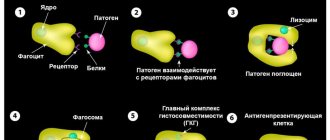
(When placing an order in the first half of the current day)
Home → Pulse oximeters → Pulse oximeters - oxygen norm in adults and children
Home (12) Professional (5) Children's (3) Finger (16) Wrist (16) With verification (16) Portable (16) Stationary (16) ARMED (2) ChioceMMed (5) All pulse oximeters (16)
The normal values of pulse oximeters correspond to the values of blood oxygenation and pulse rate in a healthy person.
Pulse oximeters: blood oxygen saturation rate and heart rate
In medicine, saturation is the amount of oxygen contained in the blood, or more precisely, the percentage of oxyhemoglobin to hemoglobin. The norms for measuring saturation (SpO2) with a pulse oximeter are 96-98%. A decrease in this indicator to a level of less than 94% indicates disorders in the body, and a SpO2 value less than 90% is a signal for taking urgent action and oxygen therapy. Causes of falling oxygen levels in the blood:
- disruption of lung function and insufficient oxygen supply from the air;
- decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells;
- pathologies of cardiac activity.
During the measurement, the pulse oximeter records changes in the volume of blood vessels corresponding to pulse impulses. Usually there are 60-90 pulse beats per minute. If the heart rate is higher, this may indicate hypertension, neurological disorders, oncology, heart disease, etc. A slower pulse can signal hypotension, stomach ulcers, hypothyroidism, and heart attack.
Pulse oximeters: norms for children and adults
The age of the patient plays a significant role when performing pulse oximetry.
Adult and children's standards for oxygen levels in the blood and heart rate are different. Newborns have little iron in their bodies and their lungs are not yet developed. Therefore, in infants, the SpO2 value fluctuates between 92 and 95%, and this is not a consequence of pathology. And in premature babies, saturation can be reduced to 82%. But such children are provided with artificial ventilation immediately after birth in order to maintain the oxygen supply to the body at the proper level.
The heart rate in the first weeks after birth averages 135 beats per minute. As you grow older, this figure decreases and by the age of 15 the average number of pulse beats per minute is 77.
You can get normal pulse oximeter readings if they are not affected by:
- movement, shaking;
- bright lighting;
- severe anemia;
- vascular spasm;
- arrhythmia.
All pulse oximeter models on the market accurately determine SpO2 and heart rate. Absolute accuracy is impossible; all instruments have an acceptable error. So, for Armed pulse oximeters it is 2-3% for saturation and 1 beat per minute for pulse rate. Such devices and similar portable models that are worn on the finger make it possible to fairly objectively assess the condition of the patient’s body. [td]
Who is recommended to use
Portable Pulse Oximeter
- This is a device for home use.
It is suitable for any person who cares about their own health and wants to know all the important indicators. During the coronavirus pandemic, a pulse oximeter remains one of the most useful purchases for use at home. The procedure is simple and painless, and even a beginner can understand the instructions for the device. However, regular measurements are necessary for the following populations:
- people who are at risk of coronavirus;
- for acute and chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- with abnormal development of the heart or blood vessels;
- for various disorders of the respiratory system;
- during the recovery period after surgery;
- during rehabilitation after suffering from coronavirus.
It is important to understand that patients with various diseases that can cause a decrease in saturation need to receive accurate data. To do this, it is worth choosing a high-quality device that will record all changes and produce results without failure. One pulse oximeter is enough to measure the saturation level and pulse of the whole family. For children, you can choose special children's devices - they fit well in size, so they more accurately record the necessary data.
Pulse oximeters are also useful for athletes during training. During classes, oxygen that is in the tissues is rapidly burned, as the muscles experience increased stress. This can lead to a sharp decrease in saturation and deterioration in well-being. During this period, the athlete feels dizziness, weakness and other signs of oxygen starvation. The presence of a compact device will allow you to quickly determine the cause of poor health and select loads in accordance with the physical capabilities of the person.
To have or not to have?
We have been living for the second year in a coronavirus pandemic – a viral infection that affects the lungs and is extremely dangerous with severe complications. Having a pulse oximeter in your home medicine cabinet is, first of all, about taking care of yourself and your loved ones, the ability to recognize an impending threat in time and seek help.
People from high-risk groups must have a device for measuring saturation:
- elderly people over 65 years of age;
- patients with chronic diseases, and, in particular, pathologies of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- people with immunodeficiency;
- cancer patients.
How to measure saturation correctly
Measuring saturation at home is quite simple. To do this, place your finger in the clamp or sleeve of the pulse oximeter. It is important that the device does not dangle, but is well fixed on the finger. After pressing the button on the instrument panel, the result appears on the screen after 15 - 30 seconds.
Important! Measurement results may be incorrect or completely absent if:
- The device dangles freely on your finger and slides off it. As practice shows, it is best to take measurements on the index, middle or ring fingers. In this case, it is desirable that the nails are cut short. Sometimes the length of the nails does not allow the pulse oximeter to be firmly fixed on the finger, which is why the readings may be distorted.
- The device is not secured correctly . The fingertip is an ideal place to measure peripheral saturation, and the readings here are most reliable for interpreting the absence or presence of hypoxia (oxygen starvation). In some cases, if it is impossible to measure saturation on the fingers, it is permissible to attach the pulse oximeter to the earlobe or toe (mainly in newborns).
- The nails are coated with varnish or gel polish . Since the operating principle of a pulse oximeter is based on shining the fingertip with infrared light and reading the results obtained with a special sensor, the coating on the nails makes this process difficult. And coating with gel polish makes it completely impossible. The stream of infrared rays simply “does not penetrate” a fashionable manicure. Therefore, to obtain reliable results, nails must be clean and uncoated, preferably of any kind.
- The device was purchased without documents confirming its reliability and safety..
Research algorithm
Pulse oximetry at the South Clinic is considered an absolutely painless research method. The patient lies down on a sofa or couch. A sensor from the device is attached to his finger or wrist. There is no injury to the skin when putting on or removing the sensor. Doctors do not tighten clothespins or bracelets too much, so as not to impede blood circulation in the examination area.
In practice, it is customary to use research over a long period of time (several hours, days, night, day).
The procedure goes like this:
- Preparing for the study.
- Attach the sensor to your finger or earlobe.
- Turning on the device.
- Displaying data on the monitor.
What can affect readings when measured with a pulse oximeter
The accuracy of measurement readings is affected by:
- Choosing a location. Excessively bright sunlight or the rays of operating lamps may prevent reliable readings from being obtained. To perform the procedure, it is better to choose a room with moderate lighting.
- Human movement, shaking. Human movement, including trembling, will lead to incorrect interpretation of data. In these cases, the sensor's contact with the body shifts. It is optimal to measure indicators in a supine position. If for any reason the patient is trembling, the procedure should be performed after the trembling has stopped.
- Low battery. Errors cannot be avoided if the device’s battery is discharged; it is not advisable to measure with a discharged device. Before use, make sure there is enough charge. The charge level is shown on the screen by a special icon.
- Mounting the device. Errors in measurements can be caused by insufficient fixation on the body or excessive compression, for example, when the finger is pinched too tightly. The use of force to fix the device is unacceptable. It is also important that the distance between the LED and the photodetector is equal throughout the entire area.
- Reduced tissue perfusion. This situation entails a decrease or disappearance of the pulse wave.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning. In people who inhale smoke, the amount of hemoglobin bound to carbon monoxide increases significantly. Most instruments cannot detect the difference, so the saturation level will be exceeded.
- Availability of dyes. Gel, varnish, and shellac on nails provoke underestimated values, since the coloring substance absorbs light. Errors occur when nails are painted, as well as in cases of skin pigmentation with henna or other mixtures.
- Profound anemia. At values below 50 g/l, 100% saturation indicators are observed even with a lack of oxygen in the blood.
Using a pulse oximeter, we can promptly consult a doctor for help with coronavirus. Today, a medical device should be present in every family. Detailed information such as temperature, pulse and blood oxygen saturation will help the specialist prescribe appropriate treatment even during a remote consultation.
Indications for use
Pulse oximetry is recommended if the following symptoms occur:
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- restless sleep, sweating;
- snoring, stopping breathing during sleep;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet at night (more than 2 times);
- increased sleepiness during the day;
- feeling tired;
- increased irritability, apathy;
- blue tissue;
- the appearance of headaches after waking up;
- the appearance of belching at night.
In general, the scope of application of the device is quite extensive. It is used in the following cases.
During resuscitation measures
Continuous monitoring of blood saturation levels in people who are critically ill is very important. All parameters, as well as pressure, are recorded by special devices with an alert system. If the readings drop below the set value, the device will immediately notify the medical staff about this through special signals.
During operations on the limbs
When performing surgical interventions, it is often necessary to block the vessel. This is necessary in order to prevent severe bleeding. In this case, it is very important to control the level of tissue oxygenation in order to avoid subsequent complications and unwanted tissue necrosis.
To maintain the vitality of a person under anesthesia
A pulse oximeter helps to detect the slightest changes in a person’s condition, various reactions of the body to drugs, which helps the doctor make the right decisions in a timely manner.
In the postoperative period during vascular prosthetics, vein operations, plastic microsurgery
The device helps to assess the patency of blood vessels in individual areas of the limbs.
When transporting patients in serious condition
Due to its compactness, the device can be used in any conditions, so it is equipped with ambulances, air transport for transporting patients, and various vehicles for sanitary purposes.
In cardiology and pulmonology
If a person has problems with the heart or lungs, the device helps predict the next attack and minimize subsequent negative manifestations. This is especially true if the patient suffers from bronchial asthma or sleep apnea - lack of breathing.
In sports medicine
The device is designed to monitor the condition of an athlete; it can be used to determine the level of physical activity without harm to health.
In pediatrics, neonatology, obstetric practice
The device helps diagnose pneumonia at the initial stage in children suffering from acute respiratory viral infections. He also monitors the condition of premature babies. A device is used to prevent intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
For coronavirus
Coronavirus infection in severe cases leads to the development of pneumonia, but the pathological process in the lungs is not always accompanied by obvious symptoms. The device helps to diagnose the unfavorable development of the disease and the occurrence of complications. However, if underestimated indicators are detected, there is no need to panic; you should additionally take a test for Covid and undergo a computed tomography scan of the chest organs. It should be noted that the pulse oximeter is used not only for diagnosis, but also for oxygen therapy.
Description of the norms and deviations of readings, as indicated by the indicators
The following tables and figures will help you understand the situation.
| Patient category | Saturation level, % | Interpretation of readings |
| Children and adults | 99-100 | double-check the result, occurs during oxygen therapy |
| Children and adults | 95-98 | normal values |
| Children and adults | 90-95 | If a problem occurs, you should consult a doctor for further diagnosis |
| Children and adults | below 90 | critical indicators, life-threatening, you need to sound the alarm as urgent medical attention is needed |
Table 1. Explanation of oxygenation values
| Patient category | Pulse rates, beats per minute | Interpretation of readings |
| Children under two years old | 100-180 | considered normal |
| Children from 2 to 10 years old | 70-140 | norm |
| Teenagers | about 75 | norm |
| Adults | 60-90 | norm |
Table 2. Normal heart rate depending on age
If the contraction frequency is higher, the cause may be hypertension, heart disease, neurological disorders, or oncology. A slow heart rate indicates a possible stomach ulcer, hypothyroidism, or heart attack.
Oxygenation in adults
The normal level of oxygen in the blood of a healthy person is considered to be in the range of 95-99%. If it rapidly decreases, then the risk of developing pulmonary or cardiovascular diseases increases. A decrease in the normal indicator for a person by only 3-4% requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. A value for women and men below 90% indicates the development of respiratory failure and lung damage. The patient must be hospitalized. It should be noted that in adults with chronic pulmonary diseases, low saturation rates prevail, but the body is already adapted to such a situation.
In children
The lungs of newborn babies are not yet developed, so the optimal indicator is considered to be in the range of 92-95%. This in no way speaks of pathology. In premature babies, the saturation level drops to 82%, so after birth they are provided with artificial ventilation. In other cases, the normal level of oxygen saturation is 95-99%.
In the elderly
The development of hypoxia is an inevitable process that accompanies aging. Lack of oxygen leads to poor tissue supply, decreased body resistance to oxygen deficiency, and the development of senile changes. As a rule, an elderly healthy person has a saturation level in the range of 95-96%. It should be noted that special breathing exercises help improve gas exchange in the lungs.
How accurate are home devices?
Most healthcare professionals agree that, when used correctly, consumer models are very reliable. Experts advise sticking to finger clipping technology for now. New wearables and camera-based apps use different technology to measure oxygen saturation, and so far most of these products are unreliable. A 2021 study published in the American Journal of Emergency Medicine tested three iPhone apps that offered pulse oximetry functionality, but all fell short. The authors concluded that the apps were inaccurate and lacked the ability to accurately detect hypoxia. Thus, it is recommended to use exclusively certified and approved by doctors devices.
Types of sensors
Specialists can carry out the procedure using various sensors. Their choice depends on the purpose and features of use. Any sensor is connected via a flexible wire to the device. To carry out diagnostics in practice, the following types of sensors are used:
- Clips. Similar to the shape of a clothespin. Attaches to the index finger and earlobe. Used in the diagnosis of adults and adolescents for their observation over a short period.
- Silicone for adults. They are suitable for monitoring blood oxygen saturation over a long period (3 - 4 hours).
- Flexible silicone. Typically used in newborn studies. Attach to the side of the leg.
- Ear clips. They are distinguished by the presence of convenient clamps, with the help of which they are attached to the auricle.