pharmachologic effect
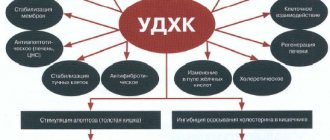
The active component is an endogenous antioxidant that is capable of binding aggressive free radicals. Alpha lipoic acid acts as a coenzyme in the transformation of substances that have pronounced antioxidant effects.
Such substances are able to exhibit protective, protective functions in relation to cells, protecting them from the aggressive effects of reactive radicals that are formed during intermediate metabolism, or at the time of the breakdown of foreign exogenous substances (including heavy metals).
The active substance is involved in the mitochondrial metabolism of substances inside the cell. By stimulating the utilization of glucose, thioctic acid is capable of synergizing with insulin . In patients with diabetes mellitus, changes in the level of pyruvic acid concentration in the blood are recorded.
According to the mechanism and nature of the biochemical effect, the active substance is similar to B vitamins . The active substance has a lipotropic effect, which manifests itself in accelerating the utilization processes of lipids in the hepatic system. Lipoic acid can stimulate the transfer of fatty acids from the liver system to various tissues in the body.
The nature of the drug is a detoxification effect when salts of heavy metals enter the body and in case of other poisoning. Thioctic acid changes cholesterol metabolism, improves the general and functional condition of the liver.
Why does vitamin N deficiency occur and why is it dangerous?
A lack of any of the microelements needed by the body is a problem, and a complex one. Also, vitamin N deficiency is just the tip of the iceberg; the essence of the problem lies much deeper and can have serious consequences.
Vitamin N deficiency is caused by:
- unbalanced diet;
- deficiency of vitamin B1 and proteins;
- liver diseases;
- dermatitis.
In the case of hypovitaminosis N, it is impossible to name a point-by-point list of possible symptoms that should signal a deficiency of the substance. Meanwhile, a long-term lack of vitamin gives rise to serious health problems.
First of all, the nervous system suffers. Convulsions, dizziness, and polyneuritis appear. And all because instead of thioctic acid, pyruvic acid accumulates in the body, and it destroys nerve cells.
Another consequence is liver dysfunction. The next stage of the disease is hepatitis and pathological degeneration of healthy organ cells into adipose tissue, the formation of bile occurs with disruptions.
Lipoic acid deficiency also affects blood vessels. And you will have to pay for an unbalanced diet with the development of atherosclerosis.
Having analyzed the possible consequences of hypovitaminosis N, it is not difficult to compile a list of possible signals. But the presence of these symptoms no longer just warns of a slight decrease in the level of alpha-lipoic acid in the body, but signals serious consequences.
Contact your doctor immediately if:
- muscle cramps recur regularly;
- dizziness appeared;
- discomfort is felt in the liver area;
- a coating appeared on the tongue;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- dark spots appeared on the body, a foul smell of sweat appeared;
- There are brown circles under the eyes.
Any of the above symptoms is a signal of alarm.
Indications for use of Lipoic acid
The medication is widely used in the treatment of liver pathology, the nervous system, alcoholism and intoxication, diabetes mellitus, and to alleviate the course of cancer.
Main indications:
- chronic hepatitis in the active phase;
- chronic pancreatitis due to alcoholism;
- chronic cholecystopancreatitis ;
- acute liver failure;
- intoxication with heavy metals, sleeping pills, carbon, carbon tetrachloride, mushrooms;
- viral hepatitis with increasing jaundice ;
- hepatic cirrhosis;
- diabetic polyneuritis;
- alcoholic polyneuropathy;
- poisoning with toadstool;
- fatty liver degeneration;
- dyslipidemia;
- coronary atherosclerosis .
During a course of treatment with Prednisolone, the medication acts as a corrector and synergist to prevent the development of “withdrawal syndrome” and gradually reduce the dose of glucocorticosteroid.
Lipoic acid for weight loss
The mechanism of action of the active substance allows the medication to be used to lose excess weight. The effect is more pronounced when simultaneously actively playing sports. Lipoic acid can trigger the fat burning mechanism, but it is not possible to burn absolutely all excess fat on its own, so intense physical activity is required.
Muscle tissue “attracts” nutrients during training, and thioctic acid can increase endurance, enhance fat burning and increase the overall effectiveness of physical activity. Simultaneous adherence to the diet allows you to achieve the greatest results.
Lipoic acid dosage for weight loss
Usually 50 mg of medication is sufficient. The minimum threshold is 25 mg. The most effective time to take the drug to achieve maximum results in the fight against excess weight:
- before or immediately after breakfast;
- at the last daily meal;
- after training, physical activity.
Reviews
The drug works well when following a diet and at the same time an active combination of exercises in the gym. On thematic forums, users discover a little secret: the drug works better when taking carbohydrate foods (semolina or buckwheat porridge, dates, honey, pasta, rice, peas, beans, bread products).
Lipoic acid in bodybuilding
Quite often in bodybuilding, thioctic acid is combined with levocarnitine ( Carnitine , L-carnitine ). This amino acid is a relative of B vitamins and can activate fat metabolism. Levocarnitine releases fat from cells, stimulating energy expenditure.
Food Sources of Vitamin N
When asked what contains the most lipoic acid, jokers answer: in pharmacy vitamins. This is actually true. But you can’t eat the “feed” of the pharmaceutical industry all your life. After all, Mother Nature also takes care of her children and has hidden some reserves of vitamin N in delicacies of animal and plant origin. So, it’s time to find out which foods contain thioctic acid, especially since a healthy body is able to provide itself with the daily requirement of the substance from food.
Leading foods containing the most vitamin N:
- offal (heart, kidneys, liver);
- red meat (beef, lamb, turkey);
- dairy products (milk, sour cream, cream, cottage cheese, kefir);
- eggs;
- yeast;
- mushrooms;
- leafy vegetables (spinach, cabbage);
- legumes;
- rice;
- Wheat groats;
- fruits.
Side effects
- diarrhea syndrome;
- epigastric pain;
- nausea;
- anaphylactic reactions;
- skin rashes;
- vomit;
- convulsions;
- increased intracranial pressure ;
- disorders of glucose metabolism ( hypoglycemia );
- migraine -type headache ;
- hives;
- itching;
- tendency to bleeding (with functional disorders of platelets );
- pinpoint hemorrhages;
- diplopia;
- difficulty breathing.
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, nausea, vomiting.
In case of acute overdose (when using 10-40 g), serious signs of intoxication may be observed (generalized convulsive seizures; severe disturbances in the acid-base balance leading to lactic acidosis; hypoglycemic coma; severe bleeding disorders, sometimes leading to a fatal outcome).
If a significant overdose of the drug is suspected (doses equivalent to more than 10 capsules for adults or more than 50 mg/kg body weight for a child), immediate hospitalization is necessary.
Treatment: symptomatic (including gastric lavage, taking activated charcoal), if necessary - anticonvulsant therapy, measures to maintain vital functions. There is no specific antidote. Hemodialysis is not effective.
Lipoic acid, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
300-600 mg of thioctic acid is administered intravenously daily, which corresponds to 1-2 ampoules of 10 ml and 1 ampoule of 20 ml of concentration 3%. The duration of therapy is 2-4 weeks, after which treatment is continued in tablet form at a daily dose of 300-600 mg.
Instructions for use of Lipoic acid tablets
Orally 30 minutes before meals. Tablets should not be broken or chewed. Daily dose: 1 tablet 1 time per day (300-600 mg). The therapeutic effect is achieved by taking 600 mg per day. In the future, the dose can be halved.
For diseases of the liver system, tablets are prescribed: up to 4 times a day, 50 mg for a month. A repeat course can be carried out after 1 month.
Treatment of diabetic neuropathy and alcoholic polyneuropathy: begin with intravenous injections with the transition to a tablet form of 600 mg per day.
Thioctic acid: antioxidant therapy for neurological diseases
The use of thioctic acid in medical practice is largely associated with the development of ideas about “oxidative stress” and lipid peroxidation as a fairly universal pathogenetic mechanism of cell and tissue damage [24]. The antioxidant effect of thioctic acid is due to the presence of two thiol groups in the molecule (hence the prefix “thio”), as well as the ability to bind free radicals and free tissue iron (preventing its participation in lipid peroxidation) [10]. Thioctic acid not only has independent antioxidant potential, but also provides powerful support for the work of other antioxidant units in the body [23]. In this regard, its protective effect is closely related to homeostasis in the glutathione and ubiquinone system [8]. The production of reactive oxygen species increases significantly with inflammation, immunological disorders, hypoxia, hyperoxia, exposure to drugs, radiation, and antioxidant deficiency.
Thioctic acid is one of the most powerful antioxidants used in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy [2, 25]. Thioctic acid is a coenzyme of key enzymes in the Krebs cycle, which explains its effectiveness. An additional advantage in the mechanism of action of thioctic acid is its clearly documented effect of glucose utilization [15]. The high efficiency and pathogenetic effect of thioctic acid have been proven by numerous experimental and clinical studies. The adequate and rational use of thioctic acid preparations is based on the results of numerous studies (ALADIN I, ALADIN II, ALADIN III, ORPIL, NATHAN, DECAN, SYDNEY), which tested the dose, frequency of administration and course duration (Table 1).
A multicenter, randomized, double-blind study (SYDNEY II) assessed the effectiveness of thioctic acid in the treatment of patients with diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) [1, 3]. The study was conducted from 2004 to 2006, it involved 87 patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) of type 1 and 2, who were undergoing inpatient (National Healthcare Institution Central Clinical Hospital No. 1 of JSC Russian Railways) and outpatient treatment (Department endocrinology of the State Educational Institution of Additional Professional Education of the Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education (Roszdrav). The SYDNEY study concluded that intravenous alpha lipoic acid for 3 weeks. causes a significant reduction in neuropathic symptoms and neurological objective symptoms that are painful for patients. Considering the dose-dependent effect of side effects, the optimal dosage is 600 mg of thioctic acid. The authors concluded: as a result of a comprehensive clinical and neurophysiological study of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, it was noted that the earliest EMG indicator of sensory nerve damage in diabetes is a decrease in the action potential. Pain reduction occurred from the 2nd week. taking thioctic acid at a dose of 1800 mg/day, from the 4th week. reception - at a dose of 1200 mg and only by the 5th week. - while taking 600 mg of thioctic acid [3]. In patients with DPN (n=24) participating in the study, using thioctic acid at a dose of 1800 mg/day for 3 weeks. neuropathic symptoms and neurological deficits decreased; the incidence of side effects was comparable to the placebo group [29].
In medical practice, a number of thioctic acid preparations are used for therapeutic purposes, which are represented by its three main salts: ethylenediamine, trometamol and megluminic [12]. One of the drugs whose active substance is thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid is Thiogamma® (pharmaceutical (Germany)). Thiogamma® is a meglumine salt of alpha-lipoic acid, polyethylene glycol is used as a solubilizer, their advantages are to suppress the formation of free radicals, improve the energy metabolism of neurons, and restore impaired endoneurial blood flow. The drug is available in the form of tablets containing 600 mg of the drug, a solution for intravenous infusion in bottles containing 600 mg of the drug in the form of meglumine salt, and ampoules. Meglumine (N-methyl-D-glucamine) is known to be used as a stabilizer in many pharmaceutical products [12]. Meglumine is also used to reduce the toxicity of gadolinium in magnetic resonance contrast media. It is used as the antimonate meglumine to treat leishmaniasis. It was demonstrated that in the experiment, mice accepted a dose of up to 1 g/kg when administered intraperitoneally without side effects. There is only one report of the development of an anaphylactic reaction in a patient with osteoid osteoma after the use of gadoteric and gadopentetic acid during an MRI study. No descriptions of other negative effects of meglumine could be found. Thus, we can conclude that of all the stabilizers used for the manufacture of dosage forms of thioctic acid, meglumine is the least toxic.
Instructions for use of the drug Thiogamma® were approved on 04/15/1999 by the State Pharmacological Committee of the Ministry of Health of Russia, re-registration on 05/24/2010 (for tablet forms), 02/29/2012 (for injection forms) [19]. The drug is prescribed 1 r./day 300–600 mg, taken without chewing, with a small amount of liquid. According to the ALADIN I study [28], the effect of alpha-lipoic acid on positive neuropathic symptoms at doses of 600 and 1200 mg is practically the same. In a clinical study of 3 weeks of intravenous alpha-lipoic acid, side effects (headache, nausea, vomiting) were more common with 1200 mg (32.6%) than with 600 mg (19.8%) with placebo. (20.7%) [28]. It was concluded that a dosage of 600 mg of alpha-lipoic acid is optimal both from the point of view of clinical effectiveness and taking into account the possibility of developing side effects.
The clinical use of thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid (in particular, Thiogamma®) is based on the many biochemical and physiological effects of this substance [6]. The main mechanisms of action of Thiogamma®, according to those set out in the Methodological Recommendations of V.V. Gorodetsky (2004) [8], can be presented as follows:
- influence on energy metabolism, glucose and lipid metabolism (participation in the oxidative decarboxylation of keto acids) with activation of the Krebs cycle; increased uptake and utilization of glucose by the cell and oxygen consumption; increase in basal metabolism; normalization of gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis; inhibition of cholesterol formation;
- cytoprotective effect: increased antioxidant activity (direct and indirect through the vitamin C/E, cystine/cysteine and glutathione systems); stabilization of mitochondrial membranes;
- influence on the reactivity of the body: stimulation of the reticuloendothelial system; immunotropic effect; anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity (associated with antioxidant effects);
- neurotropic effects: stimulation of axon growth, positive effect on axonal transport, reduction of the harmful effects of free radicals on nerve cells, normalization of abnormal glucose supply to the nerve, prevention and reduction of nerve damage in experimental diabetes;
- hepatoprotective effect: accumulation of glycogen in the liver, inhibition of lipid accumulation in the liver (in some pathological conditions), increased activity of a number of enzymes, improvement of the functional activity of the liver;
- detoxification effect (FOS, lead, arsenic, mercury, sublimate, cyanides, phenothiazides, etc.).
The main indications for the use of the drug Thiogamma® in the treatment of diseases accompanied by neurological symptoms are focused on diabetic and alcoholic polyneuropathy [18]. Currently, thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid, in particular Thiogamma®, is the most effective agent in the treatment of peripheral polyneuropathy, which has been confirmed by large-scale multicenter long-term studies, such as the ALADIN Study (Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy) [16]. However, the antioxidant activity of thioctic acid is used in many areas of medicine [10] (Table 2).
Thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid is a powerful lipophilic antioxidant and is rightfully considered the “gold standard” for the pathogenetic treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) [8]. A number of studies have shown that the use of alpha-lipoic acid at a dose of 600 mg/day intravenously or orally for 3 weeks. up to 6 months reduces to a clinically significant extent the main symptoms of DPN, including pain, paresthesia and numbness. It is known that the cause of a 50–70% decrease in the rate of insulin-dependent transmembrane glucose transport in diabetes is oxidative stress. The basis for treating DPN with thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid drugs is the fact that in diabetes there is a deficiency of alpha-lipoic acid, and alpha-lipoic acid (which has a powerful antioxidant effect), in turn, increases the bioavailability of glucose in insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent tissues , increases the absorption of glucose by peripheral nerves to normal levels, and also promotes an increase in endoneurial glucose reserves, which has a beneficial effect on the restoration of energy metabolism of nerves. It is believed that the administration of thioctic acid is advisable for insulin-resistant forms of diabetes [10]. In this case, it is considered optimal to prescribe an intravenous drip of alpha-lipoic acid solution at the beginning of treatment for 3 weeks. (15 droppers) followed by taking 600 mg of the drug in tablet form (1 r./day 30–40 minutes before meals) for 1–2 months. [8].
The effectiveness of Thiogamma® in DPN has been convincingly demonstrated in many clinical studies. At the Sofia Medical University (Bulgaria), T. Tankova et al. (2000) conducted a randomized, open, placebo-controlled study [7–9] to evaluate the effectiveness of the drug Thiogamma® using a 2-stage prescription regimen: after a period of intravenous infusions, the drug was administered orally. A constant dose of 600 mg/day was used, intravenous administration was carried out for 10 days, oral administration for another 50 days. A pronounced clinical effect appears after the first 10 days of therapy. When compared with the control group, in patients receiving Thiogamma®, the intensity of spontaneous pain in the legs decreased by 40%, and vibration sensitivity, which was significantly reduced before treatment and determined in various areas of the foot, increased by 35%. By the end of the course of therapy, positive dynamics were noted in reducing the severity of pain according to VAS and increasing vibration sensitivity. Positive dynamics of indicators characterizing the severity of damage to the autonomic nervous system were also obtained: over 60 days of therapy, manifestations of autonomic neuropathy decreased by 40% and the drop in systolic blood pressure during an orthostatic test decreased by 2.5 times, which indicates an improvement in the function of the autonomic nervous system.
As part of another monocenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 120 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes were examined, of which 60 received placebo and 60 received alpha-lipoic acid (at a dose of 600 mg in 225 ml of saline at a time of intravenous drip administration 30–40 min) [1]. We studied the effect of this drug on the clinical manifestations of DPN, electromyographic (EMG) indicators, indicators of quantitative sensory and autonomic testing in 60 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The duration of the study was 4 weeks. Positive neuropathic symptoms were chosen as the main criterion for the clinical effectiveness of the study drug due to the fact that they primarily disrupt the patient’s quality of life. An improvement in the distal latency indicator in an EMG study indicates that the main unpleasant sensations (pain, burning, numbness, paresthesia), which worsen the patient’s quality of life, decreased during alpha-lipic acid therapy due to improved peripheral nerve function. Thus, the drug has been shown to be highly effective in relation to most of the studied indicators of the condition of peripheral nerves. It was concluded that thiocotic (alpha-lipoic) acid preparations can be successfully used in the treatment of symptomatic DPN.
In a study by I. I. Matveeva et al. [13], conducted in the “Diabetic Foot” office of the Izhevsk Endocrinology Center, examined 126 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (screening), who were prescribed the drug thioctic acid intravenously for 10 days at a dose of 600 mg, subsequently in tablets of 600 mg. mg daily for 8–10 weeks. Based on the results of the study, it was concluded that the drug thioctic acid is highly effective in the treatment of distal DPN, clinical symptoms and the condition of peripheral nerves improve, oxidative stress and insulin resistance decrease.
In another study [14], 50 patients with diabetic and hypothyroid distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy were prescribed the drug Thiogamma®, first at a dose of 600 mg (equivalent to 1167.70 meglumine salt of alpha-lipoic acid) intravenously, drip for 10 days, 1 injection per day , the injection rate was no more than 50 mg/min. It is also important to note that a distinctive feature of the drug Thiogamma® is the release form, which allows the drug to be administered intravenously, by drip, without requiring prior dilution. Then, for 30 days, patients took Thiogamma® 600 mg in the morning and on an empty stomach. During the study, the author came to the conclusion that among all forms of DPN, the greatest effect of using the drug Thiogamma® was noted in the treatment of acute sensory polyneuropathy and radiculoplexopathy; in the treatment of progressive sensorimotor polyneuropathy, the use of Thiogamma® also showed a statistically significant therapeutic result. In relation to hypothyroid polyneuropathy, Thiogamma® showed high efficiency, in particular for reducing and eliminating pain, however, the positive dynamics during treatment with Thiogamma® clearly correlated with adequate replacement therapy with thyroid hormones.
In a study by E. Yu. Komelyagina et al. (2006) [11] presented the results of a comparison of the effectiveness of two options for treating DPN with thioctic acid drugs: option 1 - oral administration of 1800 mg/day (600 mg 3 times/day) for 4 weeks. (n=15) and 2nd option - oral administration of 600 mg/day for 3 months. (n=15). The study showed that in both modes of use, the drug thioctic acid provides a significant reduction in the severity of neuropathic complaints in patients with diabetes with a satisfactory level of compensation for carbohydrate metabolism. Based on the results of the study, the authors came to the conclusion: “... the choice of treatment regimen for DPN using thioctic acid drugs is individual and depends on the specific situation: in case of severe pain symptoms, a shorter course with a high dosage of the drug (1800 mg/day for 4 weeks. ), with unexpressed symptoms - a longer course with a lower daily dosage (600 mg/day for 3 months)...".
The range of use of drugs containing thioctic acid, both as monotherapy and as part of complex therapy, is constantly expanding. In a comparative open randomized study [5], conducted at the Department of Occupational Diseases of the St. Petersburg State Medical Academy named after. I. I. Mechnikov, evaluated the effectiveness of the drug, the active substance of which is thioctic acid, in the complex treatment of manifestations of vibration disease (syndrome of vegetative-sensory polyneuropathy of the extremities, angiodystonic syndrome). Use at a dosage of 600 mg daily as part of complex therapy for 21 days significantly reduces the frequency of subjective complaints of patients, leads to a persistent reduction in relapses of pain in the extremities, a decrease in the frequency of attacks of vasospasms, enhancing the effect of therapy in general. Thus, the effectiveness of this drug has been shown in relation to vascular tone, blood filling and venous outflow, which, according to the authors, causes the development of anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, analgesic effects and contributes to the normalization of homeostasis.
Research by M. Senoglu et al. (2009) [27] showed the effectiveness of alpha-lipoic acid against such clinical symptoms as pain, paresthesia, hypoesthesia in patients with compressive radiculopathy due to discoradicular conflict. The results of this study correlate with a study in which M. Ranieri et al. (2009) [26] assessed the effectiveness of the additional use of a combination of alpha-lipoic and gamma-linolenic acid in a 6-week rehabilitation program for patients with discogenic radiculopathy when compared with a similar group of patients receiving only a rehabilitation program. A case of effective use of the drug thioctic acid (600 mg/day for 1 month) as part of complex therapy in a patient with stage III Lyme disease (neuroborreliosis, changes in the central nervous system, damage to the cranial nerve, peripheral polyneuropathy due to neuroborreliosis) is described [4].
Employees of the Clinic of Neurology and Neurosurgery of the Medical Faculty of the Russian State Medical University (now Russian National Research Medical University) E. I. Chukanova et al. (2001–2014) [20–22] a number of studies were conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the use of thioctic acid in the treatment of patients with discirculatory encephalopathy (DE) and when prescribed in complex pathogenetic therapy of vascular cognitive impairment. Based on the example of a study of 49 patients with DE, it was shown [20] that when prescribing thioctic acid in a dosage regimen of 600 mg 2 times / day for 7 days, switching to 600 mg 1 time / day for 53 days orally in 30 min before meals allows you to achieve a positive effect by the 7th day of treatment (at a dose of 1200 mg/day); when the dose is reduced to 600 mg/day (from the 8th day of treatment), the positive effect of the drug on the dynamics of the neurological status is maintained and is most pronounced by 60th day. Positive dynamics were noted in the neurological and neuropsychological status of patients with DE. Based on the results of the study, it was concluded that thioctic acid is effective not only in the treatment of patients with DE with elevated glucose levels, but also in patients with cerebrovascular insufficiency without diabetes [20]. In a study of a group of 128 patients with DE [21], a pharmacoeconomic analysis of the effectiveness of treatment with thioctic acid was conducted in patients with different stages of chronic cerebral vascular insufficiency. The drug thioctic acid was prescribed orally at a daily dose of 600 mg 2 times/day for 7 days, switching to 600 mg 1 time/day for 23 days 30 minutes before meals. The study established: in patients with stage I DE. — regression of asthenic syndrome, vestibular ataxia, axial reflexes; in patients with stage II DE. — increasing the effectiveness of influencing the indicators of the “movement” scale, ataxia, pseudobulbar syndrome; in patients with stage III DE. — a positive effect on the indicators of the “movement” scale, ataxia (frontal and cerebellar), pseudobulbar syndrome, which persisted until the 12th month. observations, and also showed a statistically significant effect on the dynamics of the amyostatic syndrome score. The authors of the study concluded that treatment with thioctic acid in patients with DE leads to significant clinical improvement, reduces the risk of strokes during the course of the disease and reduces the percentage of disease progression in patients with stage I and II DE. A small percentage of side effects were noted. Thioctic acid is well tolerated by patients, including patients of older age groups. Thioctic acid therapy is preferable from an economic point of view compared to the cost of treatment of patients in the control group who received antihypertensive and antithrombotic therapy, which is associated with its high effectiveness in influencing the risk of TIA, stroke and progression of DE.
Conclusion
The data available today allow us to recommend that a doctor prescribe the drug Thiogamma® in the treatment of patients with neuropathy of somatogenic origin. The developed scheme of 2-stage administration of the drug Thiogamma® is successfully used with a high degree of efficiency: intravenous infusions of the finished solution of the drug Thiogamma® for 10 days (in bottles of 50 mg of solution for infusion of 12 mg/ml, which is equivalent to 600 mg of thioctic acid, with the time of intravenous drip administration for 30–40 minutes) followed by administration of the tablet form of the drug (600 mg/day) for 50 days. From the point of view of clinical effectiveness and taking into account the possibility of side effects, a dosage of thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid of 600 mg/day is optimal. Individual approach to the dosage regimen: for severe pain symptoms - a shorter course with a high dosage of the drug (1800 mg/day for 4 weeks), for less severe symptoms - a longer course with a lower daily dosage (600 mg/day for 3 months).
It is important to note that a distinctive feature of the drug Thiogamma® is its release form, which allows the drug to be administered intravenously, by drip, without requiring prior dilution.
Literature
- Ametov A.S., Strokov I.A., Barinov A.N. and others. Alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: symptomatic diabetic neuropathy (SYDNEY) trial // Farmateka. 2004. No. 11 (88). pp. 69–73.
- Ametov A.S., Strokov I.A., Samigullin R. Antioxidant therapy of diabetic polyneuropathy // Breast cancer. 2005. T.13. No. 6. pp. 339–343.
- Ametov A.S., Soluyanova T.N. Efficacy of thioctic acid in the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy // Breast Cancer. 2008. No. 28. P. 1870–1875.
- Antelava O.A., Ushakova M.A., Ananyeva L.P. and others. Clinical manifestation of neuroinfection in Lyme disease against the background of immunosuppressive therapy // Breast Cancer. 2014. No. 7. pp. 558–563.
- Artamonova V. G. Lashina E. L. Use of the drug thiolept (thioctic acid) in combination therapy of vibration disease // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after. S. S. Korsakova. 2011. T.111. No. 1. P.82–85.
- Vorobyova O. V. Thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid - spectrum of clinical use // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after. S. S. Korsakova. 2011. T.111. No. 10. P.86–90.
- Galieva O.R., Janashiya P.Kh., Mirina E. Yu. Treatment of diabetic neuropathy // Breast cancer. 2005. T.13, No. 10.
- Gorodetsky V.V. Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy and other dystrophic-degenerative and inflammatory diseases of the peripheral nervous system with metabolic drugs // Methodological recommendations. M., 2004. 30 p.
- Janashiya P.Kh., Mirina E.Yu., Galieva O.R. Treatment of diabetic neuropathy // Breast cancer. 2005. No. 10. P.648–652.
- Ivashkina N.Yu., Shulpekova Yu.O., Ivashkin V.T. Do we all know about the healing capabilities of antioxidants? // RMJ. 2000. No. 4. P. 182–184.
- Komelyagina E.Yu., Volkova A.K., Myskina N.A. and others. Comparative effectiveness of various regimens of oral administration of thioctic acid (thioctacid bv) in the treatment of painful forms of diabetic distal neuropathy // Farmateka. 2006. No. 17: https://medi.ru/doc/144422.htm
- Korpachev V.V., Borshchevskaya M.I. Dosage forms of thioctic acid // Problems of endocrine pathology, 2006, No. 1: https://farmak.ua/publication/338
- Matveeva I.I., Trusov V.V., Kuzmina E.L. and others. Frequency of distal neuropathy and experience with the use of Thioctacid in patients with first diagnosed type 2 diabetes // https://medi.ru/doc/144420.htm
- Pimonova I. I. Use of the drug Thiogamma for diseases of the peripheral nervous system // https://www.medvestnik.ru
- Rachin A.P., Anisimova S.Yu. Polyneuropathy in the practice of a family medicine doctor: diagnosis and treatment // Breast Cancer. 2012. No. 29. pp. 1470–1473.
- Thioctic acid: instructions for use: https://www.rlsnet.ru/mnn_index_id_852.htm
- Thiogamma®: instructions for use: https://medi.ru/doc/1712.htm
- Tiogamma®: instructions for use: https://www.novo.ru/aptekan/tiogamma.htm
- Chukanova E.I. The influence of Thioctacid on the clinical manifestations and course of dyscirculatory encephalopathy // Breast Cancer. 2010. T.18. No. 10. P.1–4.
- Chukanova E.I., Chukanova A.S. Use of antioxidant drugs in complex pathogenetic therapy of vascular cognitive impairment // Breast Cancer. 2014. No. 10. pp. 759–761.
- Chukanova E.I., Sokolova N.A. Efficacy of thioctacid in the treatment of patients with dyscirculatory encephalopathy // https://medi.ru/doc/144418.htm
- Alpha lipoic acid therapy. Thiogamma. Scientific review. Verwag Pharma GmbH and Co., 2003.
- Arivazhagan P., Juliet P., Panneerselvam C. Effect of DL alpha-lipoic acid on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in aged rats // Pharmacol. Res. 2000. Vol. 41(3). P. 299–303.
- Gurer H., Ozgunes H., Oztezcan S. et al. Antioxidant role of alpha-lipoic acid in lead toxicity // Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999.Vol. 27(1–2). P. 75–81.
- Jacob S., Ruus P., Hermann R. et al. Oral administration of RAC-alpha-lipoic acid modulates insulin sensitivity in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus: a placebo-controlled pilot trial // Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999. Vol. 27(3–4). P. 309–314.
- Ranieri M., Sciuscio M., Cortese AM et al. The use of alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), gamma linolenic acid (GLA) and rehabilitation in the treatment of back pain: effect on health-related quality of life // Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009. Vol. 22 (3 Suppl). P. 45–50.
- Senoglu M., Nacitarhan v. , Kurutas EB et al. Intraperitoneal Alpha-Lipoic Acid to prevent neural damage after crush injury to the rat sciatic nerve // J. Brachial. Plex. Peripher. Nerve. Inj. 2009. Vol. 4. P. 22.
- Ziegler D., Hanefeld M., Ruhnau KJ et al. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the antioxidant α-lipoic acid. A 3-week multicentre randomized controlled trial (ALADIN Study) // Diabetol. 1995. Vol. 38. P.1425–1433.
- Ziegler D., Nowak H., Kempler P. et al. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with antioxidant α-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis // Diabetic Med. 2004. Vol. 21. P. 114–121.
Interaction
The medication can enhance the effects of glucocorticosteroid drugs. Suppression of the activity of Cisplatin . The drug enhances the effect of hypoglycemic agents (oral forms) and insulin.
It is not recommended to use with medications that contain metal ions (calcium, magnesium, iron) due to the ability of lipoic acid to bind metals.
If there is an urgent need to use drugs, it is recommended to maintain a certain time interval (at least 2 hours). Ethanol metabolites and ethanol itself weaken the effect of thioctic acid.
How to understand that there are already too many vitamins
It is not clear by whom and when the invented principle “The more, the better” has found its application in few places. In most cases, it only serves as an example of bad manners and bad taste. And in the story with vitamins, it can even put you on a hospital bed.
Meanwhile, it is worth understanding: vitamin N obtained from food can never provoke an overdose of the substance in the human body.
The only cause of hypervitaminosis is the synthetic form of thioctic acid, taken in a dosage significantly higher than the daily norm.
It is a little easier to determine an overdose of lipoic acid than its lack in the body. Symptoms traditional for hypervitaminosis:
- increased stomach acidity;
- heartburn;
- pain in the pit of the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- skin allergies: urticaria, itching, inflammation.
In most cases, getting rid of unpleasant symptoms is easy: just give up the synthetic vitamin. But it’s even better to forget about the practice of arbitrarily prescribing medications or vitamins for yourself, and then also about. There are doctors for these purposes. Only they, after carefully studying various blood tests and other examinations, are able to prescribe an adequate dose of deficient minerals and vitamins.
special instructions
The main metabolic pathways are oxidation and conjugation.
Benefits and harms
Lipoic acid is a natural antioxidant and vitamin. It helps normalize and accelerate metabolic processes, stimulates the pancreas, removes toxins from the body, lowers blood sugar levels, improves visual perception, has a beneficial effect on heart function, lowers cholesterol , and helps normalize blood pressure.
With the use of Lipoic acid, there is a decrease in the severity of negative reactions that occur after chemotherapy in cancer patients.
The drug has a beneficial effect on the condition of nerve endings damaged as a result of diabetes. Rarely do negative reactions occur during the use of the medication.
Vitamin for obesity
Just a few decades ago, it never occurred to anyone that excess weight, along with cardiovascular diseases, would soon be named one of the main problems of the century. “Getting rid of excess is easy! To lose weight, you need to reduce the portions you consume per day!” – skinny people who have no idea about the causes of obesity never tire of giving advice. An overweight person is not always a glutton. Stress, poor environment, irregular nutrition (often due to a specific work schedule), “sedentary” work, heredity - these are not all the reasons for possible excess weight gain caused by metabolic disorders. And the metabolism, as luck would have it, if it is disrupted, is often in the direction of slowing down. So we get a paradox with a “glass of water”, which turns into fat deposits on the sides.
And the pharmaceutical industry never tires of replenishing the arsenal of pharmacies with weight loss products. And the plump people are buying everything at breakneck speed, so as not to accidentally miss a miracle pill that can get rid of fat in a month/week/day. But, as in the old joke, we have two news for you: good and bad. The bad thing is that miracles don’t exist and you can’t lose weight in a day. And now - a good one: a pill for excess weight was invented a long time ago. It modestly lies on the shelves of all pharmacies in the world with a price tag of a penny. It is also called modestly - lipoic acid, or vitamin N, or has some other trade name, but in parentheses the name common to all countries is always indicated - thioctic acid.
The unique properties of this substance help regulate fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the body, reduce cholesterol and blood glucose levels, and improve liver function.
But how do these beneficial properties affect the process of weight loss? How to lose weight with lipoic acid and is it even possible?
Vitamin N is fundamentally different from all “diet pills.” Most anti-obesity drugs, weight loss programs and diets are aimed at active fat burning, which subsequently has an even worse effect on the already disrupted metabolic process. Lipoic acid has a different tactic: it does not burn fat, but converts it into energy, which, from the point of view of nature, is more correct and beneficial for the body, and has a better result.
How vitamin N is useful for losing weight:
- reduces weight without fasting;
- normalizes rather than changes metabolism;
- improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- prevents the development of gallstone disease;
- strengthens blood vessels and heart muscle;
- has a positive effect on vision;
- eliminates stretch marks.
Similar drugs
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Verona
Phibs
Gastrikumel
Fitogastrol
Thyroidea Compositum
Berlition
Thiolepta
Gastric collection
Espa-Lipon
Brewer's yeast
Rosehip syrup
Octolipen
Thioctacid
Thiogamma
Figurin
Preparations containing thioctic acid:
- Berlition
- Thiolepta
- Octolipen
- Thioctacid
- Tiogram
- Alfa-Lipon
- Espa-Lipon
Use in cosmetology
The skin on the face is the most delicate, but at the same time most often susceptible to the negative effects of the sun, wind, and frost. Therefore, more often than other areas, it requires careful care. And α-lipoic acid is best suited for facial skin as a “tasty” nourishment.
By the nature of its effect on the epidermis, thioctic acid is more reminiscent of vitamins A, E, C - it protects against free radicals and improves metabolism at the cellular level. But in addition to this, vitamin N effectively rejuvenates the skin, tightens it, and gets rid of wrinkles and acne. This vitamin of youth is found in all anti-aging creams (both the most expensive and very cheap). Lipoic acid is responsible for beautiful skin in the décolleté and neck area, making it soft, smooth and tender.
By regularly using thioctacid externally, you can forget about skin imperfections in the form of small acne scars or minor injuries, pustules and pimples.
Creams containing alpha-lipoic acid relieve swelling, inflammation, cracks, and protect collagen molecules from destruction.
Lipoic acid for cosmetic purposes can be used as a finished product or prepared independently by enriching a cream, tonic or lotion with vitamin N. The yellow powder is first dissolved in alcohol or oil and then added to the finished cosmetic product. If you don’t like this form of release, you can buy the vitamin in ampoules or capsules at the pharmacy and add it to cosmetics in this form.
How to properly dilute vitamin
- Skin cleansing oil. Add a few milliliters of alpha lipoic acid in liquid form or a few milligrams in powder. Stir.
- Serum for moisturizing. Vitamin saturation should not exceed 1 percent.
- Tonic. Dilute lipoic acid in alcohol, stir thoroughly and pour the mixture into tonic.
- Cream. Dilute the powder in an oil base (or add the vitamin in liquid form), mix with the cream.
Adviсe
- You cannot heat up the vitamin mixture and then cool it - it loses its beneficial properties.
- Store the finished fortified cosmetic product in a cool, dark place.
- If you feel a burning sensation after using the drug, reduce the percentage of vitamin saturation. Therefore, to begin with, fortify cosmetics with a small portion of lipoic acid.
- In case of contact with mucous membranes, rinse with plenty of water and consult a doctor.
Two beauty recipes
And now it’s time to find out how to prepare a delicious skin product at home, the effectiveness of which is no worse than expensive creams.
Remedy No. 1
You will need:
- alpha lipoic acid – 1 ml;
- ascorbic acid – 8 ml;
- 10 ml syringe;
- fragrant water;
- kudesan (coenzyme in water-soluble form).
Draw ascorbic acid and lipoic acid into the syringe. In a separate container, mix coenzyme and fragrant water. Soak a cotton pad with the prepared acid mixture and apply it to your facial skin. Wait until the vitamin mix is absorbed. Spray your face with a mixture of coenzyme and fragrant water. After 15-20 minutes, wipe the skin with any tonic.
The result is radiant, soft skin with a beautiful color.
Remedy No. 2
You will need:
- macadamia nut oil – 10 ml;
- lipoic acid – 2 ml;
- green tea or grape extract.
Dissolve lipoic acid in nut oil and mix thoroughly. Add a little vitamin-containing extract (optional). Apply the finished mixture onto the face with massage movements. Keep the oil mask on for 20 minutes. Blot your face with a paper towel to remove any remaining product.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The result is moisturized and vitamin-enriched facial skin.
Lipoic acid reviews
The medication is well tolerated and has proven itself as an effective drug for intoxication, poisoning, and diseases of the liver system.
Reviews of Lipoic acid for weight loss
There are a variety of reviews. Some felt absolutely no effect, maintaining their weight despite regularly taking the medication. Some users note that taking Lipoic acid in combination with intense cardio exercise and following a certain diet can significantly reduce weight without harming their health.
Patients suffering from diabetes mellitus note that the medication can reduce the severity of negative reactions of hypoglycemic drugs (in some cases it was possible to reduce the dosage) and improve overall well-being.
Lipoic acid price, where to buy
Most often, the drug is purchased for weight loss. You can buy Lipoic acid in a pharmacy in Russia for about 100 rubles.
The price of Lipoic acid in Ukraine is about 100 UAH.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Lipoic acid caps.
Doctor's Best/Doctor Best 230 mg 60 pcsDoctor's Best 3919 rub.order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Lipoic acid Vitamir tablets No. 30 Square C
85 rub. order
show more
For pregnant
When planning pregnancy, it is important to replenish all vitamin depots of the body. After all, very soon a woman will have to “feed” not only herself, but also the child, whose health at first completely depends on the health of the mother. But the course of vitamin therapy should be determined by a doctor, especially since in gynecology the emphasis is on vitamins responsible for women’s health.
Only the attending doctor can adequately determine which vitamin and in what doses a woman needs for prevention or treatment, which form of the drug is best suited, and which microelements it is better to stay away from.
It is especially important not to engage in vitamin therapy without permission during pregnancy and breastfeeding. During this special period, many doctors generally prohibit their patients from taking dietary supplements and vitamin preparations. Meanwhile, laboratory studies have shown how lipoic acid (in adequate doses) is beneficial for pregnant women. Vitamin N reduces the risk of miscarriage and abnormal development of the nervous system of the unborn baby.
Benefits of thioctic acid for women's health:
- gives additional energy;
- important for kidneys and liver;
- prevents toxicosis;
- removes toxins from the body;
- controls blood glucose, cholesterol and lipid levels;
- creates a barrier to ultraviolet radiation;
- regulates the functioning of the thyroid gland.