muscle activity, blood flow speed at the injection site, the administered drug and its dose. The effect of a substance can be different not only in different people, but also in the same person, depending on his condition.
Injection technique
Insulin can be administered independently, without assistance. To do this, you can use an insulin syringe or a special syringe pen. The latter method is more preferable, since it allows you to more accurately measure the required amount of substance. Another advantage is that the injection can be given directly through clothing, which is especially convenient for patients with diabetes who lead an active lifestyle: studying at a university, working in offices.
It is imperative to comply with all antiseptic requirements: wash your hands with soap, use only disposable syringes, treat the injection site with alcohol or alcohol-based antiseptic wipes. It should be remembered that alcohol destroys insulin, therefore, after treating the injection site, you must wait until the alcohol-containing liquid used for disinfection has completely dried, and only then inject. Do not inject the drug into the same place multiple times. Each time you need to retreat from the previous puncture by 2-3 centimeters. Changing the area of drug administration is done to prevent lipodystrophy.
Another method of administering insulin is called an insulin pump, which provides a continuous supply of the hormone. The system is a kind of syringe dispenser, consisting of the pump itself, a small computer designed to calculate the dose and control the drug administration regimen, a reservoir with the drug and a thin needle (cannula) for administering the drug.
This method of treatment is becoming increasingly widespread, since it allows one to take into account the amount of residual insulin in the blood and the amount of food entering the body. For administration using an insulin pump, ultra-short and short-acting drugs are used, but the number of skin punctures is minimized.
When using an insulin pump (doser), patients with diabetes have a more stable course of the disease, the quality of life increases, and the likelihood of complications decreases. At the same time, skeptics also note the negative aspects of using this method. First of all, this is an inconvenience, especially for those who want to lead an active lifestyle. In addition, a patient with diabetes is completely dependent on technology, because the process is completely automated. A malfunction of the program, failure of the device, or sudden loss of battery charge can lead to ketoacidosis. Another negative factor that is significant for many Russians is the high cost of the device.
What do the analysis results mean?
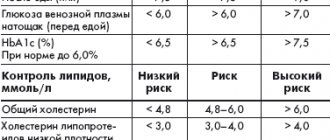
During the study, blood is drawn from a vein, after which the concentration of the hormone is determined using a chemical analysis. A value in the range from 2.6 to 24.9 µU/ml of blood is taken as normal.
If the norm is exceeded, the patient is sent for additional diagnostics to determine possible causes. The most common ones are:
- acromegaly;
- insulinoma;
- pancreas cancer;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- obesity of varying degrees;
- intolerance to simple carbohydrates (glucose, galactose, fructose).
Insulin in bodybuilding
Some athletes and coaches believe that insulin drugs, especially short-acting ones, in combination with anabolic steroids and androgenic substances used in sports, will allow them to achieve better results. Indeed, regardless of whether the drug is administered to a sick or healthy person, its mechanism of action will be the same. In particular, the permeability of cell membranes in muscle tissue will increase. As a result, the process of penetration of steroids into cells will accelerate. Even if there is a small amount, the consequences can be more significant than without the use of insulin.
But athletes, like patients with diabetes, should carefully monitor compliance with the dosage and not forget about other, no less important rules:
- control the amount of nutrients entering the body, an excess of which will lead to their deposition as fat;
- reduce the amount of simple carbohydrates consumed;
- control not only the weight, but also the volume of the biceps, shins, and thighs.
The appearance of fatty deposits and folds indicates an incorrect calculation, the need to reduce the dose or completely stop introducing insulin drugs into the body.