What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is an infectious liver disease that can occur in different clinical forms.
With this pathology, the damage to liver cells is autoimmune in nature. In the acute stage, the disease develops within 6 months from the moment of infection. For a long time, the course of hepatitis is mild; most infected people do not experience any symptoms other than weakness, which is caused by an increase in the viral load. In 20% of cases, patients with acute hepatitis B require hospitalization.
Anti‑HBs total, antibodies to the HBs antigen of the hepatitis B virus in Moscow from day 1
from 390 ₽
Sign up
Anti-HBe, antibodies to the HBe antigen of the hepatitis B virus in Moscow from day 1
from 530 ₽
Sign up
HBe-antigen of hepatitis B virus in Moscow from 1 day
from 695 ₽
Sign up
According to WHO, the epidemiology of hepatitis B is as follows:
- South and North America - 1.2%;
- countries of Southeast Asia - 2.1%;
- Mediterranean countries - 3.5%;
- African continent, Western Pacific - 6.5%.
Quite often, the carrier of the infection does not suspect that he is sick, so the asymptomatic spread of the virus is possible for a long time.
The virus that causes hepatitis B belongs to the hepadnavirus family. The viral genome is integrated into the genome of human hepatocytes, causing changes at the genetic level and provoking liver cancer.
At room temperature, the virus can remain active outside the human body for up to 2 months; a temperature of 120°C is required for its inactivation, that is, it can be destroyed by processing in an autoclave for 1.5 hours or in a dry-heat oven for an hour at 180°C.
Disinfectants that can inactivate the virus:
- formalin;
- chloramine;
- hydrogen peroxide.
In the blood, the virus can remain active for many years, and if a person’s immunity weakens, the virus causes an infectious disease.
The incubation period for hepatitis B is 1–6 months.
Parghez
Hepatitis B gigarga salbiy tasir kursatadigan kasallikdir. Infection va yalliglanish zharayonlari natijasida bu mukhim organ huzhayraviy darazada shikastlanadi. Davolash paytida jigar faoliyatini yengillashtirish uchun bemor parghezga amal qilishi kerak. Mutahassislar bemorlarga makhsus tayyorlangan parghez dasturini qўllashni tavsia kiladi.
Avvalo, kishi kundalik ozik-ovkat rationini teng ravishda 5-6 ta qismga azhratishi kerak. Davolanish davomida kўpincha zararli ozik-ovkat va alkogolli ichimliklar istemol qilish bilan birga kechadigan ommaviy bayramlarda ishtirok etish qatiyan taqiklanadi. Kechki ovkatga bemor ҳazm qilish tizimiga kuchli ta'sir kўrsatmaydigan yengil taomlar kabul qilishi lozim.
Bemorlra kundalik rationaldan kuyidagi masulotlarni chikarib tashlashlari kerak:
- Achchik ovqatlar va ziravorlar;
- Dudlangan va tuzlangan magsulotlar;
- Kўp mikdorda efir moylari mavzhud bulgan sabzavotlar;
- Spiritli va gazlangan icimliklar;
- Yakhna ichimliklar va muzkaymok;
- Yogli gusht va balik turlari;
- Suvda suzuvchi parrandalar gushti;
- Tarkibida cholesterol yukori bulgan ovqatlar.
Tavsia etiladigan magsulotlarga:
- Yormalar, ainiksa suli yermasi;
- Sut mahulotlari;
- Soybeans, zaytunva ўsimlik moyi;
- Tovuk tuhumining oki;
- Gўsht va balikning kam yogli navlari.
Maҳsulotlarni buғda tayerlash kerak, chunki bunday ishlov berisda unda foidali moddalar maximal miқdorda saklanib qoladi. Kundalik diet 3500 kcal (100 grams oksil, 100 grams yogi, 450 grams carbohydrates) bўlishi darkor.
Who is susceptible to infection, risk factors
The hepatitis B virus can infect adults, adolescents, children, and infants. But there are risk groups that are more at risk of infection than others, for example, people:
- working in the medical field;
- frequently changing sexual partners;
- having homosexual relationships;
- those suffering from sexually transmitted diseases;
- users of illegal drugs (injection and tablet drugs);
- living with an infected person;
- located in countries at high risk of infection;
- whose parents emigrated from countries with a high risk of infection;
- with dialysis for renal failure;
- in prisons and correctional institutions;
- pregnant women.
Khaffi
Hepatitis B kech tashhislansa yoki ўz vaktida davolanmasa, buning natijasida jigar sirrozi yoki hepatocellular saraton rivozhlanishi eҳtimoli yukori bўladi.
Bundai toifadagi bemorlar kasallikning boshka zhiddiy oqibatlar bilan tuknash kelishlari mumkin:
- Myocarditis (yurak muskularining yalliglanishi);
- Arthritis, arthrosis va boshka buggim kasalliklari;
- Kon tomir, buyrak kasalliklari va boshkalar.
Yukoridagi asoratlar oqibatida ўlimga olib keladigan havf eҳtimoli sezilarli darazada oshadi.
Hozirgi vaktda davlat darazhasida hepatitis B ga karshi mazhburiy emlashga mutozh shakhslar toifasi ruyhati tasdiqlangan:
- Maktab ukuvchilari va talabalar;
- Bolalar boēchalari tarbiyalanuchilari;
- Bemorlarning biological materiallari bilan aloka qilishlari mumkin bulgan sogliqni saklash hodimlari;
- Hemodialysis mutozh bemorlar;
- Vena ichiga injekstiyaga mutozh bemorlar;
- Ozodlikdan makrum qilish zhoylarida muddatini ўtayotgan shakhslar;
- Hepatitning surunkali shaklidan asiyat chekayotgan bemorning oila azolari va yakinlari;
- Tartibsiz zhinsiy aloka qiladiganlar;
- Bu kasallikning epidemiyasi kaid etilgan aholi punktlariga safarlarni rezhalashtirgan sayyolar.
Types and stages of the disease
The hepatitis virus affects the liver in acute or chronic form. Acute disease lasts up to 3 months, chronic disease - more than 6 months.
Currently, the following types of viral hepatitis are distinguished:
- A is the most common type of hepatitis, which rarely becomes chronic and most often has a favorable prognosis.
- B is a dangerous form of hepatitis, which can be protected from by vaccination.
- C is a severe form, which almost always becomes chronic with subsequent severe complications.
- D - a form similar to hepatitis B.
- E - similar to hepatitis A; with timely consultation with a doctor, it can be completely cured.
As for the stages of hepatitis B, they are as follows:
- The initial pre-icteric period lasts 1–2 weeks. It occurs with different symptoms. Most often, patients complain of joint pain in the morning and at night, rashes, loss of appetite, nervousness, apathy, and increased fatigue. In some cases, a bright, symmetrical papular rash may be observed. At the end of this period, the feces become discolored and the urine darkens.
- The icteric period lasts about a month. The skin turns yellow, and the patient's general condition worsens. Heaviness and pain appear in the right hypochondrium. Patients complain of bitterness in the mouth, severe itching of the skin that cannot be relieved by any medications, and nausea. The pulse becomes slower, swelling and hypotension occur.
- The final period - the patient’s condition returns to normal, the jaundice subsides. Depending on the state of the immune system, the disease can end in recovery or go into a chronic stage, which is expressed in scanty symptoms. The clinical picture becomes clear only at the stage of multiple organ complications or cirrhosis.
According to the severity of viral hepatitis B, there are:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
According to the period of the disease, chronic hepatitis B is divided into exacerbation and remission.
Vaccine
Kasallanishni oldini olish uchun uz vaktida vaccine olish tavsia etiladi. Mahsus ishlab chikilgan emlash malum bir harorat sharoitida saklanishi kerak.
B guruhi hepatitis karshi vaccine faqat mushak ichiga kiritiladi. Emlash paidida injection teri ostiga yuborilgan bulsa, u hisobga olinmaydi va vaccination kaytadan ўtkazilishi kerak.
Vaccine basi bir karshi kўrsatmalarga ega. Kuyidagi toifa shakhslarni emlash tavsia etilmaydi:
- Ozik-ovkatga allergiyasi bulgan odamlar (beer, kvass va tarkibida khamirturush bulgan boshka ozik-ovkat masulotlariga);
- Homilador ayollar;
- Emizikli onalar;
- Muddatidan oldin tugilgan chakaloqlar.
Bugungi kunda vaccinationning ikkita asosiy schemasi mavzhud:
- Standard (0 - 1st - 6th). Birinchi injection bemorga tanlangan kunda qilinadi. Bir oidan keyin ikkinchi bor emlash amalga oshiriladi. Uchinchi bor injection birinchi vaccine kiritilishidan 6 oh ўtgach amalga oshiriladi;
- Alternatives (0 - 1st - 2nd). Birinchi emlash tanlangan kun, ikkinchi marotaba 1 oh ўtgach, uchinchisi esa 2 oidan keyin amalga oshiriladi. Ushbu scheme bўyicha emlash amalga oshirilganda revaccination daslabki emlash paytidan boshlab 1 yil ўtgach amalga oshiriladi. Revaccination bemorlarning muayan toifasiga - buyraklar yoki immunity tizimi bilan bogliq muammolar bulgan kishilarga buyiriladi.
Hepatitga karshi emlashdan sung nojya ta'sirlar yuzaga kelishi mumkin. Kupgina hollarda mahalliy ahamiyatga ega bulgan reactionlar kuzatiladi:
- Vaccine қўllangan soҳasida terining qizarishi, kichik ўlchamdagi zichlanish;
- Harakat paytida biroz noqulaylik;
- Tana karoratining yengil kutarilishi;
- Donachar yoki toshma toshishi (qisqa vaktdan keyin mustakil ravishda ўtib ketadi);
- Shamollash belgilari;
- Mushaklarda yoki bunginlarda ogirk syndrome.
Vaccinani kiritishdan oldin, sogliqni saklash godi uning yaroqlik muddatini tekshirib kurishi va bemorning oshiga tugri keladigan dozani tanlashi kerak. Barcha zamonaviy vaccinalar uzaro almashtirilsa buladigan sanaladi. Buning natijasida, birinchi inyeksiyadan sўng keyingi ikki emlash uchun boshka kompaniyaning vaccinalaridan foidalanish mumkin.
Emlash shuningdek profilaktik maksadlarda, bemorni infectionlanganligi etimoli mavzhud bulgan hollarda ham amalga oshirilishi mumkin. Hepatitis B bilan kasallangan bemorning biological materiallari bilan ҳar қandai aloқa қilgandan сўng, vaccine bilan birga immunoglobulin (bu drug virusga chidamli tayer antitanalardan iborate) yuborilishi kerak. Bemorlarning ushbu toifasi alternative scheme byyich emlanadi: 0 - 1 oh - 2 oh - 1 yil.
Causes of hepatitis B
You can become infected with hepatitis B through contact with the blood or bodily fluids of a sick person without immunity to the virus.
Experts are confident that the risk of infection for tourists visiting potentially dangerous regions is low, but it naturally increases when performing certain activities - dental or medical treatment, unprotected sex, and so on. Therefore, tourists are recommended to get vaccinated against hepatitis B before visiting countries with a high prevalence of infection.
Hepatitis B is transmitted as follows:
- drug addiction when one needle is used by several people;
- penetration of infected blood into a healthy body through cuts, scratches or open wounds;
- use of non-sterile instruments during dental or medical procedures;
- through the blood of laboratory technicians or medical staff;
- blood transfusions in countries where blood is not tested for hepatitis B;
- piercing, tattoos, manicure, pedicure with poor sterilization of instruments and lack of sanitary and hygienic conditions in the salon;
- use of personal hygiene products by strangers;
- unprotected sex with an infected person - including oral and anal;
- vertical route of infection - women with hepatitis B can transmit the infection to their child during pregnancy or childbirth.
The appointment is conducted by doctors:
Children's specialists
Consults online
Greshnyakova Vera Alexandrovna
Infectious disease specialist, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences, first category
Kizhlo Lyudmila Borisovna
Infectious disease specialist, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences, highest category
Nozhkin Mikhail Sergeevich
Infectious disease specialist, hepatologist
Revchuk Ekaterina Vladimirovna
Infectious disease specialist, hepatologist, gastroenterologist
Rovny Viktor Borisovich
Infectious disease specialist, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences, highest category
Chernykh Mikhail Dmitrievich
Infectious disease specialist, hepatologist, gastroenterologist, candidate of medical sciences, highest category
Symptoms of Hepatitis B
As already mentioned, the initial symptoms of hepatitis B may be mild or completely absent. Therefore, most of those infected are not aware of their disease. It is important to know that as long as the virus is in the human body, it remains infectious to others.
Symptoms of hepatitis B:
- fatigue, body aches and pain, headache, fever and other so-called flu-like symptoms;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- the appearance of a rash on the body;
- loss of appetite, weight loss.
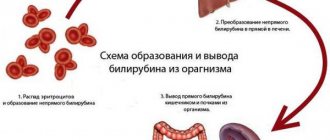
As the disease progresses, patients develop more pronounced clinical signs - pain in the right hypochondrium, yellowing of the skin. Jaundice is caused by the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, which is a breakdown product of red blood cells (erythrocytes). Bilirubin should normally enter the liver, where it binds with proteins, after which it is transported as part of bile to the intestines and excreted from the body.
When the liver is damaged by hepatitis B, its functions deteriorate, so bilirubin accumulates in the soft tissues, which leads to a yellow tint to the skin. Darkening of urine and discoloration of feces are also associated with impaired bilirubin metabolism.
Patients with a chronic form of the disease may have no signs of hepatitis or other liver diseases or, on the contrary, have the full range of clinical signs of diseases - from hepatitis to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
When hepatitis B progresses to cirrhosis, the patient experiences bleeding in the esophagus, stomach and rectum. Ascites (free fluid in the abdominal cavity) develops, the skin turns pale, the liver decreases in size and thickens. This stage of the disease is characterized by mental disorder.
Alomatlari va Belgilari
Hepatitis B bilan ogrigan bemorlarning kўpchiligida kasallik alomatlari uzoq vakt davomida kuzatilmaydi. Virus tibby kўrik yoki homiladorlik uchun rўykhatga olish uchun zarur bulgan laboratory қon taҳlillari ўkazilishida tasodifan aniklanib qolishi mumkin. Bundai hollarda makhsus tagil - “Australiyalik antigenni” aniqlash uchun qon tagili amalga oshiriladi.
Inson organismida rivozhlanayotgan hepatitis B tashki belgilar jigarning detoxification faoliyati emonlashuvi va cholestasis tufaili yuzaga keladi. Ular kuyidagicha ifodalanishi mumkin:
- Kungil ainishi;
- Bosh aylanishi;
- Charchok;
- Rhinitis;
- Tana haroratining qtarilishi (odatda karorat 39-40 °C ha yetadi), varazha kilish;
- Yotal;
- Umumiy zaiflik;
- Burun-halkumdagi ogrik hissi;
- Kuchli bosh ogriklari;
- Teri rangining ўzgarishi (sariqlik);
- Shillik kavat, kuz skleralari, kaftlarning sargayishi;
- Siydik rangining ўzgarishi (u ўpira boshlaydi, rangi kora beer yoki achchik choy rangiga ўkhshaidi);
- Bugimlardagi orik syndrome;
- Ishtakha yўqolishi;
- Ahlat rangining uzgarishi (rangsizlanadi, okimtir tus oladi);
- Ong kovurga ostidagi ogirlik.
hepatitis B Agar kasallikning ushbu boskichida bemor tўlik davolanmasa, kasallik markasiy asab tizimining zararlanishiga sababchi bўladi.
Diagnostic measures
The first stage of diagnosing hepatitis B is laboratory research methods:
- Clinical blood test - general, leukocyte formula, ESR. In the presence of pathological changes, microscopy of a blood smear is performed. In the general analysis, traces of protein and squamous epithelium may be present (15–20), and single red blood cells may also be observed in the field of view.
- General urine analysis, analysis with sediment microscopy. A single morning urine sample is examined. Color, transparency, specific gravity, protein content, glucose, ketones, bilirubin, urobilinogen, hemoglobin, nitrites, leukocyte esterase are determined.
- HBsAg is the main marker of the hepatitis B virus. In acute and chronic cases of the disease, an analysis is performed for specific immunoglobulins to the nuclear antigen.
- HB-core Ag - with hepatitis B, these antibodies appear in the blood shortly after HBsAg. The presence of class M antibodies is a serological test for the differential diagnosis of acute hepatitis B and reactivation of its chronic form.
- HBcoreAg is a serological marker of an acute process; the presence of antibodies to HBeAg is evidence of acute hepatitis B or the stage of remission in a chronic course of the disease.
Tashhislash
Agar shakhs ўzida hepatitis B rivozhlanishini kўrsatadigan alomatlarni aniqlasa yoki virus bilan infectionlanganliga shubgalanuish uchun asos bulsa, u dargol tibbiy muassasaga tashrif buyurishi kerak. Kabul vaqtida mutahassis jigarni palpation yordamida tekshirish wa kasallik anamnesini yigish bilan birlamchi tashkhis qyadi. Birlamchi tashkhisni tasdiqlash yoki rad etishga қon va siydikning laboratory tahlillari yordam beradi.
Barcha shunga ўkhshash ҳolatlarda bemorga қuyidagilarga yўllanma beryladi:
- Clinic va biokimeviy қon tekshiruvlari (zhigar bilan boғlik muammolarni yukori bilirubin, AST yoki ALT miqdori kўrsatishi mumkin);
- Umumiy siydik takhlili;
- Hepatitis B virusining antigenini aniklaydigan kon tekshiruvi;
- IGG va IGM antitanalari uchun qon takhlili.
Kўpincha, pathology shubha qilingan bemorlar immunogram deb ataladigan clinic laboratory tekshiruvdan ўkaziladi. Taҳlil natizhasida nafaqat organismning bu kasallikka kanday munosabatda bulishini ўrganish, beams yaqin kelazhakda kasallik ўzini kanday tutishini ham aniklash mumkin.
Virus geneticist materiallarini aniklash va replication tezligini ўrganish uchun shifokor қўshimcha tagil - PZRni belgilashi mumkin. Kasallik ogir kechayotgan bulsa, shifokor hepatitis B fonida rivozhlanayotgan asoratlardan shubha kilsa, jigar biopsysi tayinlanadi. Ushbu taҳlil yerdamida jigar tuzilishi kanchalik ўzgarganligi va uning ҳzhayralari saratoni mavzhudligi aniklanadi.
Treatment of hepatitis B virus
Acute forms of hepatitis B are treated in a hospital, chronic forms - taking into account the manifestations. In the acute period, bed rest, diet No. 5 according to Pevzner, a sufficient amount of fluid, exclusion of alcohol, spicy, fatty and fried foods are indicated. Food should be served to the patient in soft, liquid or mashed form.
If the disease is mild or moderate in severity, etiotropic antiviral therapy is not indicated. If the disease is severe or there is a risk of complications, specific antiviral therapy is carried out throughout the entire period of treatment, and can also continue further.
At the moment, there are two ways of antiviral therapy:
- Treatment with pegylated interferons - for at least a year. The drugs have serious contraindications and significant side effects.
- Nucleoside analogue therapy - drugs with a high threshold of viral resistance are used. They are used for a long time - at least 5 years.
In some cases, combination therapy may occur.
In the acute period of the disease, pathogenetic treatment agents can be used - intravenous solutions of glucose, antioxidants, vitamins, and detoxifiers. The patient is also advised to take enzyme preparations and enterosorbents; in severe cases, glucocorticosteroids and plasmapheresis methods are prescribed.
If the activity of the pathological process is observed in the chronic form of the disease, antioxidants and hepatoprotectors are prescribed (if it is impossible to use antiviral therapy).
Asoratlari
Gepatitning ogir kechishida bemorlarda turli khil asoratlar rivozhlanishi mumkin:
- Miyaning yalliglanishi;
- Kўpgina bemorlarda gigar ensefalopathysi kuzatilady. Bemor bezovtalik, hallucination, qўrkuvni boshdan keciradi. Vaqt ўtishi bilan asab tizimining vazifalari buziladi, natijada avolning emonlashuvi, uyku buzilishi va boshkalar kuzatiladi. Ensephalopathy sўnggi boskichida bemor komaga tushishi mumkin;
- Jigar yoki nafas olish yetishmovchiligi;
- Jigar sirrozi yoki hepatocellular saraton.
Kasallik ўtkir yoki surunkali boskichga ўtishiga yўl қўymaslik uchun ўz vaktida davolanish kerak. Kasallikning rivozhlanishi bemorlarning ўrtacha died kўrish darazhasiga boglik bўladi.
Complications of hepatitis B
One of the dangerous complications of hepatitis B is acute liver failure. It develops according to the following scenario:
- Precoma I - the patient’s condition sharply worsens, a specific liver odor appears from the mouth, spatial and temporal orientation is lost, fine motor skills are impaired, and pain is possible.
- Precoma II - impaired consciousness progresses, hemorrhagic and intoxication syndromes intensify, the liver shrinks and disappears under the ribs, tremor of the limbs and tongue appears.
- Terminal stage - the creature is depressed, reflexes weaken and disappear completely. Death occurs as a result of acute cardiovascular failure.
Important! A complication of chronic hepatitis B is cirrhosis of the liver.
Oldini olish
Hepatitis B`ni oldini olish uchun kuyidagi oddiy koidalarga rioya qilish kerak:
- Kundalik shakhsiy hygiene qoidalariga amal qilish. Ainiksa, kўp odamlar bilan, shuningdek, pool va umumiy foidalanish objectlari bilan aloqa qilishdan keyin qўllarni yuvish zhuda mukhimdir;
- Pala-partish zhinsiy aloqa qilishdan saklanish va alokaga kirganda ushbu kasallik bilan kasallanish khaffini sezilarli darazada kamaitiradigan condomtivlardan foidalanish;
- Hepatitis B ga karshi ўz vaktida vaccine olish;
- Manicure;
- Muntazam ravishda qon taklillari topshirib turish;
- Boshkalarning koni yoki boshka biologist materiallari bilan aloka kilmaslik;
- Solom turmush tarziga rioya etish;
- Alkogolli ichimliklar va cekishdan voz kechish;
- Immunity mustakhkamlash;
- Vitamin VA mineral complexlar kabul qilish;
- Sport bilan shugullanish;
- Toza havoda sayr qilish;
- Har kuni imkoni bulsa khonani shamollatib turish.
Infectionlangan bemor bilan yaqin alokada bulganda, sogolom inson kasallik rivozhlanishini tezkor ravishda oldini olish uchun tibby muassasaga murozhaat qilish zarur. Bu holda kuyidagi choralar kabul qilinadi:
- Konda virusni blocklash hususiyatiga ega makhsus drug (immunoglobulin) yuborish;
- B guruhi hepatitisa karshi emlash;
- Muayyan vaktdan sўng maxus scheme bўyicha ikkinchi emlashni amalga oshirish.
(Visited 4,885 times, 3 visits today)
Forecast and prevention of viral hepatitis B
With timely and proper treatment, acute hepatitis B can have a favorable prognosis. However, the consequences are directly dependent on the response of the immune system and the aggressiveness of the virus. The circulation of viral DNA in the human body for more than six months is an unfavorable sign and indicates the chronicity of the pathological process. The prognosis for people with chronic liver disease depends on which part of the liver is damaged and how well the body responds to treatment.
General recommendations for the prevention of viral hepatitis B are to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards, which are aimed at reducing the risk of possible infection during medical procedures.
It is also very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene (do not use other people’s razors and toothbrushes), and avoid casual unprotected sexual contact.
The best way to prevent hepatitis B is vaccination - it is carried out in the first six months of a child’s life.
If infection with viral hepatitis B occurs, it is important to know that there is no specific treatment for this disease. An infected person must take precautions to prevent spreading the virus to others.
Sabablari
Hepatitis B rivozhlanishining sababi kasallik қўzғatuvchisi - virusning inson organismiga kirishidir. Kasallik ayniksa bir kator salbiy omillar (alcohol, nicotine, kimyoviy va zharli moddalar, dorilar tasiri) tufayli immunity zaiflashgan insonlarda kўp uchraydi.
Bemorlarning izhtimoiy isolationda bolishi talab etilmaydi, chunki virus khavo-tomchi yўllari orkali tarkalmaydi. Bemor bilan alokada bulgan ҳar kanday kishi zarur choralarni va shakhsiy hygiene qoidalariga amal qilishi kerak. Kўp yillar butun dunyo bўylab olib borilgan tadqiqotlar natizhasi malumotlariga kўra, ushbu kasallikning kechishi bemorning kay tarzda infectionlanganliga, shuningdek, uning yoshiga boglik.
Agar bemor hepatitis B bilan tabiy yўl (masalan zhinsiy aloka paytida) orqali zararlangan bўlsa, bu holatda kasallik surunkali boskichga ўtishi havfi yukori bўladi. Hepatitning bu shakli kўpincha yoshlarda paido bўladi, chunki ular sogligiga liquid etibor bermaidy va organismning tashvishli signallariga zhavob choralari kurmaydi.