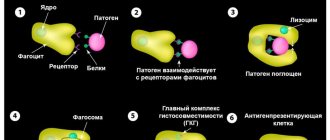
Leukocytes are the main element of the immune system. They protect the body from infections, as well as from cancer cells. In some cases, the number of white blood cells exceeds the norm. This may be physiologically normal, but if a person feels unwell for several days, he should immediately consult a doctor.
The role of leukocytes in the blood
White blood cells have an important mission for the human body - they protect it from viral and bacterial attacks, waste and toxins, and other foreign bodies. The leukocyte series consists of several types, each of which plays its own role:
- Neutrophils - detect bacterial infections and destroy them.
- Lymphocytes are responsible for the immune system and the so-called immune memory.
- Monocytes - destroy foreign elements found in the blood.
- Eosinophils are responsible for human allergic reactions.
- Basophils - play a supporting role in detecting foreign particles and are important in inflammatory and allergic reactions.
The main tasks of leukocytes include:
- Penetration into the gastrointestinal tract in order to capture nutrients and transport them into the blood. This is especially important for infants, who receive immune protection from their mother through breast milk.
- Taking part in building humoral and cellular immunity, i.e. performing a protective function.
- Dissolution of damaged tissues.
Where are they formed and how long do they live?
The bulk of white cells, namely granulocytes, are produced by red bone marrow from stem cells. From the maternal (stem) cell, a precursor cell is formed, then passes into a leukopoetin-sensitive cell, which, under the influence of a specific hormone, develops along the leukocyte (white) series: myeloblasts - promyelocytes - myelocytes - metamyelocytes (young forms) - rods - segmented. Immature forms are found in the bone marrow, mature forms enter the bloodstream. Granulocytes live for about 10 days.
- Clinical blood analysis: from light microscope to hematological analyzers
The lymph nodes produce lymphocytes and a significant proportion of monocytes. Some agranulocytes from the lymphatic system enter the blood, which transports them to the organs. Lymphocytes live a long time - from several days to several months and years. The lifespan of monocytes ranges from several hours to 2-4 days.
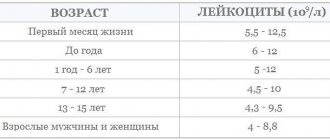
Standard indicators: general information
The normal white blood cell count may vary from person to person. Moreover, the main criterion for difference is the age of the subject. So, in children this figure will be higher than in adults. Due to the fact that the norm is estimated in units per liter of blood, diet, body condition and time of day should also be taken into account. So, in the afternoon, after eating, after any stress, physical or mental, the concentration of the indicator will be increased. Gender has virtually no effect on the number of leukocytes. The amendment needs to be made only for a pregnant woman and a woman after 50 years, when due to hormonal changes the concentration of the indicator changes.
For a healthy person, the leukocyte composition of the blood looks like this:
- 55% – neutrophils: 45-72% – segmented neutrophils, 1-6% – band neutrophils;
- 19-37% – lymphocytes;
- 3-11% – monocytes;
- 0.5-5.0% – eosinophils;
- 0.5-1% – basophils.
In a blood test, these data are taken into account in relation to the content of the total number of immune cells.
On the Internet you can find a variety of white blood cell standards that differ greatly from each other. In reality, everything is much simpler - the range from 4 to 9 * 109 is accepted as the norm, with slight adjustments for gender, pregnancy, and age. Children have their own norms, this is due to the passage of a long period of growth and development from newborns to puberty.
Victoria Druzhikina
Neurologist, Therapist
Preparation
There is no special preparation before donating blood to perform OAC. The patient must comply with a number of simple requirements:
- refrain from eating 4 hours before the procedure;
- stop smoking half an hour before the procedure;
- limit the consumption of fatty and fried foods and alcohol the night before the test;
- limit physical and psycho-emotional stress 2 hours before submitting the biomaterial.
It is allowed to drink still water before the procedure.
More detailed recommendations before taking a general blood test are given here.
Norm indicators in the table by age for women
The range of standards is indicated in reference books and regulations used by doctors.
For a woman, the normal concentration of white blood cells is 4.0 - 9.0 * 109/l. In this case, the age table will look like this:
Table of normal levels of leukocytes in the blood of women.
| Age | White blood cell count (*109) |
| up to 16 years old | 4,5 — 12,5 |
| up to 20 years | 4,2 — 10,5 |
| from 21 years old | 4 — 9.0 |
The leukocyte norm in women can vary depending on the menstrual phase and hormonal levels. The norm of leukocytes in women after 50 years is somewhat different. This is due to hormonal fluctuations.
Thus, during menopause, the concentration of the indicator increases, replacing the production of certain hormones. After menopause, on the contrary, there is a decline in the activity of a number of hormones and cells, which include white blood cells. In digital terms it will look like this:
- 45-55 years – norm 3.3 – 8.8 units. by 109 cells per liter;
- 55-65 years – norm 3.1 – 7.58 *109/l.
Normal for pregnant women
Pregnant women experience changes according to many studies. During the period of bearing a child, the concentration of leukocyte cells up to 12-15*109/l is considered the norm. By trimester it will look like this:
| Trimester | White blood cell count (*109) |
| first | 4 — 9 |
| second | 4 — 10 |
| third | 14 — 12 |
High values are due to increased protective functions of the body, thickening of the blood during pregnancy, and a decrease in the level of lymphocytes. Also during pregnancy you need to know your TSH level.
Also, an increased level of white blood cells is necessary to stimulate uterine contractions.
It is worth noting that each private laboratory has its own standards, slightly different from those prescribed in the document. This is due to the equipment used. Therefore, when donating blood privately, you should pay attention to the standards indicated on the form.
Normal for men
The leukocyte count in men is subject to less fluctuations than in women. The norm for men by age is presented in the table:
| Man's age | White blood cell count (*109) |
| 12-18 years old | 3,5 — 8 |
| 18-25 years old | 4 — 9 |
| 25-40 years | 4 — 8 |
| Over 40 years old | 3 — 9 |
Normal in children
Children tend to have higher white blood cell counts. The norm for different ages is presented in the table:
| Age | White blood cell count (*109) |
| newborn | 10 — 30 |
| from the fifth day of life | 9 — 15 |
| from the tenth day of life to one month | 8,5 — 14 |
| from month to year | 8 — 12 |
| from one to five years | 7 — 11 |
| from 5 to 15 years | 6 — 10 |
| over 15 years old | 5 — 9 |
The table shows that the norm of leukocyte content in newborn children is very different, for example, from the norm in children 5 years old.
Elevated leukocytes in the blood: causes and treatment
The condition in which white blood cells are elevated is called leukocytosis. It can occur in anyone. Short-term leukocytosis should not cause concern, because it may be associated with the influence of external factors. Thus, a newborn may react with an increased level of leukocytes to new complementary foods. For a man or woman, the norm is a slight increase in the concentration of the indicator as a result of the following situations:
- emotional tension and stress (treated by a psychologist);
- smoking (all the consequences of smoking are described here);
- consumption of certain foods;
- excessive physical activity;
- long stay in the sun or in the bath;
- change of time zones.
To eliminate errors in the analysis, it must be taken in the morning on an empty stomach in a calm state. If, when following all the canons of taking the test, the result still turns out to be above the norm, then we can talk about leukocytosis associated with the presence of some kind of disease.
The reasons why leukocyte cells are elevated may be:
- Any infectious processes.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Chronic inflammatory processes.
- Allergies (learn effective allergy remedies from this article).
- Viral infection of the body.
- Severe pain syndrome.
- Oncological processes (examination and therapy are prescribed by an oncologist).
- Burns and frostbite.
- Parasitic contamination of the body.
Causes of increased leukocytes in the blood of women
Women are more likely to have inconsistent test results than men. In addition to the above, the reasons for this may be:
- emotional and mental state;
- changes in climate and weather conditions;
- phase of the menstrual cycle (read what to do with menstrual pain here);
- medications taken;
- inflammatory processes associated with the gynecological area (therapy is prescribed by a gynecologist).
A number of processes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman determine the reasons for the increase in leukocytes in this category of people. In addition to the fact that white blood cells during pregnancy can be elevated due to physiological factors, experts separately identify the following sources:
Doctor's advice
To obtain reliable results, it is important to take a correct blood test. In emergency cases, you can do this after eating; in a planned manner, it is better to go to the treatment room on an empty stomach. It is advisable not to smoke for 2 hours before donating blood. A prerequisite is that if the test is prescribed not to assess the condition during an illness (cold, acute respiratory viral infection, sore throat, etc.), but during a medical examination, then you need to donate blood no less than 2 weeks after recovery in the case of a recent illness. If you perform a blood test a few days after illness, you may find elevated white blood cells that have not yet returned to normal due to the immune response. on the pathogen. Such results will require a second blood donation. Therefore, it is better to wait until 2 weeks have passed and then get examined.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
- allergic and inflammatory processes (treated by an allergist) associated with decreased immunity;
- taking medications to maintain pregnancy;
- worsening of chronic pathologies;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- anxiety associated with worries about the child’s development;
- hormonal imbalance (corrected by an endocrinologist), leading to blood thickening.
If a pregnant woman has an increased concentration of leukocyte cells, she will definitely be scheduled for a repeat examination to exclude pathology.
Why leukocytes may be elevated in men: reasons
In men, white blood cells can also be elevated for physiological and pathological reasons. In the first case, there is nothing to worry about: you just need to make sure that the test is taken in compliance with all the standards for passing it. Also, it is necessary to exclude the presence of a man in conditions with high air humidity and temperature immediately before the test. Pathological factors include any deviations in the functioning of the body associated with the occurrence of inflammatory, infectious or bacterial processes. This is due to the fact that it is the man’s immune system that is the first to respond to changes in the steadfastness of the internal environment of his body.
Elevated leukocytes in a child’s blood – what does this mean?
For a child, especially a small one, a condition such as constant mood swings, crying, anxiety, and fear is typical. Also, many parents misinterpret the conditions under which the child is kept. So, a comfortable air temperature for him should be in the range of 18-23 degrees. Adults are used to warmer temperatures. The same applies to baths: often a child is bathed in water that is too hot for him, despite the fact that it is comfortable for an adult. It is overheating and an unstable emotional state that are often the reason why a child’s leukocytes are elevated. Also, the reason for the discrepancy between the indicator and the norm in a child can be vaccination. If the concentration of leukocyte cells is increased significantly even after repeated analysis, then we should talk about pathological phenomena that require research and treatment.
White blood cells are increased (leukocytosis)
When the concentration of leukocytes in the peripheral blood increases, they speak of leukocytosis. The causes of this condition are:
- prolonged stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- acute/chronic inflammation;
- tissue damage, burns;
- infection of the body (viruses, protozoa, bacteria, fungi, parasites);
- malignant neoplasm;
- acute circulatory disorders in organs (myocardial infarction, stroke);
- anemia;
- poisoning by poisons, alcohol;
- allergic reactions;
- autoimmune pathology (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- leukemia.
Physiological conditions in which a slight increase in the concentration of leukocytes is not considered a pathology:
- pregnancy;
- postpartum period (first 14 days);
- menstruation;
- vaccination completed;
- overheating, hypothermia;
- dramatic climate change.
Low leukocytes: causes, treatment
If leukocytes are elevated, this is not always bad. Thus, the body reports some kind of failure and activates protective resources to combat it. A low level of leukocyte cells (leukopenia) is of greater concern. If white blood cells are low, this means that the body cannot fight pathogenic elements. Those. We are talking about the presence of some kind of disease. There are three main factors known for which leukocyte bodies are not produced in the required quantities:
- Lack of necessary substances to build new cells.
- The production of white blood cells with their simultaneous death when fighting foci of infections.
- Imbalance of bone marrow functions.
Leukopenia can be found in both men and women.
The main sign of a prolonged deviation from standard values is an infectious disease, which is manifested by fever and chills and is a consequence of intoxication that is not restrained by leukocytes.
The main factor in combating a low level of leukocyte cells is to prevent the development of infectious diseases, which consists of:
- a well-chosen diet;
- wearing a respiratory mask;
- excluding all contacts with already sick people;
- See a doctor at the slightest increase in temperature;
- treatment with folk remedies.
In severe cases of the disease, drug therapy is carried out. Often the patient is hospitalized to restore immunity.
Indications for the study
A general blood test with the determination of leukocytes, and, according to indications, the leukocyte formula, is prescribed to patients undergoing a preventive medical examination, seeking outpatient medical care or admitted to a hospital. Indications for determining the concentration of leukocytes and their forms are:
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory process of any localization;
- suspicion of helminthiasis or parasitic infestation;
- malignant processes;
- allergic reactions;
- assessment of the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory treatment;
- suspicion/presence of leukemia.
White blood cell counts can detect hidden infections and hidden undiagnosed conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiencies, and blood disorders.
Treatment of leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is usually detected only by blood tests. A person does not feel any obvious symptoms indicating a change in the blood. Thus, he may complain of a number of ailments, which are often not associated in any way with a deviation from standard values in the concentration of white blood cells:
- general malaise and fatigue;
- loss of appetite, dizziness (other possible causes of dizziness in women are described here), excessive sweating;
- joint and muscle pain;
- sleep disorder (treated by a somnologist), weakened vision (therapy carried out by an ophthalmologist).
In order to reduce the value of an indicator, the increase of which is associated with physiological reasons, it is recommended:
- avoid hypothermia and overheating;
- Healthy food;
- observe a rest regime;
- be less nervous.
Those. therapy is associated with the elimination of factors causing an increase in the indicator.
If a diagnosis of “leukocytosis” is established, self-medication should not be done under any circumstances. The doctor himself, based on repeated tests and additional examinations, will determine the etymology of the growth of leukocyte cells and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1.https://medline.ru/public/art/tom18/art6.html 2. Uncle G.I. et al. Universal reference book for a practicing physician (Section “General blood test”) // Voronezh: Scientific book. - 2021. - 512 p. 3. Kishkun A. A. Clinical laboratory diagnostics. Textbook (Chapter 2. Hematological studies) // M.: GEOTAR-Media. — 2015. — 976 p.
4. Standards for indicators of the composition of blood cells and other indicators are reflected in the ORDER of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated 09/14/2001 364 (as amended on 06/06/2008), Appendix 3 “NORMS FOR THE COMPOSITION AND BIOCHEMICAL INDICATORS OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD”
Rate how useful it was article
4.4 30 people voted, average rating 4.4
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Blood in the human body performs important functions: it carries food products that come in during the digestion of food; takes oxygen from the lungs, gives it to tissues and carries carbon dioxide from them to the lungs; maintains a constant body temperature, participates in immunity mechanisms. Blood consists of a liquid part - plasma and formed elements. Formed elements make up 45% of the total blood volume. These “components” of ours will be discussed.
The most numerous inhabitants of the blood are red blood cells. Their number is in the millions. An erythrocyte is a tiny, nuclear-free cell that, in 100-110 days of its life, runs a path of almost 150 km through the vessels, ending its life in the spleen and liver. Each red blood cell has a yellowish-red color due to the hemoglobin pigment it contains. A feature of hemoglobin is its ability to quickly become saturated with oxygen and release it to tissues. But the role of hemoglobin is not limited to oxygen transport. It also actively frees tissues from carbon dioxide formed during metabolism.
In the blood, along with “red-skinned” red blood cells, their “pale-faced” (or rather, colorless) neighbors, leukocytes, coexist. They are larger than red blood cells, contain a nucleus and have the ability to “devour” microbes.
The most numerous population of leukocytes are granulocytes (eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils). Another community of leukocytes consists of monocytes and lymphocytes. A special place is occupied by the family of blood cells such as platelets. Their main function is to participate in blood coagulation, the formation of a clot-thrombus, which “locks” the lumen of a damaged blood vessel.
In medical practice, the most common practice is to perform a standard general clinical blood test, which includes determining the concentration of hemoglobin, the number of erythrocytes and leukocytes in 1 liter of blood, calculating the leukocyte formula, calculating the color index and determining the ESR.
In most modern laboratories, basic blood parameters are determined using hematological analyzers. The designations in the analysis form for the average person are most often “Chinese letters”. "Deciphering" the test result is the doctor's priority, but by looking at your test, you can also have a general idea of your health.
Basic blood parameters on hematology analyzers
Let's consider some deviations from the accepted norm.
Hemoglobin
The level of hemoglobin in the blood can increase not only in patients, but also in healthy people living in high mountain areas (a small amount of oxygen in the air leads to a compensatory increase in the production of hemoglobin carriers - red blood cells), workers in hot shops (excessive sweating causes blood thickening and an increase in the level hemoglobin). Also, the level of hemoglobin can increase in pathological conditions not directly related to the blood system: dehydration with excessive vomiting, diarrhea, extensive burns. Blood diseases that cause an increase in this indicator are associated with increased production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. More often than an increase there is a decrease in hemoglobin content. The reasons for this phenomenon can be different: iron deficiency in food, impaired absorption of iron in diseases of the stomach and intestines, lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid in the body, blood loss (including frequent hemorrhoidal bleeding).
Red blood cells
Deviations from the accepted norm in relation to red blood cells are considered to be changes in their number, diameter, shape, color, as well as the appearance of intracellular formations in them, characteristic of certain diseases.
An increase in the number of red blood cells most often occurs in response to oxygen starvation of tissues (pulmonary diseases, heart defects), as well as blood thickening associated with loss of fluid by the body (burns, diarrhea, taking diuretics).
A decrease in the content of red blood cells is observed with blood loss, a decrease in the rate of formation in the bone marrow, or their accelerated destruction.
Color index
A diagnostically significant indicator related to hemoglobin concentration and the number of red blood cells is the determination of the degree of saturation of the red blood cell with hemoglobin - calculation of the color index. Based on this test, it is possible to differentiate blood diseases (anemia) associated with insufficient red blood cells in the blood. Thus, with anemia as a result of bleeding, decreased production of red blood cells or accelerated destruction of red blood cells, the color index often remains within normal limits; in some diseases (iron deficiency, lead poisoning, pregnancy) - decreases; in some cases (vitamin B12 deficiency, folic acid; stomach diseases) it increases.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
An increase in this indicator is a highly sensitive test indicating an actively ongoing inflammatory process. An increase in ESR is typical for infectious and inflammatory diseases, sepsis, joint diseases, liver damage, kidney damage, etc.
A decrease in ESR is observed with an increased number of red blood cells in the blood.
Leukocytes
Leukocytes are a kind of indicator that reflects the characteristics of the state of the human body.
An increase in their number is observed in many conditions associated with inflammatory diseases of various organ systems, as well as in patients suffering from acute and chronic leukemia.
A decrease in the number of leukocytes is observed in elderly people, with radiation sickness, and viral diseases.
For a more informative examination, in addition to determining the total number of leukocytes, they use the calculation of the leukocyte formula, which is understood as the percentage of different types of leukocytes.
Neutrophils
A decrease in the number of neutrophilic leukocytes can occur during chemotherapy in cancer patients, certain types of anemia (aplastic, megaloblastic), autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis), and viral diseases.
Increased numbers of neutrophils are typical for acute infectious diseases, intoxications, cancer, and leukemia.
Lymphocytes
A decrease in the number of lymphocytes is observed in some pathologies of the immune system, anemia, AIDS, radiation sickness, etc.
An increase in the number of lymphocytes is observed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic joint diseases, and viral infections.
Eosinophils and basophils
An increase in the number of eosinophils and basophils in the blood is a symptom characteristic of allergic reactions (including bronchial asthma), parasitic diseases, and decreased thyroid function.
Monocytes
An increase in the number of monocytes occurs in diseases such as leukemia, tuberculosis, syphilis, viral, fungal, protozoal infections, as well as in systemic connective tissue diseases (arthritis, periarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus).
A decrease in the number of monocytes is observed in some rare types of leukemia and aplastic anemia.
In conclusion, I would like to note that certain deviations from the accepted norm should be assessed in conjunction with data from other tests and the patient’s well-being. That is why a doctor should decipher the blood test and interpret the information received.
Trust the professionals and be healthy!
Laboratory doctor, category I N. Obedkova
Print Email