Longidaza
A drug with prolonged action proteolytic activity. Longidase® is a conjugate of hyaluronidase with a poly-1,4-ethylenepiperazine N-oxide derivative. It has enzymatic proteolytic (hyaluronidase) activity of prolonged action, chelating, antioxidant, immunomodulatory and moderate anti-inflammatory effects.
Prolonged action is achieved by covalent binding of the enzyme to a physiologically active high-molecular carrier (activated derivative of poly-1,4-ethylenepiperazine N-oxide), which has its own pharmacological activity.
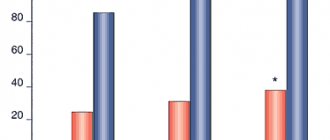
Longidase® exhibits antifibrotic properties, weakens the course of the acute phase of inflammation, regulates (increases or decreases, depending on the initial level) the synthesis of inflammatory mediators (interleukin-1 and TNFα), increases the humoral immune response and the body's resistance to infection.
The pronounced antifibrotic properties of Longidase are ensured by the conjugation of hyaluronidase with a carrier, which significantly increases the resistance of the enzyme to denaturing influences and the action of inhibitors: the enzymatic activity of Longidase is maintained when heated to 37°C for 20 days, while native hyaluronidase begins to lose its activity under the same conditions activity during the day.
The Longidaza® preparation ensures the simultaneous local presence of the proteolytic enzyme hyaluronidase and a carrier capable of binding enzyme inhibitors released during hydrolysis of matrix components and stimulators of collagen synthesis (iron, copper ions, heparin). Thanks to these properties, Longidaza® not only has the ability to depolymerize the connective tissue matrix in fibrogranulomatous formations, but also suppress the reverse regulatory reaction aimed at the synthesis of connective tissue components.
The specific substrate of testicular hyaluronidase is glycosaminoglycans (hyaluronic acid, chondroitin, chondroitin-4-sulfate, chondroitin-6-sulfate), which form the basis of the connective tissue matrix. As a result of depolymerization (breaking the bond between C1 acetylglycosamine and C4 glucuronic or induric acids), glycosaminoglycans change their basic properties: viscosity decreases, the ability to bind water and metal ions decreases, the permeability of tissue barriers temporarily increases, fluid movement in the intercellular space is facilitated, and the elasticity of connective tissue increases , which manifests itself in a decrease in tissue swelling, flattening of scars, an increase in the range of motion of joints, a decrease in contractures and prevention of their formation, and a decrease in adhesions.
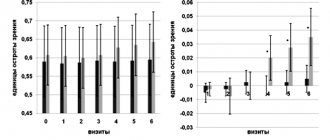
Biochemical, immunological, histological and electron microscopic studies have proven that Longidaza® does not damage normal connective tissue, but causes destruction of connective tissue altered in composition and structure in the area of fibrosis.
Longidaza® does not have mutagenic, embryotoxic, teratogenic or carcinogenic effects.
The use of Longidase in therapeutic doses during or after surgical treatment does not cause a worsening of the postoperative period or progression of the infectious process; does not slow down bone tissue recovery.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When administered rectally, the drug is quickly absorbed into the systemic circulation and Cmax is achieved after 1 hour. The bioavailability of Longidaza® rectal suppositories is at least 70%.
Distribution
The drug is characterized by a high rate of distribution: the half-life of distribution is about 30 minutes.
Metabolism
The drug penetrates into all organs and tissues (including through the blood-brain barrier and the blood-ophthalmic barrier). Does not accumulate in tissues.
Removal
T1/2 ranges from 42 to 84 hours. It is excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Examination before treatment
It is necessary to undergo a diagnosis before starting treatment.
This allows the doctor to accurately determine the stage of the disease and the activity of the inflammatory process.
The results of the initial tests will help monitor the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
Based on them, the doctor will be able to adjust the treatment regimen.
Without fail, the patient is recommended to undergo an analysis of prostate secretions.
It is possible that other organs may be involved in the inflammatory process.
Sometimes the list includes a spermogram and a semen culture tank.
If the patient has a history of allergies, it is important to exclude allergies.
An allergy test is carried out provided that the patient has never taken drugs of the prescribed group.
Your doctor may order an antibiotic sensitivity test.
Etiotropic therapy of chronic prostatitis
The etiotropic treatment of chronic prostatitis includes antibiotics of various groups.
Their choice depends on the type of pathogen:
- To treat prostatitis caused by a nonspecific bacterial infection, semisynthetic penicillins or cephalosporins are used.
- To destroy pathogens of a specific infectious process, macrolides and tetracyclines are used.
- If prostate trichomoniasis is determined (inflammation caused by the simplest single-celled microorganism Trichomonas), antiprotozoal drugs are included in the treatment.
An important condition for successful etiotropic therapy is its sufficient duration and periodic laboratory monitoring of effectiveness.
Indications for the prescription of antibiotics are the detection of pathogenic microorganisms in the secretion of the prostate gland or an increase in the number of leukocytes.
Features of antibacterial therapy
The course of etiotropic treatment takes a fairly long period.
It ranges from 2 to 6 weeks.
Antibacterial agents are prescribed in various forms, these can be tablets or injections.
Most often, the choice depends on the stage of the disease and severity.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of chronic prostatitis
Physiotherapy helps to enhance the therapeutic effect of drugs.
Prostate massage is a fairly affordable and popular method.
It can be carried out at home or in a hospital setting.
The bougie or finger method is used for massage.
The bougie is inserted into the urethra and is used for rotational massage movements.
The manipulation is carried out carefully, without sudden movements.
It must be performed by a specialist, so it is carried out only in a medical facility.
Prostate massage using the finger method is performed in the clinic.
In this case, the bladder should be full.
The finger is inserted into the lumen of the rectum through the anus to a depth of about 5 cm.
The doctor massages the prostate; it is located in the projection of the anterior wall.
After the procedure, a small amount of secretion is released.
To reduce the risk of complications, trust rectal massage only to a specialist.
Prostate massage can be performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital setting.
The following are used as physiotherapy for chronic prostatitis:
- Hydromassage;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Acupuncture;
- Laser therapy.
Patients may be prescribed a complex of therapeutic exercises.
Its task is to improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
Prevention helps prevent congestion.
Prostacor reduces swelling, improves secretory function, and increases muscle tone.
Under its influence, the likelihood of blood clots is reduced.
It is administered intramuscularly in a course of 5-10 ml once a day for 5-10 days.
Contraindicated in children under 18 years of age and with individual intolerance.
Vitaprost and Aescusan are used in the treatment of chronic prostatitis.
Vitaprost relieves swelling, improves secretion discharge, and increases muscle tone.
Stimulates blood circulation and reduces the risk of blood clots, available in the form of tablets and suppositories.
They should be taken 1-2 per day for 10 days.
As suppositories, it is used in 1 pc. 1 time per day.
Adverse reactions are possible only in the form of allergies.
Contraindicated in case of increased sensitivity to the components of the drug.
Aescusan is based on horse chestnut extract.
It has a beneficial effect on venous circulation.
Reduces vascular permeability and relieves inflammation.
It is worth taking 12–15 drops 3 times a day.
Rarely causes allergic reactions.
Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components.
Additionally, the treatment regimen may include adrenergic blockers and vascular drugs.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs for acute prostatitis are prescribed when a pathogenic microflora is detected - it is determined by the results of bacterial culture along with its sensitivity to certain antibiotics. Antibiotics include: Solutab, Sumamed, Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Amoxiclav, etc.
Self-administration of antibiotics threatens the development of resistance in bacteria! It is safe to take antibiotics only on the recommendation of a doctor, strictly in the indicated dosage and for at least the prescribed number of days.
Sex during treatment
The patient is often interested in questions regarding sexual activity.
If the cause of chronic prostatitis is bacteria, then there is a risk of infection of the partner.
The partner can also be an asymptomatic carrier of the infection.
In this case, with an active sexual life, there may be no positive result from treatment.
Important!
You should avoid sexual activity during the period of therapy.
The partner is recommended to undergo testing in case of carriage of bacteria.
In cases where the cause of chronic prostatitis is not an infection, there are no strict restrictions on sexual activity.
As a preventive measure, doctors recommend abstaining from it until the end of therapy.
If you are taking a long course of therapy, discuss possible restrictions with your doctor.
Prevention after treatment
Prevention of chronic prostatitis allows you to prevent re-infection or the development of a relapse.
Basic measures:
- Maintaining a discriminating sex life;
- Eliminate prolonged exposure to high and low temperatures;
- Timely treatment of infectious diseases of any organ system;
- Proper use of antibacterial drugs;
- Regular genital hygiene;
- Use of barrier contraception;
- Regular physical activity, sports;
- Balanced and proper nutrition;
- Taking vitamin preparations;
It is important to visit a doctor regularly and undergo preventive medical examinations.
If necessary, the attending physician may recommend a course of drug prophylaxis to the patient.
For this purpose, the drugs Vitaprost, Prostatilen, Omnic are used.
They are used in tablet form or in the form of suppositories.
Traditional medicine and chronic prostatitis
As additional methods of treatment and prevention, it is possible to use herbal medicines.
They can enhance the effect of the main therapy.
Don’t forget about the general strengthening effect.
The appointment is made by the attending physician.
Remember!
Self-medication can lead to the development of complications and irreversible reactions.
Treatment of prostatitis with prostate adenoma
In the case of a combination of these two pathologies, it is necessary to use complex therapy.
The regimen includes drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect and prevent the proliferation of fibrous tissue.
The products must have restorative properties.
Which doctor prescribes treatment for prostatitis??
Our center’s specialists can provide a consultation and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Prostatitis is treated by a urologist.
In our center you will receive high-quality, detailed advice.
If necessary, you can quickly pass all tests.