To do or not to do, to take or not to take medicine, to take a test or not to take a test. We are always faced with a choice and are often afraid of making a mistake. Iron can be said that you can’t go wrong with iron.
The adult human body contains about 3–4.5 g of iron. More than half of the iron is represented by heme in the composition of hemoglobin, a third is stored in the depot in the form of ferritin and hemosiderin. Moreover, iron deficiency is the most common deficiency condition worldwide, silently leading to anemia.
The main causes of iron deficiency:
Reduced intake of iron into the body due to impaired absorption due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, fasting, refusal, or reduced consumption of foods containing iron.
Increased iron loss during chronic, repeated blood loss (uterine, gastric, intestinal, etc.), as well as during acute massive bleeding.
Increased consumption of iron by the body in children during periods of growth, in women during pregnancy and subsequent breastfeeding of the child.
Why is there a shortage?
The most common cause is blood loss, for example due to injury or bowel disease, or due to excessive menstrual bleeding.
“Iron deficiency underlies more than half of anemia,”
says Ph.D.
cardiologist and nutritionist, GMS Clinic Natalya Polenova. “The main causes of iron deficiency: unbalanced diet, malabsorption, cyclic blood loss in women of reproductive age, donation, pregnancy, lactation, rapid growth during puberty.”
The second reason is poor absorption of iron. This can occur with medications, chronic bowel disease, inflammation, or genetic disorders.
A hematologist at the Federal State Budgetary Institution “National Medical Research Center of Hematology” of the Ministry of Health of Russia clarifies that iron deficiency conditions occur in many diseases with malabsorption, ranging from serious cancer to helminthiasis and the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, which absorb iron.
What tests show iron deficiency?
- Be sure to look at a general blood test with a leukocyte formula, since iron deficiency ultimately leads to the development of anemia. Iron deficiency anemia is indicated by a decrease in hemoglobin levels, an indicator of MCV (erythrocyte hypochromia). Often, the examination begins when there are symptoms of anemia (pallor, weakness, dizziness, loss of strength, decreased performance and attention, brittle nails and hair, etc.).
- Decreased serum iron concentration
- Increasing the total iron-binding capacity of serum
- Decreased transferrin saturation coefficient with iron
- Decreased serum ferritin concentration
It is recommended to take tests in the morning, from 8 to 11 am, since the level of iron in the serum is higher in the morning. They should also be taken in the absence of inflammation, which helps lower transferrin levels and increase ferritin levels.
The iron content in the serum is checked 5-7 days after taking vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements containing iron, or short-term use of iron supplements.
Who should take iron and how?
No one without a doctor's approval. Vitamins and dietary supplements with extra iron can be dangerous. For example, in people with impaired iron metabolism, excess iron in the diet leads to the development of liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus and cardiomyopathies.
“Iron overload due to thoughtless use of drugs leads to very dangerous consequences. In practice, several times we encountered patients with iron overload. Their liver is more like a metal basin,” says the hematologist.
If you have iron deficiency anemia, a simple diet or dietary supplements will not be enough. Such serious conditions are treated with iron injections and medications.
If the doctor sees a slight iron deficiency in the tests, then it is best to regulate it by adding foods containing iron. In food it can be heme - easily digestible and non-heme - difficult to digest. Heme iron is found in meat, poultry, fish and seafood. It is easily digestible and does not depend on other nutritional factors.
“The main sources of dietary iron are red meat and organ meats, especially liver,”
says Natalya Polenova.
— They contain a lot of iron, and it is well absorbed.
Next on the list are fish and seafood, especially sardines, tuna, shrimp, mussels and clams. In addition to the fish itself, quite a lot of iron is contained in its caviar.” Non-heme iron is found mainly in plant foods. But in order for the body to absorb it, it needs the help of organic acids, primarily ascorbic acid.
Polenova clarifies that among plant foods, the most iron is found in beets, asparagus, cauliflower and white cabbage, and spinach. But for successful absorption you will need, for example, citrus juices. When compiling a diet, you need to take into account that 10–15% of iron is absorbed from food.
How is iron deficiency treated?
It is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of iron deficiency and adjust nutrition.
If these measures do not help, and iron loss is significant, your doctor may prescribe iron-based medications. Duration of treatment with iron preparations for the purpose of restoration and replenishment of iron reserves in the depot:
- for hidden iron deficiency 1-2 months,
- for mild anemia 3 months,
- with moderate anemia 4.5 months,
- for severe anemia 6 months.
Of course, first of all, iron supplements are used in the form of tablets, drops, capsules, syrups. If your doctor has prescribed you iron supplements, you need to be prepared for long-term and comfortable treatment. This will help by following simple rules.
The dosage of the drug is also determined by the presence of anemia (this is the full therapeutic dose) and the type of iron ion that is included in the drug.
Hidden iron deficiency - how to deal with it?
I feel bad, constant weakness. I took a blood test and the doctor said it was normal. Tell me what to do...
If you get tired quickly, often suffer from acute respiratory viral infections, if you are worried about hair loss, brittle nails, dry skin, if “everything hurts, nothing helps” - it’s time to rule out iron deficiency, says OKDC doctor-therapist Tatyana Abramova
There are more and more “iron deficient” people...
Today, iron deficiency is the most common pathology. According to some reports, more than 1.5 billion people on our planet have iron deficiency. Iron deficiency anemia itself is not a disease, but it can become a symptom of a serious pathology.
The biological role of iron in the body is great - it is involved in redox processes, tissue growth and aging, immunity mechanisms, hematopoiesis, oxygen supply to organs and tissues, and the functioning of a number of enzymes.
Lack of iron and subsequent tissue and hemic hypoxia lead to significant trophic changes in hair, thinning, increased hair loss and even early greying. Along with this, brittleness of the nails, their transverse striations, jagged edges of the nails, curvature of the nail plate, flattening or concavity of the nails up to spoon-shaped appear. In this case, urinary incontinence is often observed. A perversion of taste occurs in the form of an addiction to raw meat, dough, chalk, tooth powder, etc. Patients are attracted to the smells of mold, gasoline, kerosene or acetone.
Sometimes iron deficiency leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane of the tongue, angular stomatitis, glossitis, dental caries and muscle weakness. An increase in temperature to subfebrile levels can also be a manifestation of iron deficiency.
Everything hurts...
What could be the connection between iron deficiency anemia and back pain? Imagine not getting enough sleep for several nights in a row. The body then seems sluggish, disobedient, heavy, pain appears or intensifies in those places of the spine in which it was previously felt. People suffering from chronic iron deficiency anemia experience something similar. In addition to general weakness, malaise, brittle nails and hair loss, they may also experience persistent back pain. And some complain that “everything hurts.” To understand why this happens, remember that iron deficiency anemia is characterized by a low level of hemoglobin in the blood, which is a transporter for oxygen. A person with a low hemoglobin content can breathe the purest air in a pine forest, but oxygen in the required quantity will not enter the body’s cells, because there is not enough transport - hemoglobin. In turn, oxygen is an oxidizing agent, thanks to which metabolic processes occur in cells. Not enough - they accumulate under-oxidized metabolic products, essentially poison, poisoning the body and disrupting its functioning.
Hence the weakness and lethargy, as in case of poisoning, and increased muscle fatigue. And if we take into account that nervous tissue is most sensitive to hypoxia, then the strange at first glance complaint of patients that “everything hurts” also finds an explanation.
Patients go to a neurologist, gastroenterologist or cardiologist; they have disorders of the cardiovascular system, myocardial dystrophy; vegetative-vascular and vestibular disorders occur. People suffer from frequent colds and acute respiratory infections, problems with the digestive system and kidneys. They undergo treatment for a long time, follow the instructions of specialists, but find that the expected recovery and improvement in quality of life does not exist, or they are short-lived. And all this is only because they overlooked an important one - iron deficiency. In such cases, the therapist had to conduct all the necessary research and identify the true causes of the ailment.
And there can be a lot of reasons for iron deficiency, and they are very different:
- chronic blood loss of various locations: gastrointestinal (gastroesophageal reflux disease, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach, tumors of the stomach and colon, terminal ileitis, ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, bleeding hemorrhoids);
- menstrual blood loss (menorrhagia of various etiologies, fibroids, endometrosis);
- nasal (hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and other hemorrhagic diathesis);
- iron absorption disorders
- resection of the small intestine, stomach with exclusion of the duodenum;
- increased need for iron: pregnancy, lactation, intensive growth and puberty;
- impaired iron transport (hypoproteinemia of various origins);
- nutritional deficiency.
Hidden threat
The most unpleasant thing is that latent (hidden) iron deficiency is widespread among the population, when hemoglobin levels are still normal, but transport and organ reserves of iron are already depleted. This “disguised” deficit ranges from 19.5 to 30%. In addition, 50 to 86% of women in various populations have risk factors for anemia. Therefore, the Regional Consultative and Diagnostic Center has introduced the most modern methods for identifying hidden processes of changes in blood composition and early diagnosis of iron deficiency conditions.
Therapists from the OKDC will always help you to clarify the causes of the development of anemia and iron deficiency, select the right set of diagnostic laboratory tests, and understand the causes of the pathology.
share information
0
Social buttons for Joomla
What iron supplements are there?
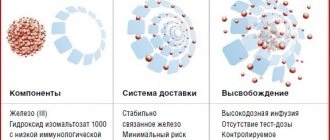
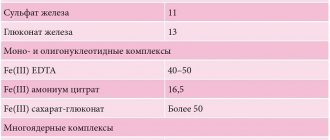
Iron in preparations can be represented by a di- or trivalent ion, designated Fe2+ or Fe3+, which is part of salts or complex complexes (for example, polymaltose complex hydroxide).
When using iron salts, you may encounter problems with its absorption. Unfortunately, not all iron from the drug is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, this process is poorly controlled, since it depends on the state of the gastrointestinal tract, food taken, and other medications. Therefore, both a lack of incoming iron and an overdose are possible. In addition, not all forms of medication are convenient to use; if some tablets are chewed, the enamel of the teeth is often stained and a metallic taste remains in the mouth for a long time. Trivalent iron preparations usually do not have these side effects.
How to increase the effectiveness of treatment
To reduce the likelihood of side effects, iron salts are taken before meals.
The absorption of iron is higher when taken simultaneously with ascorbic and succinic acids, fructose, and cysteine. This property is used in some combination drugs.
Iron absorption is reduced by certain substances from food or medications. Thus, it is reduced by tannin (strongly brewed tea), calcium salts (in milk or medications), magnesium and manganese (in mineral complexes or antacid preparations, such as phosphalugel), tetracycline antibiotics, phosphoric and phytic acids (cereal seeds, legumes). This effect is smoothed out when using preparations based on ferric iron.
Iron absorption is increased in severe iron deficiency. Therefore, you should be more careful about the prescribed dosage. Doctors often rely on a therapeutic dose of 200 mg of iron ion/day. If you understand that an iron supplement is not suitable for you due to the development of adverse reactions, difficulties in taking it, or lack of improvement in your well-being, tell your doctor about this. Under no circumstances should you change the dosage of the drug yourself. Exceeding the dose can lead to overdose and poisoning, reducing the dose can lead to useless use and lack of effect.
results
- The study included 440 patients. 97% of patients were women. The average age of the patients was 38 years.
- According to the analysis, the mean change in hemoglobin level after 2 weeks of therapy was 2 g/dL in the oral iron + vitamin C group and 1.84 g/dL during iron monotherapy (difference between groups 0.16 g/dL; 95% CI , −0.03-0.35 g/dl).
- The mean change in serum ferritin levels after 8 weeks of therapy was 35.75 ng/ml during iron + vitamin C therapy and 34.48 ng/ml during iron alone (difference between groups, 1.27 ng/ml; 95% CI, −0.70–3.24 ng/mL; P = 0.21).
- There were no significant differences between the groups in the frequency of side effects (20.9% in the combination therapy group and 20.5% in the iron monotherapy group).
- Not a single patient refused therapy due to the development of adverse events.
How is the effectiveness of treatment assessed?
During the first days of treatment with iron supplements, physical sensations are assessed.
When treating anemia, on the 5-8th day of treatment, a reticulocyte crisis is determined (an increase in the number of reticulocytes compared to the initial value, usually by 2-3% or 20-30‰).
After 4 weeks of treatment, the increase in hemoglobin is assessed. An increase in hemoglobin concentration by 10 g/l by the end of the first month of treatment with iron preparations indicates that the dose has been correctly selected and the effectiveness of therapy. After hemoglobin is restored, therapy is continued to saturate the iron depot, while the dose of the drug is reduced by 2 times.
For hidden iron deficiency, half doses of the drugs are used for 4-8 weeks. Depot saturation is determined using a comprehensive biochemical study (ferritin, transferrin, TLC).
At Lab4U you can take tests to identify iron deficiency and monitor the effectiveness of therapy with a discount of up to 50%.
Important to remember
- The causes of iron deficiency are blood loss, malabsorption, unbalanced diet, pregnancy, and helminthiasis.
- To identify a deficiency, you need to take a blood test for hemoglobin level, hematocrit, mean erythrocyte volume (MCV) and mean erythrocyte hemoglobin content (MCH).
- If there is no deficiency, then you should not take iron supplements. It may be dangerous.
- It is best to obtain iron from animal foods, in which it is in heme form.
- If you do not eat animal foods, you will need foods high in vitamin C to absorb plant non-heme iron.