The first signs of leukemia in adults and children
Leukemia is a blood disease characterized by disruption of normal hematopoiesis. The disease belongs to a malignant pathology. A pediatric hematologist-oncologist treats leukemia in a child. The true causes of the disease are still unknown. However, doctors identify a number of provoking factors, among which the main ones are:
- radiation exposure;
- high doses of chemotherapy (secondary leukemia);
- chromosomal disorders;
- immunodeficiency states;
- blood diseases;
- Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome.
The main causes of chronic leukemia in women are heredity and exposure to various mutagenic factors.
On a note
Achievements in domestic oncohematology, primarily in children, became possible thanks to the state’s attention to this branch of medicine.
41% of the funds allocated to finance the state program “7 nosologies” (which is $1.16 billion) are allocated to the treatment of patients with hematological malignancies (malignant blood diseases, which also include childhood leukemia).
In Russia, unrelated bone marrow donation programs are just beginning - such transplants began to be performed only 10 years ago. On a national scale, there are negligible numbers of them - no more than 70–80 per year. In total, 13 clinics in the country are licensed to perform transplantation, and there are 70–75 board-certified hematologists, oncologists, and transfusiologists who can perform the procedure. One of the largest transplant departments is the Scientific and Clinical Center for Pediatric Hematology, Oncology and Immunology named after Dmitry Rogachev, which opened in 2011 in Moscow.
Classification of the disease
According to the course, acute and chronic forms of the disease are distinguished.
Spicy. The disease develops very quickly and tends to progress. The fight against acute leukemia is significantly different from the treatment of chronic leukemia.
Chronic. The disease is less aggressive and is often detected during diagnosis for another pathology. The chronic form is characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbation.
On our website Dobrobut.com you can sign up for a consultation with a specialist and learn about leukemia, what kind of disease it is, and its causes. At the clinic you can undergo a full examination of the body, including laboratory and instrumental studies.
The first signs of leukemia in adults
Symptoms are nonspecific and have common features for many diseases. Manifestations depend on the massiveness of the lesion and its location.
The first signs of leukemia in adults:
- causeless low-grade fever, profuse sweating at night;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- enlarged spleen and liver;
- joint pain;
- constant headaches;
- external manifestations associated with bleeding disorders: bleeding gums, bruises, nosebleeds, the presence of red dots under the skin.
Symptoms of blood leukemia in children
The main manifestations in children are in many ways similar to the clinical manifestations of adults. Enlarged lymph nodes, weight loss, constant weakness, poor appetite, frequent colds, joint pain, low-grade fever for no reason - symptoms that require parents to make an appointment with a pediatrician. A feature of the disease in childhood is the gradual development of it.
Later symptoms of blood leukemia include: frequent bruising, pain in the spine, enlarged spleen and liver, refusal to play, pale skin, frequent nosebleeds.
Important: with a correct diagnosis and qualified medical care, the disease in childhood is curable in 90% of cases. The Children's Leukemia Foundation can provide enormous assistance in treatment.
Statistics. In infants and children under two years of age, the myeloid form of the disease is most often diagnosed. Children under 5 years of age are most susceptible to acute lymphocytic leukemia (70%). Chronic leukemia in children is extremely rare.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
More than 80% of all leukemias in children are acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The reason for its development is the chimeric TEL/AML gene, the formation of which occurs in utero, possibly as a result of spontaneous errors in the process of DNA replication and repair. The accumulation of genetic abnormalities in the tumor clone leads to a block of normal cell differentiation and disturbances in the process of proliferation and apoptosis.
In accordance with the French-American-British (FAB) classification, three morphological variants are distinguished: L1, L2, L3.
Clinical symptoms of ALL are determined by the degree of bone marrow infiltration by lymphoblasts, as well as the presence of extramedullary spread of the process. General symptoms of tumor intoxication are often observed, namely, increased body temperature, decreased appetite, weakness, and lethargy. During the process, several periods are distinguished: initial, extended, and remission.
The full-blown period is characterized by a rapid onset and a variety of clinical symptoms. Symptoms of general intoxication include bone pain due to leukemic infiltration of bone tissue (the diaphyses of long tubular bones are most often affected), and arthralgia caused by leukemic infiltration of joints. The skin and mucous membranes become pale. Unfortunately, they often develop hemorrhages caused by hemorrhagic syndrome, as well as bleeding (nasal, gastrointestinal, renal). Enlargement of peripheral lymph nodes (cervical-supraclavicular, axillary, inguinal) is one of the main symptoms of the disease. Almost all patients experience enlargement of the liver and spleen due to the proliferation of leukemia cells. In some cases, in patients, damage to the skin and mucous membranes manifests itself in the form of leukemides, necrosis, gingivitis and stomatitis.
Thus, several symptom complexes characteristic of ALL can be identified:
- hyperplastic – lymphadenopathy, bone pain, heaviness and pain in the left and right hypochondrium, hepatosplenomegaly;
- anemic - dizziness, flickering spots before the eyes, shortness of breath during exercise, palpitations, noise in the head and ears;
- hemorrhagic – skin hemorrhages, bleeding gums, nosebleeds;
- intoxication – increased body temperature, weakness, lack of appetite, ossalgia;
- syndrome of infectious complications - the addition of severe pneumonia.
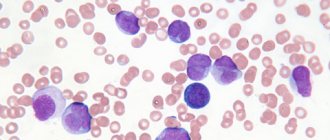
During diagnosis, the morphological features of bone marrow and peripheral blood blasts are assessed. In addition to detecting tumor cells of the lymphoid line of hematopoiesis using Romanovsky-Giemsa staining, the following research methods are carried out:
- cytochemical - allow blasts to be classified as lymphoid or myeloid lineages (test for myeloperoxidase, phospholipids, glycogen), individual cell lines;
- immunophenotypic – determine immune cell markers (CD);
- cytogenetic – determine karyotype anomalies and chromosomal aberrations (deletions, translocations, inversions, etc.);
- molecular biological – allow you to determine the number of cells with a certain aberration in the entire mass of the bone marrow.
To confirm the diagnosis of ALL, a comprehensive examination is necessary, in which the leading role is given to the morphological method.
Currently, the treatment programs BFM (BFM: Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster) and CF (MB: Moscow-Berlin) are used.
All treatment can be divided into basic and accompanying. Basic therapy consists of systemic and local chemotherapy and, if necessary, radiation therapy. Accompanying treatment is necessarily prescribed to prevent infectious complications and correct post-cytostatic reactions. The following stages are distinguished in the treatment of malignant processes: induction of remission, consolidation of remission (usually several phases), maintenance treatment.
Diagnostics
To confirm such a formidable pathology, the doctor will prescribe the following studies:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- bone marrow biopsy;
- X-ray examination;
- computed tomography.
A blood test for leukemia is of decisive importance.
It is important to differentiate leukemia from autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, neuroblastoma and infectious mononucleosis.
Failure in the immune system
Is it possible to predict the risk of developing leukemia? Unfortunately no. “99% of leukemias are completely random events,” says Deputy General Director for Scientific Work of the Federal Research Center for Pediatric Hematology, Oncology and Immunology named after Dmitry Rogachev, Director of the Institute of Hematology, Immunology and Cell Technologies (IGICT), Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Alexey Maschan . — In children, the most rapidly developing system is the immune system, and a failure in its functioning in some people leads to the development of leukemia. Every year, 4 cases of acute leukemia are registered per 100 thousand children.”
Where to go Bone marrow transplantations for children and adolescents are carried out in 13 Russian medical centers. The leading ones are located in Moscow - Federal Scientific Center for Children's and Orthopedics Orthopedics named after. Dmitry Rogachev, Russian Children's Clinical Hospital, Cancer Center named after. N. N. Blokhina. In St. Petersburg - St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. Academician I.P. Pavlov, Institute of Pediatric Hematology and Transplantology named after Raisa Gorbacheva. There are centers in Yekaterinburg and Nizhny Novgorod.
Experts recommend paying attention to the following symptoms and changes in the child’s well-being:
- the unreasonable appearance of bruises, small hemorrhagic rash - not because the child hit himself, but just like that;
- pallor, increased abdominal size;
- the appearance of strange formations on the body, enlarged lymph nodes;
- changes in blood tests;
- There may be various pains - headaches, in the stomach, but this is an optional symptom.
The first person parents should contact for advice is the local pediatrician; he will decide whether the child needs a consultation with a hematologist.
“If the fears are not unfounded, the child is transferred to the regional children's clinical hospital, to hematologists. Regional hospitals decide whether they can cope with this disease on their own: whether they have the necessary equipment and personnel,” says Elena Skorobogatova, head of the bone marrow transplantation department of the Russian Children’s Clinical Hospital of the Russian Ministry of Health, Doctor of Medical Sciences . “If it can’t be dealt with locally, the region turns to one of the federal clinics where there is a bone marrow transplant department. My advice: if your child is diagnosed with acute leukemia, do not go to private clinics, use the public network. Don't waste your time and money! "
Treatment of leukemia in children and adults
The main types of treatment include: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplantation. Appointments are strictly individual. As additional treatment, detoxification and hemostatic therapy, transfusion of leukocyte and platelet mass, and prescription of antibiotics are used. Traditional medicine recipes can only be an addition to the main treatment and are used only after consultation with a specialist.
The prognosis for leukemia of different stages depends on many factors: the stage of the disease, the type of cancer cells, the patient’s age, his general condition, the presence of chronic pathology, etc. According to statistics, children and adult patients with early detection of the disease have a greater chance of recovery and remission.
Recurrent leukemia can occur only in adults. For children who received timely qualified help, cure occurs in 95%.
If you still have questions and need advice from a highly specialized specialist, make an appointment on the website or use the phone. Our doctors will help solve any health problem.
Related services: Chemotherapy course Consultation with an oncologist
Modern approach
Therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, as a rule, consists of three stages, the goal of which is to achieve remission and restore normal hematopoiesis. They are treated with chemotherapy. “This is a very tough treatment that potentially affects all organs and systems, and the entire process of treating a tumor and especially leukemia is a constant struggle with the complications of chemotherapy,” says Alexey Maschan.
Article on the topic
Why do children get cancer? Oncologist about symptoms and prevention of tumors
Bone marrow transplantation from a related or unrelated donor is also used, but it is not performed for everyone, only about 30% of children and after achieving remission.
When a patient needs a bone marrow transplant, doctors first check his close relatives to see if any of them can be a suitable donor for the patient. If there is no such person among the relatives, they look for an unrelated donor.
Unfortunately, this can take a lot of time - first, they search for him using the Russian Register of Unrelated Stem Cell and Bone Marrow Donors; if there is no suitable donor in Russia, doctors or a charitable foundation make a request to the international register.
A drop of blood. New device diagnoses cancer at an early stage
More details