Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Candibiotic ear drops are a combination of drugs from various pharmacological groups specially selected for use in ENT practice.
An imidazole derivative, the drug clotrimazole , is an antimycotic ( antifungal ) agent with a broad spectrum of local action. The antimycotic effectiveness of clotrimazole is due to its ability to disrupt the synthesis process of a component of the cellular fungal membrane - ergosterol , which leads to a change in membrane permeability and, as a consequence, to lysis fungal cell .
A bacteriostatic antibacterial drug , chloramphenicol, is characterized by a wide spectrum of action against various, both gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms . The antibacterial effects of this antibiotic are aimed at disrupting the processes of protein synthesis in microbial cells .
The steroid hormone (glucocorticoid) - beclomethasone is included in the drug as an antiallergic and anti-inflammatory component.
The local anesthetic - lidocaine in this combination is necessary as an anesthetic , the effectiveness of which is to reversibly block the conduction of a nerve impulse by inhibiting the penetration of sodium ions .
Due to the local effect of all ingredients of Candibiotic ear drops, studies of their pharmacokinetic transformations have not been conducted.
In acute catarrhal otitis media (OCSO) and acute diffuse otitis externa (ADO), the otorhinolaryngologist usually prescribes ear drops endaurally in order to provide a rapid analgesic effect of therapy, enhance the anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effect of systemic therapy, or in mild clinical cases, ear drops act as the main component therapy of the disease. For this reason, the most popular today are ear drops containing antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory components and anesthetics. Typically, local antimicrobial therapy is prescribed empirically, without prior isolation of microflora from the inflammatory exudate [1]. It is known that the most common pathogens of ONDO are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus haemolyticus
,
Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae
[2, 3], therefore, the antimicrobial agents contained in ear drops are aimed specifically at these microorganisms. The effectiveness of such drugs is determined not only by the presence of one or another antimicrobial component in their composition, but also by its concentration and the time of exposure of the drug inside the external auditory canal.
The purpose of the study is to substantiate recommendations for endaural treatment of ONDO, OXO ear drops (candibiotic, anauran, otipax) from the position of the greatest clinical effectiveness.
Research objectives:
1. Determine in vitro
, under conditions as close as possible to
in vivo
, the optimal exposure time for candibiotic ear drops is to achieve 100% antimicrobial action against
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae.
2. In a blind randomized study, determine the analgesic activity of candibiotic, otipax and anauran ear drops in patients with ONDO and OXO using the VAS scale.
3. In a simple comparative randomized study based on otoscopy data, compare the dynamics of inflammatory changes in the treatment of acute ear diseases with candibiotic, otipax and anauran ear drops on days 3, 5, 7 and 10 of the study against the background of systemic antibacterial therapy.
Material and methods
For laboratory diagnostics, daily cultures of test strains Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae
, from which a microbial suspension containing 105 or 107 CFU/ml was prepared using standard turbidity.
The test agent was added to the microbial suspension of each test strain. The resulting mixtures were incubated at 36 °C, plating onto nutrient media (meat peptone agar, for Streptococcus pneumoniae
- 5% blood agar) at 10, 20, 30 and 40 minutes. Control inoculations were carried out on 0.1 ml nutrient media. The number of grown colonies was counted after incubation at a temperature of 37 °C for 24 hours. The results were assessed in accordance with the number of grown colonies: “—”—no growth; “+” - meager growth of up to 10 colonies = 103 CFU; “++”—moderate growth from 10 to 100 colonies = 104 CFU; “+++” - abundant growth of more than 100 colonies = 105 CFU.
To assess the analgesic effect, 45 patients with ONDO, aged 6-74 years, and 45 patients with OXO, aged 8-69 years, were examined, who at the time of treatment were tested for the analgesic effect of the test drug (ear drops candibiotic, anauran, otipax). Test method: at the initial visit, the patient assessed his pain sensations using a VAS scale, after which the doctor instilled 5 drops of the test product endaurally. After 2.5 and 10 minutes, the patient was asked to mark the level of his pain on the same scale. In the process of testing patients with ONDO, Otipax drops were used - 15 cases; candibiotic drops - 15; anauran drops - 15; testing of patients with OXO also included treatment with Otipax drops - 15 cases; candibiotic drops - 15; anauran drops - 15.
To assess the dynamics of the symptoms of ONDO and OXO, a score was used, according to which the narrowing of the lumen of the external auditory canal
: 0 points - no pathology;
1 point - narrowing to 1/3 of the lumen; 2 points - narrowing to 1/2 of the lumen; 3 points - narrowing of more than 1/2 of the lumen. Hyperemia of the skin: 0 points - pink skin; 1 point - mild hyperemia; 2 points - bright hyperemia. The amount of pathological discharge in the external auditory canal
: 0 points - no discharge;
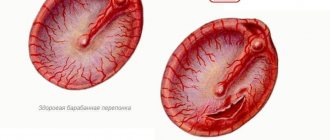
1 point - the discharge is removed until the skin is completely cleansed with a padded pad at one time; 2 points - the same thing several times; 3 points - a large amount of discharge, complete cleansing of the skin of the external auditory canal was achieved by washing. Eardrum points
- gray, identification points preserved, integrity preserved; 1 point - marginal hyperemia, identification points are preserved, integrity is preserved; 2 points - diffuse hyperemia, identification points are smoothed, integrity is preserved; 4 points - hyperemia, identification points are not visible, integrity is preserved.
The same type of complex treatment of patients was carried out. Therapy for ONDO included amoxicillin clavulanate 1000 mg 2 times a day orally for 7 days, tested ear drops 5 drops 3 times a day for 7 days. Cleaning of the external auditory canal under otoscopy control on the 1st, 3rd, 5th day of the disease. OXO therapy included amoxicillin clavulanate 1000 mg 2 times a day orally for 7 days, test ear drops 5 drops 3 times a day for 7 days. Intranasal vasoconstrictors (xylometazoline/naphazoline) 2-3 drops 3 times a day for 5 days. Cleaning of the external auditory canal under otoscopy control on the 1st, 3rd, 5th day of the disease. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs was excluded.
Results and discussion
In vitro
a study of the antimicrobial activity of candibiotic ear drops showed that the spectrum of antimicrobial action of the drug extends to all types of microflora, which are traditionally considered to be the causative agents of inflammatory diseases of the outer and middle ear with an exposure of 10 minutes. Therefore, to maximize the antimicrobial effect of candibiotic ear drops, it is recommended to ensure full contact of the skin of the external auditory canal (tympanic membrane) with the ear drops for at least 10 minutes.
A study of the analgesic effect of candibiotic, anauran, and otipax ear drops showed different rates and degrees of severity of the analgesic effect. The absolute scores for assessing ear pain ranged from 3 to 10 points in the ONDO group; in the OKSO group - ranging from 3 to 9 points.
The average scores for the sensation of ear pain by patients before treatment, as well as after 2.5 and 10 minutes of endaural exposure to ear drops, are presented in Table. 1.
With ONDO, a decrease in pain by 2 times or more after 2.5 minutes was observed in 33% of patients who received Otipax and Anauran and in 53.3% of patients who received candibiotic. After 10 minutes of application of ear drops, patients who assessed a reduction in the severity of pain by 2 times or more compared to the initial level accounted for 73.3% in the otipax and candibiotic subgroup; in the anauran subgroup - 53.3%. Considering the small number of observations in subgroups, the effectiveness of the analgesic effect of ear drops with an exposure of 10 minutes was assessed using the Wilcoxon test. In the ONDO group, when ranking the severity of ear pain before and after the experiment in the otipax subgroup, the sign ranks were distributed from 1 to 7, Wob.=59; in the anauran subgroup - from 1 to 6, Wob.=45; in the candibiotic subgroup - from 1 to 9, Wob.=68. Since the analgesic effect has been proven only when Wob > Wcrit.; The analgesic effect of candibiotic ear drops after 10 minutes of endaural application in the treatment of ONDO should be considered proven.
With OXO, a decrease in pain after 2.5 minutes by 2 times or more was observed with the application of candibiotic in 40% of patients, with the application of otipax - in 33%, with the application of anauran - in 0% of patients. After 10 minutes - in 66.7% of patients who received candibiotic endaurally, in 40% of patients who received Otipax and in 13.3% of patients who received Anauran. When ranking the severity of ear pain before and after the experiment (after 10 minutes) in the otipax subgroup, the sign ranks were distributed from 1 to 7, Wob.=48; in the anauran subgroup - from 0 to 4, Wob.=26; in the candibiotic subgroup - from 1 to 5, Wob.=37. When n=15; α=0.05; Wcrit.=63 none of the obtained indicators exceeds the critical value of the Wilcoxon test. Therefore, to ensure a significant analgesic effect in the treatment of OXO, therapy should additionally include vasoconstrictor nasal drops, etc.
An assessment of the reverse dynamics of visual symptoms of inflammation of the external auditory canal during ONDO showed a comparable picture in the subgroups. Significant differences in all subgroups were noted on the 5th day compared to the initial clinical picture; on the 10th day, the absence of symptoms was recorded. On the 5th day, a more pronounced reverse dynamics of ONDO was observed in patients who received candibiotic and otipax (Table 2).
In the group of patients with OXO, when included in the study, the severity of inflammatory changes in the eardrum was in the range of 1–3 points in all subgroups. The average scores in the subgroups that received otipax and candibiotic were 2.1±0.4 points; in the subgroup of patients who received anauran - 2.3±0.4 points. At the level of 3 and 5 days, the reverse dynamics of inflammatory changes in the eardrum were found to be comparable. The average indicators of the condition of the eardrum in the subgroup of patients who received candibiotics were 0 points; in the subgroup that received otipax - 0.2±0.2 points; in the subgroup that received anauran - 0.5±0.4 points.
conclusions
1. Ear drops Kadibiotic, Anauran and Otipax in the complex therapy of acute external and acute otitis media have a comparable anti-inflammatory effect against the background of systemic antibacterial therapy. The analgesic effect in the treatment of acute external otitis is significantly more pronounced with the application of candibiotic drops. In an in vitro
candibiotic demonstrates antimicrobial effectiveness against all typical pathogens of otitis externa.
2. It is most rational to relieve ear pain syndrome with external otitis using candibiotic drops. Relieving ear pain syndrome in acute catarrhal otitis media using ear drops alone is ineffective.
3. For empirical local antimicrobial therapy of ONDO, it is advisable to use candibiotic ear drops. When treating external otitis with drops of Otipax, Anauran, systemic antibacterial therapy with a spectrum of action that extends to staphylococcus is necessary.
Indications for use
Candibiotic ear drops are prescribed for the treatment of inflammatory and allergic ear diseases , including: acute otitis media ( medium , diffuse external ), exacerbation of chronic otitis , painful conditions that have developed as a result of surgical interventions on the hearing organs.
Reviews about Candibiotic
Almost all the reviews about Candibiotic ear drops found on the Internet are positive. The vast majority of patients using these drops to treat their own painful conditions of the hearing organs noted the high effectiveness of this remedy in the complete absence of any side effects. Naturally, such a drug can only be prescribed by an otolaryngologist and only for the treatment of ear pathologies corresponding to the drug.
Candibiotic price, where to buy
The average price of Candibiotic ear drops is 270 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Candibiotic ear drops complete with stopper pipette 5 mlGlenmark Pharmaceuticals LTD RUB
429 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Candibiotic (ear drops 5ml)Glenmark Pharm
RUB 388 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Candibiotic 5 ml No. 1 ear drops Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd., India
143 UAH.order
PaniPharmacy
- Candibiotic liquid Candibiotic k/ush 5ml India, Glenmark
155 UAH order
show more
Candibiotic ear drops 5ml bottle with pipette
Indications
Allergic and inflammatory diseases of the ear, including:
- acute diffuse external otitis;
- acute otitis media;
- chronic otitis in the acute stage;
- condition after ear surgery.
pharmachologic effect
The drug has local antimicrobial, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and local anesthetic effects.
Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotic. Disturbs the process of protein synthesis in the microbial cell. Active against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Beclomethasone dipropionate - GCS. Has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects.
Clotrimazole (imidazole derivative) is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent for topical use. The antifungal effect of clotrimazole is associated with a disruption in the synthesis of ergosterol, which is part of the cell membrane of fungi, which changes the permeability of the membrane and causes subsequent cell lysis.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic. Causes a reversible blockade of impulse transmission along nerve fibers by blocking the passage of sodium ions through the membrane.
Drug interactions
Drug interactions of the drug have not been studied.
Dosage regimen
The drug is used topically. Instill 4-5 drops into the external auditory canal 3-4 times a day.
Improvement occurs within 3-5 days. The course of treatment is 7-10 days.
Before opening the package and using the drug for the first time, you must warm the bottle in your hand for 3-5 minutes to room temperature. For further use and storage at room temperature, additional heating is not required.
Overdose
Data on drug overdose are not provided.
Contraindications for use
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- violation of the integrity of the eardrum;
- children under 6 years of age.
Use in children
The use of the drug is contraindicated in children under 6 years of age.
Restrictions for children
Use with caution
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The question of the advisability of prescribing the drug during pregnancy is decided by the doctor individually. Prescribing the drug is possible when the expected benefit of therapy for the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Restrictions during pregnancy
Use with caution
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children, protected from light at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C. Do not freeze.
Terms of sale
The drug is available with a prescription.
special instructions
Visual impairment
With systemic and local use of GCS, visual impairment may occur. If the patient has symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, the patient should be advised to consult an ophthalmologist to identify possible causes of visual disturbances, including cataracts, glaucoma, or rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC), which have been observed in systemic and local use of GCS.
Side effect
Local reactions: rarely - itching, burning at the site of application of the drug; allergic reactions are possible.
From the organ of vision: rarely (≥1/10000-
Possible product names
- Candibiotic cap. ear with pipette 5 ml.
- CANDIBIOTIC EAR DROPS 5 ML
- CANDIBIOTIC 5ML EAR DROPS
- CANDIBIOTIC EAR DROPS. 5 ML. (+ CORK-PIPPETTE) X1
- CANDIBIOTIC EAR DROPS FL. 5ML COMPLETE WITH PIPETTE CAP
- CANDIBIOTIC EAR DROPS 5ML FL. X1
- (Candibiotic) Candibiotic drops. ear with pipette 5 ml.