Ceftriaxone has analogs for the active substance - Rocephin, Lendatsin, Azaran. The first drug is the most expensive, but it is original. It is more often prescribed to children due to its high degree of purification. If you need to replace it with tablets, then take into account that Cephalexin is weaker, Pantsef and Suprax will help with infections of the ear, throat, and urinary tract, but do not give results with pneumonia. Zinnat is safe and is indicated for mild forms of infection.
To replace Ceftriaxone in ampoules with a stronger drug, Cefotaxime and Cefepime are prescribed, and Cefazolin will have a weaker effect. Of all the cephalosporins, only Ceftriaxone is administered once a day, while the others need to be injected more often. When prescribing potent tablets, Sumamed or Mofloxia may be indicated. Suprax or Cephalexin in the form of a suspension is recommended for children.
Cephalosporin antibiotics
Cephalosporins are a group of antibacterial agents that are widely in demand in the treatment of infectious lesions of the respiratory system, including pneumonia. They are used for inpatient and outpatient treatment, are well tolerated by patients, have low toxicity, and rarely provoke the development of adverse reactions. In pharmacology, cephalosporin antibiotics are classified as follows:
- first generation
- Cefazolin, Cephalexin, Cefadroxil; - second generation
— Cefuroxime, Cefaclor, Cefamandole; - third generation
- Cefotaxime, Cefoperazone, Ceftriaxone, Ceftibuten, Ceftazidime; - fourth generation
- Cefpirom, Cefepim; - fifth generation
- Ceftobiprole, Ceftaroline.
In the treatment of bacterial or mixed pneumonia, antibacterial drugs of the second and third generations, including Ceftriaxone, have proven well.
Its closest analogues are representatives of the cephalosporin group. But there are other antibacterial agents for adults that are similar in effectiveness, safety, list of indications and method of use with Ceftriaxone.
What it is
It is impossible to imagine treating serious diseases without the use of antibiotics. Ceftriaxone is one of the strongest antibacterial pharmaceuticals of the third generation of a number of cephalosporins. The drug is aimed at inhibiting the enzymes that produce murein, which leads to the death of bacteria. Extensive indications and affordable cost make the drug very popular for use in various medical areas:
- infectious diseases of the respiratory organs, including pneumonia, tonsillitis, purulent pathologies of the lungs with severe course;
- skin infections, non-infectious soft tissue pathologies;
- sexual infections;
- diseases of the abdominal organs, including peritonitis;
- infections of the skeletal system;
- in the process of treating burns, wound surfaces, injuries.
The successful action of the antibiotic begins from the third day of use, which makes it one of the favorites of most doctors.
Solution for infusion Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin is an antibacterial agent from the fluoroquinolone group. Gram-positive enterococci, Staphylococcus aureus and epidermal staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci, gram-negative Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus and many other pathogens have not lost sensitivity to its active substance.
Its use in the treatment of pneumonia in adults leads to blocking of DNA supercoiling processes. The cells also stop producing proteins to build their membranes, so they are destroyed under the pressure of the intercellular fluid.
Levofloxacin in combination with Ceftriaxone has recently been especially often used in the treatment of pneumonia caused by coronavirus.
The antibacterial agent is administered intravenously by drip with a constantly increasing dose - from 250 mg to 750 mg. The duration of therapy depends on the sensitivity of the causative agent of pneumonia, ranging from one to two weeks. If necessary, treatment continues with Levofloxacin in tablet form.
The drug is not prescribed to patients with hypersensitivity to quinolones, epilepsy, tendon lesions caused by taking fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Levofloxacin can only be used in the treatment of pneumonia in adults. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the drug is used for health reasons.
Rocephin for injection
Rocephin is a structural analogue of Ceftriaxone, which is produced by a Swiss pharmaceutical company. It has identical active substance, indications and contraindications for use. It costs 3-4 times more than the domestic product, but this does not affect its effectiveness. Like Ceftriaxone, Rocephin is intended for parenteral use.
The antibiotic has a long-lasting effect, and its bactericidal activity is based on the suppression of the biosynthesis of cell membranes and RNA replication. Adults are prescribed 1-2 g of the drug once a day. Depending on the clinical situation, the daily dose is increased to 4 g. Before intramuscular injection, the powder is diluted in Lidocaine for local anesthesia. In other cases, sterile water or isotonic sodium chloride solution is used.
The duration of the therapeutic course is individual, but usually for pneumonia, Rocephin is administered for another 2-3 days after the temperature normalizes. The list of contraindications for the antibacterial agent includes hypersensitivity to cephalosporin drugs and auxiliary ingredients. It is necessary to inject it with caution if you are individually intolerant to any penicillins. This is also true during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Ceftriaxone: analogues
Ceftriaxone has analogues in composition (Rocephin, Lendatsin, Avexone), a group of 3rd generation cephalosporins (Cefotaxime, Cefoperazone, Ceftazidime). Cephalosporins, but not direct synonyms of ceftriaxone, can be in capsules (Suprax, Cephalexin).
For children, suspensions containing cefixime (Pancef, Suprax) are used. Even the same drugs have differences in the active substance, and the question of what can replace Ceftriaxone can only be decided by a doctor. The price of all these medications varies significantly (see table).
| Drug name | Active substance | Manufacturer | Release forms | Price, rubles |
| Rocephin | Ceftriaxone | Hoffmann La Roche, Switzerland | Bottles of 1 g | 490 |
| Azaran | Ceftriaxone | Hemofarm, Serbia | Bottles of 1 g | 305 |
| Lendatsin | Ceftriaxone | Lek, Slovenia | Bottles of 1 g | 142 |
| Medakson | Ceftriaxone | Medokemi, Cyprus | Bottles of 1 g | 145 |
| Cefatrin | Ceftriaxone | Jepak International, India | Bottles of 1 g | 42 |
| Ceftriaxone-Kraspharma | Ceftriaxone | Kraspharma, Russia | Bottles of 1 g | 22 |
| Cephalexin | Cephalexin | Hemofarm, Serbia | Capsules 500 mg No. 16 | 95 |
| Pantsef | Cefixime | "Alkaloid", Macedonia | Capsules 400 mg No. 6 | 745 |
| Suprax | Cefixime | "Hikma", Jordan | Capsules 400 mg No. 6 | 795 |
| Zinnat | Cefuroxime | Glaxosmithkline, UK | Tablets 250 mg No. 10 | 490 |
| Amoxiclav | Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid | Lek, Slovenia | Tablets 1 g No. 14 | 390 |
The best manufacturers
Hoffman La Roche is considered the best manufacturer of Ceftriaxone; it produces it under the name Rocephin. The original drug is characterized by a high degree of purification, numerous clinical trials and proven effectiveness against the most common infections.
An antibiotic made in Slovenia, Lendatsin, has also proven itself very well. It can be considered the best option in terms of price and quality ratio.
The Serbian Azaran is more expensive, but there is no significant difference in clinical effectiveness between them.
When purchasing budget drugs, it is best to choose Russian ones produced by Biosintez, Kraspharma, Biokhimik and Sintez. In their absence, it is permissible to use Belarusian analogues; Indian generics are slightly worse in action.
We recommend reading about how to use Ceftriaxone for sinusitis. From the article you will learn why Ceftriaxone is prescribed for sinusitis, sinusitis and other ENT diseases, as well as how to inject the antibiotic correctly and what to do if it does not help. And here is more information about whether it is possible to combine Ceftriaxone and alcohol.
Imported analogues: Avekson, Lendatsin
Avekson is an imported analogue of Ceftriaxone, produced by Aversi-Rational in Georgia. Release form: powder in 1 g bottles. Used to treat infections in adults and children, administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Currently, it does not have a registration certificate in Russia, therefore Avekson is not represented in the pharmacy chain. In terms of effectiveness, it fully corresponds to domestic antibiotics. The situation is exactly the same for the drugs Lorakson (Exir Pharmaceuticals, Iran) and Blicef (Ildong Pharmaceuticals, Korea).
Lendacin is a medicine containing ceftriaxone sodium salt, it is produced by Lek (Slovenia). Prescribed for severe forms of infection:
- peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum);
- postoperative wound infection or its high probability;
- polytrauma;
- typhoid fever;
- salmonellosis;
- gonococcal infection;
- syphilis;
- bacterial meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain);
- Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis);
- acute and subacute endocarditis (damage to the valvular apparatus of the heart);
- common infections of the skin and bone tissue;
- extensive pneumonia.
It is recommended more often for intravenous administration in the first 3 days, then for 4-7 days they switch to intramuscular injections.
Alternative - expensive analogues: Rocephin, Azaran
Rocephin and Azaran are among the most expensive analogues of Ceftriaxone in terms of cost; their choice is most often recommended in the treatment of children, especially newborns, since they are characterized by a high degree of purification. There are fewer cases of allergic reactions to them in the form of:
- difficulty breathing, coughing;
- skin rashes, itching, redness;
- hives;
- fever;
- serum sickness - the formation of immune complexes with pain in muscles, joints, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, decreased blood pressure, inflammation of the kidneys;
- anaphylactic shock - rapidly appearing pain, swelling at the injection site, swelling, itching and a sharp drop in pressure, chest pain, bronchospasm, suffocation, pallor and bluish skin, this is an extremely dangerous complication, and in the absence of help, death occurs;
- stomach ache;
- changes in blood composition (increased eosinophils).
What can you replace the antibiotic with to drink?
Ceftriaxone is an antibiotic that is used only in injections, so replacing it with drugs to drink (tablets, capsules, suspension) will always not be completely equivalent:
- Cephalexin is a 1st generation cephalosporin with a lower potency, does not overlap the antibacterial spectrum of Ceftriaxone, and has a very weak effect on gram-negative flora;
- Cefixime (Pancef, Suprax) – 3rd generation of cephalosporin drugs, low effectiveness against staphylococcus, enterococcus and Proteus;
- Cefuroxime (Zinnat) is used to treat mild respiratory, skin and kidney diseases.
Other oral forms (for internal use) containing other antibacterial drugs (for example, Amoxicillin, Azithromycin) have their own indications and contraindications for use.
In most cases, these tablets, capsules or children's suspension are prescribed for initial signs of exacerbation of chronic diseases, mild or moderate inflammation, as well as for continuing the course of treatment after injections. It is strictly forbidden to change antibiotics yourself.
Watch this video about analogues of the drug Ceftriaxone:
Cefazolin powder
Cefazolin is an antibacterial drug of the cephalosporin series. Its active component is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, so in treatment it is used in the form of intravenous and intramuscular injections. An absolute contraindication is pregnancy. Patients with renal, liver failure, and pseudomembranous enterocolitis are treated with caution and under the supervision of a physician.
Unlike Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin should not be used with aminoglycosides, as the likelihood of irreversible kidney damage increases.
Cefazolin should not be used if you are hypersensitive to any cephalosporin or other beta-lactam antibiotics. For intramuscular injection, the antibiotic is mixed with water or isotonic sodium chloride solution and then injected deep into the muscle.
For intravenous injection, Cefazolin is diluted in an isotonic sodium chloride solution or in a 5% glucose solution. For severe bacterial pneumonia, 0.5-1 g of the drug is prescribed every 6-8 hours. The duration of therapy depends on the clinical situation and the presence of concomitant pathologies in the patient.
Which is better for pneumonia - Cefazolin or Ceftriaxone - depends on the severity of its course. The latter remedy is considered more effective in clinical practice. Including due to the possibility of combining it with antibiotics of other groups.
A little about generics
Generic Ceftriaxone differs from the original Rocephin in that they do not have sufficient clinical studies. Often, the manufacturer copies the antibiotic molecule, but the technology and degree of purification are not the same. Therefore, in severe cases of the disease, the introduction of the original is recommended.
A more expensive but reliable option is chosen for children, especially infants, patients with drug allergies, and kidney and liver diseases. If financially possible, you should always buy the original drug.
Semi-synthetic antibiotic Amikacin
Amikacin is a representative of the group of aminoglycosides - organic compounds that are united by the presence in their chemical structures of amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds to aminocyclic rings. This analogue of Ceftriaxone in ampoules for adults.
Unlike Ceftriaxone, staphylococci, which often act as infectious agents of pneumonia, are slightly more sensitive to Amikacin.
Its active substance interferes with the biosynthesis of RNA in bacteria, which causes their death. Many pathogenic microorganisms have not developed resistance to the effects of the drug.
However, as with Ceftriaxone. Therefore, the answer to the question of which is better - Amikacin or Ceftriaxone - is obvious - the effectiveness of the drugs for pneumonia is approximately the same. The antibiotic is intended for intramuscular and intravenous administration. The maximum daily dose for adults is 15 mg/kg. The solution is prepared immediately before use by mixing the contents of the bottle with the following solvents:
- water for injections;
- 0.9% sodium chloride solution;
- 5% dextrose solution.
The duration of the therapeutic course for intravenous administration varies from 3 to 7 days, for intramuscular administration - from 7 to 10 days. Amikacin is contraindicated during pregnancy, acoustic neuritis, and severe kidney disease.
Ceftriaxone: analogues in suspension
Ceftriaxone analogues in suspension are used in pediatric practice. Although the instructions for the drugs Suprax, Cephalexin or Biseptol include a dose for an adult, this form of release is economically very unprofitable, since a course may require from 3 to 5 or more packages, which increases the cost of treatment.
Suprax
The suspension is prepared from powder by adding 40 ml of boiled and cooled water (to room temperature) to the bottle. It is best to divide the required volume into 2 parts and shake thoroughly at each time until completely dissolved. The bottle comes with a dosing spoon. It contains 5 ml of solution, and the active substance in it is 100 mg. When applying, they are guided by the following rules:
- the daily dose is 8 mg per kg of body weight, the doctor can prescribe it once or divide it into 2 doses (morning and evening at the same time - for example, 8 am and 8 pm);
- from 6 months to 2 years, a total of 2.5 to 4 ml of ready-made suspension is needed per day, from 2 to 4 years the volume increases to 5 ml, and from 5 to 11, 6-10 ml is recommended;
- The minimum course of treatment is 7 days, the maximum is 10 days.
The drug is prescribed to children for otitis media, tonsillitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, and less commonly used for inflammation of the kidneys and bladder. Contraindicated in cases of impaired renal function, previous intestinal inflammation and up to 6 months.
The price of granules is 540 rubles.
Cephalexin
To prepare the suspension, you must first shake the bottle so that the powder is well separated from the bottom, then pour 74 ml of boiled water at room temperature into it. The required quantity will be indicated by a mark on the bottle. The resulting dosage form contains 250 mg of the drug per 5 ml.
The daily dosage is calculated per 1 kg of weight and ranges from 25 mg for a mild form of infection to 100 mg for a severe form of infection. It is divided into 3 or 4 doses. The intervals between them must be strictly the same. Most infections require a 7-10 day course of treatment. The dose for a child depending on age is indicated in the table.
| Age in years | Number of measuring spoons (5 ml each) of Cephalexin suspension (with a concentration of 250 mg/5 ml) | How many times to take |
| 1 | 0,5 | 3 |
| 1-3 | 1 | 3 |
| 3-6 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 6-10 | 2 | 3 |
| 10-14 | 2 | 4 |
Children are prescribed Cephalexin for inflammation of the middle ear, tonsils, skin, and bronchi. It can also be used to treat uncomplicated pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and bone damage. Contraindicated in case of intolerance, ineffective in case of blood poisoning or penetration of infection into brain tissue. The price of the bottle is 70 rubles.
Watch this video about the mechanism of action and indications for use of the drug Cephalexin:
Biseptol
Biseptol is not an antibiotic; it is a sulfonamide drug, which, with the advent of new antibacterial drugs, gradually lost its relevance. However, a number of pediatricians also prescribe a children's suspension for:
- sinusitis;
- otitis;
- exacerbation of chronic bronchitis;
- bronchiectasis;
- cystitis, pyelonephritis;
- infections of the digestive system.
The drug is contraindicated in children with liver disease, severe renal impairment, folate deficiency anemia, congenital glucose-6-dehydrogenase deficiency, and blood diseases.
To prepare the suspension, pour 80 ml of water into the bottle and mix thoroughly. Take the drug 2 times a day:
- from 2 months to six months, 2.5 ml;
- from 6 months to 5 years, 5 ml;
- from 6 to 12 years, 10 ml.
The minimum duration of use is five days; if necessary, the course can be extended to 1.5 weeks. The price of Biseptol suspension is 150 rubles.
Cefotaxime injections
Cefotaxime is a member of the third group of cephalosporins, like Ceftriaxone. The product copes well with almost all gram-negative and gram-positive pathogens, destroying their cell membranes, blocking reproduction. It is prescribed for the treatment of severe infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to this drug. Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone are not the same thing. The drugs vary:
- active substances;
- lists of contraindications and potential side effects;
- single and daily doses.
Cefotaxime is diluted in the same way as Ceftriaxone, but adults can mix it with Novocaine for intramuscular use. It is administered every 4-12 hours for 1-2 g. The duration of therapy depends on the severity of the clinical picture, the type of pneumonia, and the general health of the patient. For patients with hepatic and renal pathologies, doses are adjusted downward.
Cefotaxime is not used during pregnancy, in case of intolerance to antibiotics from the clinical and pharmacological groups of penicillins, other cephalosporins, carbapenems. Treatment of adults is carried out with caution during breastfeeding, in the presence of chronic renal failure. In case of nonspecific ulcerative colitis, including a history of it, treatment of pneumonia with another antibiotic is advisable.
Contraindications
The antibiotic is contraindicated for use in the following cases:
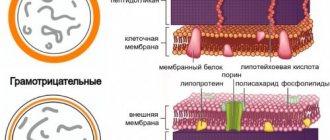
- the presence of allergic reactions to cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems and penicillins (due to the presence of a lactam ring in all these drugs);
- prematurity (infant less than 41 weeks of age, including gestational age): cephalosporin can bind to plasma proteins, replacing bilirubin, which can lead to encephalopathy;
- the neonatal period is less than 28 days in the presence of conditions associated with impaired bilirubin metabolism;
- the neonatal period is less than 28 days in the presence of conditions requiring infusions of solutions and/or calcium preparations (due to the risk of the formation of calcium and ceftriaxone precipitates).
When administering lidocaine solutions intramuscularly, make sure that the patient has no contraindications to its use.
Intravenous administration of lidocaine-containing solutions is prohibited.
Cefepime from the group of cephalosporins
Cefepime is a drug from the group of new generation cephalosporins with a wide spectrum of antibacterial action. It is directed against gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens of pneumonia. Including strains resistant to aminoglycosides and 3rd generation cephalosporins, which is Ceftriaxone.
The mechanism of bactericidal action is based on the ability of Cefepime to disrupt the biosynthesis of the cell wall of microorganisms. It is distinguished by better resistance to hydrolysis of beta-lactamases produced by pathogens. To treat pneumonia, the drug is administered intravenously by infusion at a dosage of 1-2 g twice a day for 10 days. Cefepime is diluted with a 5% dextrose solution, less often with a 0.9% sodium chloride solution. In case of severe pneumonia, the amount of antibacterial agent is increased to 2.0. The average duration of therapy is 10 days.
Cefepime is also used for intramuscular injections, but in the treatment of pneumonia, this method of administering the solution is considered very ineffective. An absolute contraindication for adults is hypersensitivity to the ingredients. During pregnancy, Cefepime is used only when absolutely necessary. And in cases where the expected benefit to the woman is higher than the potential risk to the fetus. During lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped for the entire period of treatment.
Cephalosporin Ceftazidime
Ceftazidime is a drug from the group of 3rd generation cephalosporins, which is considered the most effective antibacterial agent against pathogens of nosocomial pneumonia. It has such a wide spectrum of action that its use is practiced even before the results of laboratory tests are obtained. Ceftazidime is started immediately to improve the patient’s well-being, and then the therapeutic regimen is adjusted. The drug disrupts the production of membrane components, which causes an imbalance of bacterial cells.
Its undoubted advantage is its resistance to the effects of most beta-lactamases. The drug in ampoules is administered intravenously or intramuscularly in individual doses. The amount of solution and its concentration depend on the severity of pneumonia, the age of the patient and the state of kidney function. Typically, therapy is carried out as long as necessary to eliminate fever and chills. On average, Ceftazidime is used in a dose of 1-6 g per day, divided into 2 or 3 injections.
The list of contraindications for the drug only includes hypersensitivity to Ceftazidime and other cephalosporins. Its administration during pregnancy or breastfeeding is possible if safer means are ineffective. Ceftazidime is used with caution in cases of severe renal impairment.
Indications for use
The antibiotic is used for infectious diseases whose pathogens are susceptible to the action of the drug. Similar diseases include:
- pathology of the bronchopulmonary system (especially pneumonia), ear infections;
- infections of the digestive tract, hepatobiliary system and inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis);
- infectious processes of the kidneys, ureters, bladder;
- microbial pathology of the reproductive system (including gonorrhea);
- blood poisoning (sepsis);
- bacterial inflammation of the meninges;
- infections of the skin, bones and muscles (including wounds);
- disseminated infections (including Lyme borreliosis);
- bacterial pathology in patients with weakened immune systems.
If there is a risk or confirmed infection, cephalosporin drugs are used to prevent sepsis in patients who have undergone surgery on the digestive tract, pelvis and biliary system.
Carbapenem Meronem
Meronem is an antibacterial agent from the carbapenem group, used only for parenteral use. It has a pronounced bactericidal effect by blocking the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. The drug is often used in the treatment of severe pneumonia, since a wide range of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria have not lost sensitivity to it.
The difference between Ceftriaxone and Meronem is the latter's greater ability to penetrate bacterial cell walls, greater stability to beta-lactamases, and significant affinity for penicillin-binding proteins. For adults with pneumonia, the medicine is administered intravenously at 500 mg every 8 hours, after diluting it with water for injection.
| Contraindications to the treatment of pneumonia with Meronem injections | |
| Absolute | Relative |
| Hypersensitivity to any antibiotic with a beta-lactam structure, including cephalosporins and penicillins | Gastrointestinal disorders, including diarrhea |
| Hypersensitivity to Meropenem or other carbapenems | Concomitant use of potentially nephrotoxic drugs |
There are no contraindications for pregnancy and lactation. But doctors prescribe Meronem to women extremely rarely for health reasons. During lactation, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding during treatment.
Features of application
The start of treatment should be preceded by an allergy test for the drug, especially in patients with a history of episodes of allergy to other antibiotics.
Long-term therapy with Ceftriaxone should be carried out under supervision and with a comprehensive clinical blood test.
1 g of antibiotic contains 3.6 mmol of sodium.
Ceftriaxone may give a false-positive reaction to galactosemia testing and the Coombs test.
When performing injections with lidocaine, you must make sure that the needle does not fall into the vessel (pull the syringe plunger slightly toward you: there should be no blood in the needle) and only then begin administering the drug.
Ceftriaxone crosses the placenta. Animal studies have not revealed a teratogenic effect of the drug, however, in early pregnancy its use is recommended only if the health benefits outweigh the risks.
Macrolide Azithromycin
Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug from the group of macrolides. The drug is not stronger than Ceftriaxone, but it cannot be called weaker either. Despite the fact that Azithromycin was synthesized more than ten years ago and is often used without a doctor’s prescription, many pneumonia pathogens are susceptible to its bactericidal (in high doses) and bacteriostatic (in low doses) effects. The active substance even affects intracellular infectious agents.
The antibiotic is used only intravenously in the treatment of adults. For the treatment of pneumonia, it is prescribed at a dose of 500 mg once a day for 2 days or more. In case of severe disease, the solution is administered for five days, and then the achieved result is secured by taking tablets.
The antibiotic is not intended for treatment of hypersensitivity to macrolides, liver or kidney failure. And also during lactation. Azithromycin is used with caution during pregnancy and various arrhythmias.
Note!
The description of the drug Ceftriaxone on this page is a simplified author’s version of the apteka911 website, created on the basis of the instructions for use.
Before purchasing or using the drug, you should consult your doctor and read the manufacturer's original instructions (attached to each package of the drug). Information about the drug is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a guide to self-medication. Only a doctor can decide to prescribe the drug, as well as determine the dose and methods of its use.
The best of Ceftriaxone analogues
Treatment of pneumonia, especially of moderate and severe severity, is not complete without parenteral administration of Ceftriaxone. It affects not only the symptoms of the disease, but also the cause of its progression - representatives of pathogenic microflora that have entered the body.
Therefore, if for some reason it is impossible to use Ceftriaxone, the doctor urgently selects equivalent analogues. Usually, the pulmonologist prefers to replace it with a drug from the group of 2-4 generation cephalosporins. There are few differences between them and Ceftriaxone, and in terms of therapeutic activity they are not inferior to it.
Antibiotics Ceftriaxone: side effects
Undesirable reactions of the body to the drug include:
- fungal diseases of the mucous membranes (mycoses);
- bleeding disorders, anemia, reversible suppression of hematopoiesis;
- allergies (including anaphylaxis);
- episodes of convulsions, dizziness, headaches;
- symptoms of bronchospasm;
- inflammation of the pancreas, oral mucosa and tongue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis;
- increased activity of liver enzymes;
- rashes, swelling and itching of the skin;
- impaired renal function (decreased amount of urine produced, blood in the urine);
- fever, chills;
- local reactions to injection of the drug (phlebitis, pain).