Among the many dermatological diseases, keratosis pilaris (ICD code – L87) is distinguished. People simply call it “goose bumps”.
This is explained by the fact that the skin is constantly in an inflamed state and is completely covered with “pimples.” A similar phenomenon occurs due to the growth of the keratinized layer of the epidermis.
In fact, the ailment is more of a cosmetic nature, and does not particularly cause physical discomfort if appropriate measures are taken. It may also be accompanied by itching.
Follicular keratosis: causes of the problem
To date, all the causes of keratosis pilaris have not been precisely established. Clinical studies are still underway regarding the symptoms and sources of this disease.
It was precisely established that the lesion occurs due to blockage of the follicles by keratinized skin particles.
This type of keratosis occurs when the human body produces an excess of keratin protein. As a result, tubercles appear, which often turn red. Follicular keratosis can be congenital or acquired.
And the provoking factors are the following:
- lack of vitamins in the body (A, , B, , D) or their excess;
- incorrect approach to nutrition: excessive consumption of spicy, salty and fatty foods, as well as strong coffee;
- endocrine disruptions, which often occur while taking hormonal drugs, while a woman is carrying a child or during menstruation;
- puberty in adolescents (keratosis appears on the face);
- use of inappropriate skin care cosmetics or poor personal hygiene (applies to children);
- HIV infection;
- allergy;
- constant exposure to radiation (relevant for workers in X-ray rooms or solariums);
- frequent contact with chemicals;
- emotional instability (depression, nervousness, increased irritability);
- serious mental disorders;
- overweight;
- wearing tight and poor-quality shoes;
- exposure to negative weather conditions.
40-50% of the world's population suffers from this disease, many do not even know that they have keratosis, citing rashes, irritation, etc.
Dermatologist Alicia Zalka
In winter, people affected by keratosis experience an exacerbation, and in warm periods there is a remission.
There are frequent cases of keratosis affecting children. The disease also appears at the age of 20-30 years and gradually gains momentum.
In children, keratosis is manifested by the same dense nodular rashes that feel rough to the touch.
During remission, the rash does not cause physical discomfort, but in case of exacerbation it begins to itch and turn red. If rashes appear on the palms and soles, the doctor usually diagnoses hereditary keratosis.
Dermatological surgeon Robert Weiss
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist. If it really is keratosis pilaris, then the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment and give recommendations for caring for problem skin.
No special procedures are required to make a diagnosis. A visual examination is enough for the doctor.
Hyperkeratosis of the skin. Hereditary keratoderma.
Keratoses (keratoses; Greek keras, keratos horn, horny substance + -osis) are a group of skin diseases characterized by excessive keratinization of individual areas or (less often) the entire skin. There is no generally accepted classification of keratoses due to the unclear etiology and pathogenesis of many of them, as well as the wide variety of clinical forms.
Based on their origin, they distinguish between acquired and hereditary keratoses. According to the clinical picture there are:
- diffuse keratoses, characterized by damage to large areas or the entire skin:
- follicular keratoses, characterized by impaired keratinization mainly in the area of the mouths of hair follicles (follicular hyperkeratosis) and the disseminated nature of the lesion;
- warty keratoses, in which the horny layers have the appearance of warty growths; keratoderma with predominant lesions of the skin of the palms and soles;
- keratoses multiforme, in which there are foci of excessive keratinization of the skin;; usually combined with damage to the nervous and skeletal systems, mucous membranes, changes in nails, hair, teeth, etc.
Hereditary keratoderma Hereditary keratoderma appears in early childhood and gradually progresses. In the middle part of the palms and on the soles, massive horny layers are formed symmetrically, surrounded by a purple border. The lesion is limited to healthy skin; its surface can be dotted with painful bleeding cracks. Often, horny layers spread to the back of the hands and feet. At the same time, individual foci of keratosis may appear, for example on the knees and elbows. Keratoderma can be combined with progressive periodontal disease, leading to tooth loss and degeneration of the alveolar processes (Papillon-Lefevre syndrome), as well as other developmental anomalies.
Keratoderma is a heterogeneous group of diseases characterized by diffuse or focal thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis of the palms and soles, in some patients in combination with keratoses of other localization, ectodermal dysplasia and inflammation. Epidemiology: There are no exact data on the prevalence of keratoderma. The incidence of damage does not depend on gender.
Classification Based on clinical signs, keratoderma is divided into diffuse and focal. The main diffuse forms include hereditary Tost-Unna keratoderma, Greiter's keratoderma, Werner's keratoderma, mutilating keratoderma, Meleda Island disease, Papillon-Lefevre keratoderma.
Focal keratoderma can be large- and small-focal, as well as linear. The most common are Siemens keratoderma and spotted disseminated, symmetrical keratoderma (Buschke-Fisher keratoderma).
Etiology of Keratoderma - hereditary diseases with autosomal dominant (Tost-Unna keratoderma, epidermolytic keratoderma, Vohwinkel mutilating keratoderma, Buschke-Fisher keratoderma, Siemens keratoderma) or autosomal recessive (Meleda Island disease, Papillon-Lefevre keratoderma) type J inheritance ovaniya. There are also acquired keratodermas (for example, climacteric keratoderma).
Pathogenesis In some forms, mutations of genes encoding the formation of keratin were found (for example, keratin 1 in Tost-Unna keratoderma, keratin 9 in Werner keratoderma), as well as linkage to the 1p34-36 locus in Greiter keratoderma. Morphologically, hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, as well as inflammatory infiltration of the papillary layer (mainly around blood vessels) are determined. Clinical signs and symptoms
In most cases, keratoderma develops during the first year of life, but can exist from birth or occur later. With Tost-Unna keratoderma, there is continuous hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles with a strip of livid-like erythema at the border with healthy skin. Similar to this form are Werner's keratoderma, characterized by the presence of blisters, more often detected during histological examination, as well as mutilating keratoderma, characterized by the honeycomb-shaped nature of the lesion, the presence of foci of hyperkeratosis on the dorsum of the fingers and the stellate outline of foci of keratosis in the area of the wrist joints. Greiter's keratoderma is characterized by the presence of inflammatory changes, the transition of the lesion to the dorsum of the hands and feet, and a decrease in the severity of clinical manifestations with age.
Focal keratoderma is characterized by small lesion sizes - from pinpoint to several centimeters in diameter. .
Autosomal recessive forms of keratoderma (Meleda Island disease, Papillon-Lefevre keratoderma) are characterized not only by diffuse keratinization, but also by a pronounced inflammatory reaction, involving the dorsum of the hands and feet, knee and elbow joints in the process; In addition, the presence of periodontal disease is typical for Papillon-Lefevre keratoderma.
Diagnosis of keratoderma and recommended clinical studies: Diagnosis is based on clinical signs, and in case of Werner's keratoderma, also on histological examination data (granular degeneration of cells of the upper and middle parts of the epidermis, as in congenital bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma;). Patients with autosomal recessive forms of keratoderma should be consulted by dentists for the timely detection and elimination of periodontal disease. When keratoderma is combined with esophageal cancer, all family members suffering from keratoderma should be monitored by an oncologist. In the presence of focal painful areas of keratoderma in combination with keratitis, it is necessary to exclude | tyrosinemia type II. Differential diagnosis is carried out with lesions of the palms and soles of psoriasis and Devergie's disease.
Tsyganov P.V.
Signs of keratosis
Keratosis pilaris can appear on the scalp, elbows, shoulders, knees, buttocks and thighs - where the skin is driest.
In the first case, the symptoms are as follows:
- The skin becomes rough and rough.
- Multiple red bumps appear, like pimples.
- The skin is extremely itchy.
- Hair falls out and breaks a lot (sometimes leading to baldness).
- Dandruff appears.
If you have dry skin, you are more likely to develop keratoses.
Dermatologist Dendy Engelman
If left untreated, this type of keratosis will spread to other parts of the body.
When the face is affected, partial thickening and drying are noted, but without the formation of small scales. In severe cases, these areas become covered with a thick crust.
If goose bumps are found on the legs, shoulders and elbows, many do not take any action to treat the disease because they do not pay special attention to it. Such inaction leads to complications in the form of bleeding cracks, stiffness and pain during movement.
Dermatologist Emily Altman
Causes of hyperkeratosis
Etiological factors that provoke the development of pathology can be of endogenous and exogenous origin. This list includes conditions such as:
- wearing tight clothes that compress soft tissues;
- uncomfortable or unsuitable shoes - if the patient has obesity, flat feet, lameness, the likelihood of hyperkeratosis increases significantly;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- congenital defects of keratin formation;
- systemic lesions with a chronic course;
- hereditary diseases accompanied by a violation of the process of keratinization of the skin;
- psoriasis;
- mycoses;
- poor posture, in which there is an irrational distribution of the load on the legs and torso;
- seborrhea – underlies the pathogenetic chain of seborrheic hyperkeratosis ;
- menopause;
- shingles.
Possible complications
If you categorically refuse treatment for such a diagnosis, serious health problems may arise.
In particular, there is an accumulation of other diseases. This happens because the skin surface begins to crack and access for pathogenic fungi to enter the body is opened.
Then keratosis smoothly turns into a chronic form. Against the background of weakened immunity, the body is not able to counteract the negative effects.
Although keratosis pilaris is not fatal, treatment is still necessary. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the faster the recovery will occur. The disease is diagnosed upon examination without any laboratory tests.
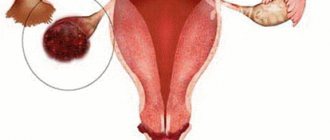
Hyperkeratosis and pregnancy
This disease can be diagnosed in girls during pregnancy. Risk factors are a decrease in the body's immune defense, changes in hormonal levels, disruption of the endocrine glands, metabolic pathologies, chronic injuries, trauma to the vaginal mucosa during medical procedures, inflammatory and infectious gynecological diseases. In this case, women may develop hyperkeratosis of the cervix of the vulva or vagina. There are no specific symptoms of the disease; patients often do not even suspect its presence. The only indirect sign of impaired desquamation of the epidermis is pathological discharge from the vagina.
Pathology can be detected during a preventive examination, which all pregnant women are required to undergo - an analysis for tumor markers. Colposcopy, biopsy of a tissue fragment, cytological and histological examination of the material can also be used. If this form of the disease is identified during pregnancy planning, it is advisable to undergo a course of therapy before conception, since changes in hormonal levels significantly affect the course of the disease. The same applies to hyperkeratosis of the nails, elbows, hands, lips, heels. However, the treatment carried out in the initial stages of pregnancy is harmless to the fetus. This pathology can be dangerous as it is considered a precancerous condition, which in the future can develop into cervical cancer. Treatment is carried out by removing hyperkratosis; for this, surgery, exposure to laser radiation, and low temperatures can be used.
Ways to cure the disease (2 approaches)
Keratosis pilaris does not always require treatment. If the manifestation is minor, it will be enough to eliminate the itching and inflammation so that the skin defect is not so visible. There are several ways to relieve symptoms of the disease.
Use of medications
Since the development of this skin anomaly is mainly associated with a deficiency of vitamins, the doctor first prescribes tablets that help fill the deficiency (like Etretinate and Notigazon).
Dosage varies depending on the severity of the lesion and is usually prescribed in the range of 25-75 g per day.
You cannot take several medications with retinoids at the same time.
Dermatological surgeon Christian Halvorson
To restore the skin when treating keratosis pilaris, special creams and ointments are often used.
Typically, they contain: salicylic acid and AHA acid. They promote the rejection of keratinized crust from the skin surface.
Ointments with vitamin A are also recommended for use (Tazarotene, Uriage and Klindovit gels have proven themselves to be excellent).
On Rusmedserver (medical discussion forum) you can find many positive reviews regarding Uriage Keratosane urea cream. Of all those available, it gives the most effective result in the fight against cutaneous keratosis.
Release form: metal tubes with a capacity of 40 and 75 ml. The price for this product varies between 700-1500 rubles.
This cream-gel is cloudy white in color, easy to apply and quickly absorbed without leaving a trace. After it there is a short feeling of tightness.
Due to the urea in the composition, the skin is moisturized and receives protection in the form of a film that retains moisture inside and minimizes the impact of external factors. Urea also removes dead skin particles well, relieves pain and accelerates healing.
Cosmetological approach (4 procedures)
A cosmetologist in the salon will help you get rid of the stratum corneum and nourish the skin with important components. Treatments for keratosis pilaris include:
- Chemical peeling. The skin is exposed to acids due to the application of various active compounds. Depending on the degree of impact, peeling can be superficial, medium and deep. It is selected depending on the skin type and the strength of its keratinization.
- Brossage. Facial cleansing using a special device with a rotating head on which an antiseptic gel or scrub is applied.
- Ultrasonic exposure . Cleanses the skin without mechanical influence. Ultrasonic waves are used here to create acoustic pressure. In this way, it is possible to quickly and painlessly remove the dead layer of the epidermis.
- Cryotherapy. Based on the action of liquid nitrogen. As a result, the skin takes on a healthy appearance and metabolic processes at the cellular level are normalized.
Laser treatment of keratosis is also used. But this method should be resorted to only when the disease is advanced.
Glycolic scrubs or chemical peels work great. Glycolic, retinol and trinion creams also help.
Dermatological surgeon Ben Behnam
How to cope with illness at home
At home, keratosis pilaris can be cured using various homemade masks and peels. After such procedures, any nourishing cream must be applied.
To help smooth out skin texture, start with a daily cleansing routine. This could include dry brushing before showering or using an exfoliator that contains glycolic or salicylic acid.
While skin feels damp after swimming, immediately apply a moisturizer containing lactic acid, glycolic acid, salicylic acid, ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or a combination of these.
Dermatologist Alicia Zalka
It is recommended to systematically scrub the skin, but without fanaticism - twice a week is enough. Otherwise, irritation may occur.
Along with the use of emollient creams and ointments, you can use folk remedies:
- Aloe - compresses are prepared from it. To do this, succulent leaves are plucked from plants older than 5 years. They are washed and frozen. Then they are cut into thin strips and applied to problem areas with fixation with an adhesive plaster or film and bandage. Leave the compress on all night. The procedure is repeated every other day.
- Propolis - used in the form of compresses. The propolis composition is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas, covered with cling film on top and tied with a bandage.
- Potatoes - application similar to previous options. Unpeeled tubers are finely grated and the resulting pulp is placed in gauze, then applied to the skin with keratosis. After 2 hours, the compress is removed.
It is important to first exclude the cause, otherwise local treatment will not bring the desired result.
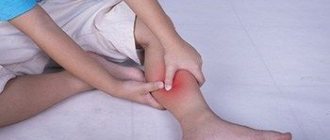
Effective prevention of foot hyperkeratosis
Most often, hyperkeratosis of the feet occurs as a result of the development of other disorders existing in the body. Therefore, the main preventive measure is their timely detection and treatment.
In order not to encounter hyperkeratosis of the feet in life or to prevent its relapse, it is necessary to exclude factors that provoke this disease:
- You need to choose the right shoes, especially those that are intended for daily wear. It should be the right size, not put pressure on the foot, and also be comfortable.
- If your work requires you to be on your feet all day (standing or moving), you can contact an orthopedic salon, where they will make insoles according to individual measurements.
- Avoid the formation of a hard keratinized layer, as well as its growth to critical sizes. Proper foot hygiene will help with this, which consists of regular washing and exfoliation of the feet.
- If you have diseases that cause metabolic disorders, it is necessary to choose certain care products that do not injure the skin, as well as specialized medications.
- It is also important to constantly visit your doctor and follow all the recommendations he gives.
If hyperkeratosis of the feet has gone too far, you need to consult a podiatrist, since it is unlikely that you will be able to cope with this problem on your own. Only he can prescribe effective treatment.
It must be remembered that hyperkeratosis of the feet is not always an exclusively cosmetic defect. In some cases, it can indicate the presence of disorders in the body related to the functioning of internal organs, and can also lead to quite serious complications. To treat this disease, various methods can be used, including the use of medications, folk remedies or hardware procedures.
Nowadays, you no longer have to spend a lot of time performing complex and unpleasant procedures at home. It is much easier to seek help from real professionals - the Veronika Herba beauty and health center, equipped with effective and modern equipment.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can undergo treatment for hyperkeratosis of the feet at a reasonable cost, and you will be treated by one of the best specialists in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!
Principles of therapy for children
Often in children, keratosis pilaris does not require emergency treatment, but the doctor recommends constantly moisturizing and exfoliating the skin, as well as reducing itching with the help of special anti-inflammatory drugs. They are sold in pharmacies and are intended specifically for young patients.
If they resort to treatment, then its principle does not differ from the approach to adults. All therapeutic activities are carried out at home.
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky advises using moisturizing creams and taking salt baths. Sometimes all this is no longer necessary - just stick to a special diet.
Treatment of hyperkeratosis
Therapeutic measures can have different directions, which are determined by a specific nosology. Eg:
- replenishment of the vitamin depot by taking multivitamin complexes is acceptable for vitamin deficiencies;
- wearing a special corset, physical therapy exercises are prescribed if hyperkeratosis occurs as a result of poor posture;
- therapy aimed at correcting flat feet or lameness.
If the disease that causes a violation of the desquamation of epidermal cells has a chronic course, dermatologists recommend following the following recommendations:
- use peeling for hyperkeratosis;
- daily apply a cream or ointment to the affected area that has the effect of softening the skin;
- use medications to moisturize.
An important aspect is compliance with the rules of daily personal hygiene, especially in the affected area, and a proper varied diet.
Question answer
Since keratosis pilaris often appears in men, especially young men, many are interested in whether they are recruited into the army with such a diagnosis. Definitely yes, since this disease is safe both for the patient himself and for others. The exception would be cases when a young person suffers from severe itching and the affected area is constantly increasing.
On thematic forums you can often find questions about whether it is possible to get a tattoo with keratosis. Experts say that this disease is a clear contraindication to such actions. This can cause serious complications.
This is not a fatal pathology. But, nevertheless, if nothing is done, it can progress and bring discomfort to a person (for example, severe itching).
Diagnosis of hyperkeratosis
Making a clinical diagnosis is based on the patient’s specific complaints and anamnestic data - while the doctor pays special attention to asking about the presence of probable risk factors and concomitant pathologies that could provoke the development of the underlying disease.
The list of necessary tests for hyperkeratosis of the feet, face, skin of the legs, palms is prescribed by the attending physician; they are aimed at identifying the cause of the disease. It is standard to conduct a study of biochemical and general parameters of blood and urine. A skin biopsy may be needed. Specific prescriptions are selected individually for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the skin thickening process.
Diet
The underlying cause of keratosis is often a lack of certain vitamins and microelements in the body, which leads to impaired absorption.
If this pathology is not eliminated, then no drugs will help. Therefore, you should first of all pay attention to your daily diet, which should include foods containing vitamins: A, B, E, C and D.
Recommended food set:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- red fish and seafood;
- dietary meats;
- fermented milk products (cottage cheese, milk, pure yogurt);
- chicken and quail eggs;
- odorless vegetable oils;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- whole wheat bread;
- various cereals.
You need to drink more water per day - optimally 50 ml per 1 kg of your own weight.
I advise you to exclude dairy products, soy and gluten from your diet. These are inflammatory foods and can make your eczema worse. This really helps!
Dermatological surgeon David Hansen
Following a healthy diet will help restore skin structure and improve overall well-being.
Preventive measures
It is unlikely that it will be possible to prevent the appearance of keratosis pilaris, but it is quite possible to reduce its symptoms and avoid exacerbation. It is enough to follow a number of rules:
- protect the skin from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- during the cold period, lubricate the skin with a rich cream every day before going outside;
- switch to proper nutrition;
- in spring and autumn, take a multivitamin complex;
- wear clothes exclusively from natural materials;
- Avoid contact with allergens if possible;
- use mild detergents.
To prevent keratosis from causing physical discomfort, it is important to follow all medical prescriptions and listen to the advice of professional cosmetologists. You also need to follow simple rules of personal hygiene.
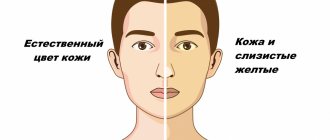
Symptoms and signs of hyperkeratosis
The clinical picture of the disease can be varied, but its form is important. Typical manifestations of a violation of keratinization of the epidermis are as follows:
- decreased or complete loss of sensitivity in the affected area;
- dry skin;
- loss of physiological properties of the skin such as elasticity, turgor;
- the appearance of minor surface damage in the form of cracks;
- yellowish tint of the skin;
- coarsening of the epidermal layer.
Expert opinion
- Cosmetologist
- Surgeon
Deborah Longwill
practicing dermatologist-cosmetologist
Keratosis is a common inherited skin condition affecting the hair follicles, called chicken skin. It's sometimes mistaken for pimples, but the white cap on the hair follicles isn't pus, it's dry, dead skin cells. There is no single treatment plan for the pathology. Each person has his own approach. An integrated approach is also needed. It is important to review your diet; chemical peels and laser procedures are useful.
Aisha Baron
plastic surgeon
This pathology is more common in children than in adults, since many of us “grow out” of this condition.
It is associated with atopic dermatitis or eczema and typically appears in people with allergies, hay fever, eczema and asthma. Despite the fact that keratosis pilaris is not considered a particularly dangerous disease, it does cause significant discomfort.
Treatment means diet, replenishment of the body with missing vitamins and elimination of provoking factors. This is the only way to avoid relapses in the future.
Hyperkeratosis in children
Disorders of keratin metabolism also occur in childhood. The reasons for the development of this condition can be stressful situations, a lack of vitamins and minerals in the baby’s body, poor nutrition, wearing clothes of the wrong size or made from synthetic fabrics, chronic diseases of the digestive tract, and washing hands with products that excessively dry the skin. Manifestations of the disease depend on its form. The signs, diagnosis and treatment of the disease correspond to those in the adult population. The only difference is that when prescribing medications, the doctor must take into account the age of the child.