Five years of experience in using the drug Sorbifer Durules in the treatment of iron deficiency conditions
AND
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is one of the most serious medical problems.
According to WHO data [1], 20% of the world's population has iron deficiency to varying degrees. Anemia due to iron deficiency accounts for 80–95% of all anemias
[2]. In women it is detected much more often than in the male population. In 60% of cases, IDA occurs in patients over 65 years of age [3].
Iron is an essential and indispensable component of various proteins and enzymatic systems, providing the necessary level of systemic and cellular aerobic metabolism, as well as redox homeostasis in the body as a whole. Iron plays an important role in maintaining high levels of immune resistance. Adequate iron content in the body contributes to the full functioning of nonspecific defense factors, cellular and local immunity (Kazakova L.I. et al., 1990).
Daily iron requirement
is 10 mg, for women 18 mg (during pregnancy and lactation - 38 and 33 mg, respectively). In the body, iron is contained in hemoglobin (about 65.5%), in depot (31%), a small part is in myoglobin (3.5%), heme-containing enzymes and in blood plasma [1, 6].
The development of IDA is caused by chronic blood loss, impaired iron absorption, an increase in the body’s need for iron during growth, pregnancy and lactation, and insufficient nutritional intake of iron into the body [3].
The clinical picture of IDA consists of symptoms characteristic of any anemia (increased fatigue, decreased exercise tolerance, dizziness) and signs associated with tissue sideropenia. Trophic disorders are associated with a lack of enzymes containing iron: hair loss, brittle nails, dry skin, cracks in the corners of the mouth, perversion of taste. With severe tissue iron deficiency, koilonychia, dysphagia, impaired gastric secretion, and urinary incontinence when laughing or coughing appear. Changes in the cardiovascular system in patients with IDA manifest themselves with slight physical exertion as shortness of breath, palpitations, and tachycardia in 60% of cases. Experimental and clinical studies have established that with IDA, one of the most important functions of the blood is disrupted - the transfer of oxygen to tissues with the development of tissue hypoxia and changes in the cardiovascular system [5, 6].
A.V. Lierman et al. [7] draw attention to the fact that iron deficiency conditions in young people are often interpreted as neurocirculatory dystonia: with increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, enlarged or normal boundaries of the heart, and systolic murmur at the apex of the heart.
A number of studies have noted [8,9] that in elderly people with IDA, with aging, there is a decrease in the level of iron in the blood serum and bone marrow, a decrease in the efficiency of iron inclusion in erythrocytes, which correlates with a decrease in hemoglobin levels and the severity of changes in the cardiovascular system. There is an exacerbation of coronary heart disease and congestive heart failure. Works have appeared [4] indicating that patients with IDA were diagnosed with silent myocardial ischemia, which increased as the severity of the disease increased. The cause of its occurrence is myocardial hypoxia, which increases with physical activity.
Thus, the question of the relationship between the severity of damage to the cardiovascular system and iron deficiency in patients with IDA is of scientific and practical interest, especially with regard to the reversibility of these changes.
Our study aimed to evaluate the tolerability and effectiveness of treatment of iron deficiency anemia, including those with concomitant cardiovascular pathology, with the drug Sorbifer Durules.
Material and methods
Over the course of 5 years, the study included 1426 patients aged from 18 to 70 years (the average age of men and women was 48.3±4.5 and 42.5+2.3 years, respectively). Of the examined patients, 5% had newly diagnosed IDA, 24% of patients suffered from anemia for a year, 71% for 5 years. The cause of IDA in young women was prolonged menorrhagia (46%), in 28% - menorrhagia associated with the presence of uterine fibroids. In 14% of patients (mostly in men), the cause of IDA was previous gastrointestinal bleeding, in 12% it was malnutrition.
The patients were treated with Sorbifer Durules
within 4 weeks. When passing through the gastrointestinal tract from the porous matrix of Sorbifer Durules tablets, a continuous release of divalent iron ions occurs for 6 hours. Due to the slow release of iron ions, a high concentration of iron is not formed locally and thus it is possible to avoid irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. The coated form of the drug prevents the formation of a yellow border on the teeth during long-term use. The drug contains 320 mg of ferrous sulfate, corresponding to 100 mg of ferrous iron, and 60 mg of ascorbic acid, which improves absorption and assimilation of the microelement. We used a dosage regimen of 1 tablet 2 times a day.
Laboratory parameters were assessed over time: the beginning of the study, after 2, 3, 4 weeks of treatment with the drug. Clinical blood analysis was carried out on an automatic analyzer. The laboratory parameters included in the study were: red blood cell count, hemoglobin, color index, hematocrit, mean red blood cell volume, mean hemoglobin content in red blood cells, mean hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells. Laboratory parameters characterizing iron metabolism in the body were used: serum iron (SI), total iron binding capacity of serum (TIBC), latent iron binding capacity of serum (LIBC) and transferrin saturation coefficient (TSC). Instrumental research methods included ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity (ultrasound), ECG-ST monitoring according to Holter before and after treatment in case of detected changes in the ECG. Statistical processing of the material was carried out using the medical and biological statistics program.
results
Mild IDA was detected in 36.4% of the examined patients, moderate in 27.3%, and severe in 18.2%.
Before treatment, 36% of patients complained of increased fatigue, 18% of palpitations and 46% of tissue manifestations of iron deficiency (koilonychia, dysphagia, impaired gastric secretion, urinary incontinence when laughing, coughing).
48 patients had a history of coronary heart disease (CHD) and changes were detected during ECG monitoring. Patients noted complaints of increased chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath.
The effectiveness of treatment was determined every week based on the patients’ subjective assessment of drug tolerance, the degree of improvement in well-being, and according to peripheral blood counts. The drug was well tolerated, with constipation noted only in a few cases during the first week of therapy. No other side effects of the drug were identified.
After two weeks of treatment, the subjective assessment of the effectiveness of treatment was determined by patients as “the condition has improved” - in 36%, “the condition has improved significantly” in 18%, and in 18% – “the condition has improved little.” After 4 weeks of taking the drug, patients noted a significant improvement in their condition, so 54% of patients rated their condition as “significantly improved.” At the same time, 55% had no complaints, 18% noted increased fatigue, manifestations of tissue iron deficiency were noted only in 18% of patients, and 9% of patients complained of palpitations.
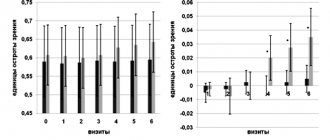
The laboratory data obtained confirm the general trend of improvement in the clinical condition of patients during therapy. The increase in hemoglobin and hematocrit is shown in Fig. 1. The level of hemoglobin in the blood increased significantly already in the 2nd week of treatment. Hematocrit increased on average from the initial value of 26.8±1.3% to 39.0±2.5% after treatment.
Rice. 1. Dynamics of hematological parameters during treatment with Sorbifer Durules
The number of red blood cells increased from 3.2±0.51 to 4.7±0.21x1012/l. A significant increase in this indicator was observed in the 3rd week of treatment. Analysis of the dynamics of the color index, determined by the level of average hemoglobin content in an erythrocyte and the average volume of an erythrocyte, indicates a transition from the state of hypochromia to a normochromic characteristic (Table 1).
Serum iron content before treatment was 6.2±0.3 µmol/l, after treatment after 4 weeks it significantly increased to 13.6±1.2 µmol/l (p<0.05), CVS returned to normal after 4 weeks in 86% of patients (Fig. 2).
Rice. 1. Dynamics of hematological parameters during treatment with Sorbifer Durules
In 48 patients with IDA with concomitant coronary artery disease, ventricular extrasystole was noted in 38.2% of cases, and sinus tachycardia was noted in 14 patients. A shift of the ST segment down from the isoline during ECG monitoring was detected in 36 patients with IDA, including 24 who had painless episodes of myocardial ischemia. Therapy with Sorbifer Durules led to relief of cardialgia in 16 patients and tachyarrhythmias in 4 patients. In addition, in 18 patients, according to 24-hour ECG monitoring, there was a decrease in the number and duration of episodes of painful and silent myocardial ischemia against the background of standard antianginal therapy.
Complete clinical and hematological remission (normalization of hemoglobin levels and ferrokinetic parameters) were obtained after 4 weeks from the start of treatment in 75% of patients. To maintain the achieved remission, with persistent blood loss caused by cyclic menorrhagia, it was recommended to continue taking Sorbifer Durules 1 tablet for the next 4 months after the course of treatment.
Treatment of IDA should begin immediately after the diagnosis has been verified and the causes of iron deficiency have been established. It should be noted that in order to correctly select an iron supplement, it is necessary to take into account the amount of microelement in each tablet of the drug. The drug should have a prolonged effect, which reduces the frequency of administration and is well tolerated by patients. The daily and course dose of the drug is calculated taking into account the severity of the anemic syndrome, visceral lesions, and serum iron levels.
Thus, the main principles of treatment for IDA are the correction of the causes underlying iron deficiency, the elimination of not only anemia, but also iron deficiency in the blood and tissues.
Patients should be informed that compensation for iron deficiency and correction of IDA cannot be achieved using special diets. The high content of ferrous iron in the drug Sorbifer Durules, its high therapeutic efficacy and good tolerability with minimal side effects, which the drug demonstrated in our study, allow us to recommend it for widespread use in the treatment of iron deficiency conditions. Literature:
1. Beloshevsky V.A., Minakov E.V. Anemia in chronic diseases./ Voronezh University Publishing House. 1995 – From 34–37.
2. Volkov V.S. , Kirilenko N.P. Iron deficiency states./ Cardiology – No. 6, – vol. 31., 1991, – P 64–67
3. Wood Marie E., Bann Paul A., Tokarev Yu.N., Bukhni A.E. Secrets of hematology and oncology. / under. ed., M.: BINOM, 1997.
4. Gorokhovskaya G.N., Ponomarenko O.P., Parfenova E.S. State of the cardiovascular system in iron deficiency anemia./ Kremlin Medicine, Clinical Bulletin – No. 2, 1998, – P. 34–37.
5. Kozinets G.I., Makarov V.A. Study of the blood system in clinical practice./ Ed. , M.: Triada-X, 1997.
6. Korovina N.A., Zaplatnikov A.L., Zakharova I.N. Iron deficiency anemia in children./Moscow 1999, pp. 25–27.
7. Lirman A.V., Strenev F.V. About changes in the heart in iron deficiency conditions. / Wedge. Med., 1986, t 64, No. 5, – pp. 69–72.
8. Meerson D.Z., Sukhomlinov A.B., Evseeva M.E., Abdikaliev N.A. Prevention of myocardial damage in hemolytic anemia using antioxidants. / Cardiology., 1983., t. 23, No. 6, – pp. 94–99.
9. Strenev F.V. About changes in the heart, central hemodynamics and physical performance under the influence of mild and moderate iron deficiency anemia. / 1989, – pp. 45–47.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The medicinal properties of the drug are due to the presence of iron in its composition in combination with ascorbic acid .
Iron , in itself, is an integral part of the human body, its important functional unit. It is part of hemoglobin and takes part in oxidative reactions in tissues. Ascorbic acid improves the quality and affects the rate of absorption of iron by the body.
The special form, matrix , in which the drug is released, ensures a gradual and slow release of iron. The process does not take place in the stomach, but in the duodenum and jejunum , under the action of peristalsis . The process is characterized by a high degree of absorption and bioavailability . More than 90% of active iron is bound to blood proteins. The half-life is approximately six hours.
Contraindications
- drug allergy;
- hemosiderosis and hemochromatosis ;
- other types of anemia ;
- thrombosis and thrombophlebitis ;
- diabetes mellitus and fructose intolerance ;
- stenosis of the gastrointestinal tract;
- urolithiasis and other serious kidney diseases;
- children (up to 12 years old);
- parallel use of drugs containing iron, problems with the absorption of iron in the body.
For inflammation and peptic ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract, the drug is used only as directed and under the supervision of a physician.
Interaction
You should not combine the drug with ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, levofloxacin, ofloxacin and moxifloxacin .
The combination of dietary supplements containing calcium and magnesium, captopril, clodronate, cimetidine, levodopa, zinc, desferoxamine, methyldopa, tetracycline, penicillinamine, thyroid hormones, pancreatin, ethanol and tocopherol with Sorbifer is not recommended. The interval between taking medications should be less than two hours.
Combining the drug with ascorbic acid can lead to an overdose of iron.
The absorption process of the drug worsens when combined with milk, eggs, tea, coffee, juices, bread, and foods rich in plant fiber. Oral contraceptives and chloramphenicol also negatively affect absorption .
Side effects
The most common side effects are:
- constipation, diarrhea, nausea and pain in the epigastric region;
- redness and itching of the skin, possible Quincke's edema ;
- hyperglycemia;
- taking the drug promotes the formation of stones and sand in the kidneys;
- thrombocytosis, erythrocytopenia, leukocytosis;
- deviations from the normal content and metabolism of zinc and copper in the body are possible;
- headache, weakness, rapid heartbeat, dizziness;
- blackening or darkening of stool.
Consequences of drinking alcohol
The consequences of synchronizing the medication with alcohol is the progression of anemia due to the lack of a therapeutic effect from the drug.
Main symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- increased heart rate;
- unstable blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- asthenia (neuropsychological weakness).
When drinking alcohol-containing drinks, it is possible that side effects that accompany the use of iron-containing medications may increase:
- constipation (constipation) or diarrhea;
- dizziness;
- cephalgic syndrome (headache).
Clinical consequences are manifested by changes in blood parameters:
- erythropenia (low red blood cell count);
- thrombocytosis (increased platelet count);
- leukocytosis (increased white blood cells);
- hyperglycemia (increased glucose concentration).
If you are prone to allergic reactions, skin rashes may appear.