Pharmacological properties of the drug Iron sulfate
Ferrous iron, which is part of the salt, compensates for the deficiency of this microelement in the body (in particular in iron deficiency anemia), stimulates erythropoiesis, and takes part in metabolic processes. Iron ions are components of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and many enzymes. Iron deficiency in the body occurs when there is a lack of this element in food, when absorption in the digestive tract is impaired (diarrhea, large-scale operations associated with resection of the stomach, intestines), with an increased need for iron (pregnancy, active growth), with blood loss (hypermenorrhea , hemorrhagic complications during surgical interventions). When carrying out a course of treatment of iron deficiency anemia, there is a gradual regression of clinical signs of anemia (general weakness, fatigue, dizziness, tachycardia, soreness and dry skin) and laboratory test indicators. 325 mg of iron sulfate corresponds to 0.105 g of elemental iron.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia and iron deficiency
27.05.2021
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia and iron deficiency
About modern ideas about the correction of iron deficiency and the main characteristics of iron-containing drugs, the principles of their selection and dosage in iron deficiency states. Diet for iron deficiency and sources of iron in food
The main source of iron for humans is animal products. In nature, iron exists in two chemical forms: 2-valent (heme) and 3-valent (non-heme). Heme iron is well absorbed in the intestine. The richest meats in heme iron are beef, especially beef and blood sausage. There is much less heme iron in poultry and fish. Liver (pork and veal), kidneys, heart, liver sausage are rich in ferritin and hemosiderin, containing non-heme iron (the latter is poorly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract). A lot of non-heme iron is found in some brands of red wine, fruit juices, apples, pomegranates, buckwheat, dairy products, eggs, nuts and chocolate. The bioavailability of such iron is minimal, and all these products are not a source of iron. Vegetarianism is a strong risk factor for iron deficiency anemia (IDA) at any age. At the same time, the diet should include greens, vegetables, and fruits, since iron absorption improves with the presence of vitamin C in food. Iron absorption is impaired by tannin (found in tea and coffee), phytin (found in rice, soy flour), milk and cottage cheese due to its high calcium content. Since the absorption of iron from food is limited, drug therapy for anemia is the mainstay.
The World Health Organization (WHO) conducted a global study between 1993 and 2005, which showed that 24.4% of all inhabitants of the globe suffer from various forms of anemia. Anemia most often occurs in preschool children (47% of the general population), pregnant women (41.8%) and non-pregnant women of childbearing age (30.2%). In the structure of anemia: 37% is iron deficiency anemia, 27% is anemia due to chronic diseases (CD).
Among women of fertile age, iron deficiency anemia (IDA) occupies a leading position. Anemic syndrome is the most common hematological syndrome encountered in clinical practice. Anemia is not a diagnosis, but only a syndrome that requires a special differential diagnostic algorithm.
WHO research indicates that IDA is the third most common cause of temporary disability in women aged 15–44 years. Along with IDA itself, there is a hidden iron deficiency, which in Europe and Russia is 30–40%, in some regions – 50–60%. According to WHO, iron deficiency is determined in 20–25% of all infants, 43% in children under 4 years of age and up to 50% in adolescents (girls). Thus, the most common anemias both in Belarus and in other countries are IDA and ACD. Anemia is a leading factor in the deterioration of a patient’s well-being; according to rough estimates, it affects 2.4 billion of the world’s population.
The main reasons for the development of iron deficiency anemia are: blood loss (heavy menstrual bleeding, pregnancy, childbirth, gastrointestinal, pulmonary, kidney disease); iron absorption disorders (resection of the stomach and intestines, pancreatic insufficiency, celiac enteropathy, Crohn's disease); increased need for iron (rapid growth, premature babies, newborns, adolescents, pregnancy and lactation); insufficient dietary intake (vegetarian or vegan diet).
It must be remembered that IDA is the final stage of severe iron deficiency, in which erythropoiesis (hematopoiesis) decreases and, as a result, the hemoglobin content decreases.
There are three stages of iron deficiency:
- prelatent;
- latent;
- manifest.
Prelatent iron deficiency is characterized by a decrease in microelement reserves without a decrease in iron consumption for erythropoiesis. Latent iron deficiency is observed when the microelement reserves in the depot are completely depleted, but there are no signs of the development of anemia. Manifest iron deficiency, or iron deficiency anemia (IDA), occurs when the hemoglobin pool of iron decreases and has characteristic symptoms. A decrease in serum ferritin concentration below 12 μg/L in healthy children and 15 μg/L in adults, adjusted below 30 μg/L in children and 70 μg/L in adults with infectious or inflammatory diseases, means an inevitable decrease in hemoglobin concentration in the future.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia. The principles of treatment of IDA include the following:
- the effect cannot be achieved with diet alone;
- Iron supplements are prescribed mainly orally, before meals;
- An improvement in the general blood test does not mean that the body’s iron supply has been restored;
- After normalization of hemoglobin levels, iron intake should be continued for another 1–2 months. with a reduction in the daily dose by half to fill the depot.
The basis of pathogenetic therapy for IDA is the use of iron supplements orally. Treatment with iron supplements should be long-term and depend on the initial severity of anemia (hemoglobin level and iron deficiency).
At the outpatient stage, treatment is carried out when the hemoglobin level is >80 g/l and the patient’s general condition is satisfactory. Oral administration of iron-containing drugs at a dose of 200-300 mg/day for 4-6 weeks until hemoglobin levels normalize, after which the drug continues at a dose of 100 mg/day for 2-3 months until the ferritin level is at least 40 μg/l. It is necessary to find the cause of iron deficiency and eliminate the cause of iron deficiency - this is treatment of the underlying disease that caused iron deficiency.
Principles for choosing an iron supplement for therapy
Currently, oral iron preparations are divided into two main groups: ionic and nonionic (the latter are represented by the protein and hydroxypolymaltose complex of ferrous iron).
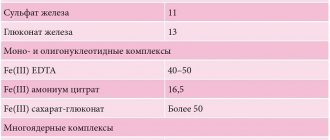
Ionic preparations are represented by salts of 2-valent iron, including iron sulfate (ferrofol, tardiferon, ferroplex, sorbifer, ferro-foil, etc.); ferric chloride (hemofer); polysaccharide compounds - gluconate-fumarate combinations (heferol, ferronal, megaferrin). Ferrous chelates (citrate, lactate, gluconate, succinate) are better absorbed than ferrous sulfate. In case of intolerance to salt preparations of ferrous iron, which are currently the most effective in treating anemia and replenishing iron depots, it is possible to use nonionic preparations of ferrous iron in the form of a hydroxypolymaltose complex (maltofer, biofer, ferrum lek, etc.).
When choosing a drug and the optimal dosage regimen, it is necessary to remember that an adequate increase in hemoglobin levels in IDA can be ensured by the intake of 30 to 100 mg of ferrous iron into the body. Considering that with the development of IDA, iron absorption increases by 25–30% (with normal iron reserves in the body - only 3–7%), 100 to 300 mg of ferrous iron per day is prescribed. The use of higher doses does not make sense, since iron absorption does not increase. The degree of absorption of 2-valent iron salts is several times higher than that of 3-valent iron, therefore preparations containing 2-valent iron give a quick effect and normalize hemoglobin levels on average after 1–2 months, and normalization of iron levels in the depot occurs after 3 –4 months from the start of treatment and depends on the severity of anemia and the dose of the drug. Longer use of drugs containing iron in the 3-valent state is required; in case of copper deficiency in the body, they will be ineffective. Normalization of hemoglobin levels during treatment with a ferric iron preparation will occur only after 2–4 months, and replenishment of iron deficiency in the depot will occur after 5–7 months from the start of therapy. The degree of absorption is also reflected in the incidence of side effects. The undesirable effect of solid forms of iron preparations (tablets, capsules) on the gastrointestinal mucosa can be reduced by taking them with meals, but this reduces the absorption of iron.
When taking the drugs in a sufficient dose, an increase in the number of reticulocytes is observed on the 7-10th day from the start of treatment. Normalization of hemoglobin levels is observed after 3–4 weeks from the start of treatment, and in some cases it lasts up to 6–8 weeks. The total duration of treatment depends on the initial severity of anemia. Standard terms for ferrotherapy of IDA: for mild severity - 4-6 weeks, for moderate severity - 8-12 weeks, for severe severity - 16 weeks or more. When using ferrotherapy drugs internally, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, constipation most often occur (since iron binds hydrogen sulfide, which is a physiological stimulant of motility), less often - diarrhea, a metallic taste in the mouth, staining of the mucous membranes and teeth black, allergic reactions , headache. These side effects lead to frequent refusal of treatment by patients.
The bioavailability of divalent iron salts is several times higher than that of trivalent iron salts, since they diffuse freely through the channels of DMT1 proteins and ferroportin. The pharmacological effect of the drugs is rapid, and normalization of hemoglobin levels occurs on average after 2 weeks - 2 months, and replenishment of iron stores occurs within 3-4 months from the start of treatment, depending on the severity of anemia and the dosage of the drug. Therefore, WHO recommends ferrous iron preparations as initial therapy for iron deficiency anemia. The absorption of ions from ferric iron preparations is slower, since active (energy-dependent) transformation with the participation of ferrooxidases is required. Therefore, such drugs require longer use, and in case of copper deficiency in the body they will not be effective at all.
The medicinal product Ferrofol produced by Minskintercaps Unitary Enterprise
contains in one capsule 50 mg of iron (II) sulfate and 500 mcg of folic acid.
Using Ferrofol in an average daily dosage of 1 capsule 2-3 times a day 1 hour before meals (100-150 mg per day), the goal of treating iron deficiency anemia is achieved - the introduction of iron in the amount necessary to normalize hemoglobin levels, complies with WHO recommendations on optimal therapeutic dose. The drug Ferrofol meets the basic requirements for treatment with iron supplements:
- sufficient elemental iron content in the preparation;
- the use of ferrous sulfate, which provides the greatest bioavailability;
- administration of folic acid, which plays an important role in hematopoiesis, with an iron supplement; the lack of these vitamins causes a disruption of DNA synthesis in hematopoietic cells, which negatively affects the rate of hemoglobin synthesis.
Advantages of the drug Ferrofol:
is produced in the form of long-acting capsules, the active ingredients are contained in pellets (microgranules), which ensure their absorption in the upper part of the small intestine, and therefore there is no local irritant effect on the gastric mucosa, which ensures good gastrointestinal tolerability. The use of pellets in Ferrofol capsules allows you to isolate the active substances from each other - folic acid and iron in one finished form. Folic acid increases DNA synthesis in hematopoietic cells, which has a positive effect on the rate of hemoglobin synthesis, which means faster relief of anemia.
The drug Ferrofol is indicated for the prevention of latent iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia, especially during pregnancy.
Prevention of iron deficiency anemia and latent iron deficiency is indicated for patients at risk, which include:
- pregnant women and during lactation;
- women with an interval between pregnancies of less than 2 years;
- ongoing or recurrent bleeding of a person with hereditary hemorrhagic hemostasiopathies;
- persons with chronic kidney disease with established iron deficiency;
- persons with blood ferritin levels less than 30 mcg/l (tissue iron deficiency);
- women with menstruation lasting more than 5 days.
Ferrofol is a combination drug that replenishes the deficiency of iron and folic acid in the body.
Capsules should be swallowed whole with a glass of water. The capsule must not be dissolved, chewed or kept in the mouth.
Administration is carried out before or during meals, depending on gastrointestinal tolerance.
There are medical contraindications and adverse reactions.
BEFORE USING THE MEDICINE, READ THE INSTRUCTIONS
Properties
Anhydrous sulfate consists of colorless crystals, is odorless, and has a distinctly astringent, “iron” taste. Actively absorbs moisture from the air, dissolves well in water, and does not dissolve in alcohol. Forms crystalline hydrates with 1, 4 and 7 water molecules. 7-hydrate crystalline hydrate is called ferrous sulfate or ferrous sulfate. Reagents with 4 and 7 water molecules consist of greenish, sometimes blue-tinged crystals; hydrate with 1 water molecule is colorless. All crystalline hydrates gradually lose water when stored in air. Anhydrous sulfate and its crystalline hydrates do not burn or explode; low toxic.
The reagent is oxidized by oxygen to iron (III) sulfate. When heated, it decomposes into iron (III) oxide and oxides of tetravalent and hexavalent sulfur.
| Iron (II) sulfate 7-water. tech. GOST 6981-94 | Iron (II) sulfate 7-water. "why" |
Being in nature
The mineralogical form of iron (III) sulfate is mikasaite, a mixed iron-aluminum sulfate. Its chemical formula is (Fe3+, Al3+)2(SO4)3. This mineral contains the anhydrous form of ferrous sulfate and is therefore very rare in nature. Hydrated forms are more common, for example:
- Coquimbite - Fe2(SO4)3 9H2O - nonahydrate - the most common form in nature.
Crystal structure of cokimbite
- Paracoquimbite is another nonahydrate, a rare form.
- Cornelite (English kornelite) - heptahydrate - and quenstedtite (English quenstedtite) - decahydrate - are also rare.
- Lausenite is a hexa- or pentahydrate (the independence of this mineral is questionable).
All of the above natural iron hydrates on the Earth's surface are unstable. But their reserves are constantly replenished due to the oxidation of other minerals (mainly pyrite and marcasite).
Mars
Ferrous sulfate and jarosite were discovered by two Mars rovers: Spirit and Opportunity. These substances are a sign of strong oxidizing conditions on the surface of Mars. In May 2009, Spirit got stuck while driving on the planet's soft soil and hit iron sulfate deposits hidden under a layer of normal soil. Because iron sulfate has a very low density, the rover got stuck so deep that part of its body touched the surface of the planet.
Ferric iron preparations
Benefits of ferric iron supplements
- Low toxicity. They cannot be overdosed.
- Better tolerated.
- They can be taken before, during, and after meals, without fear of inflammation or ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
- Fewer drug interactions.
- Fewer food interactions.
Disadvantages of ferric iron preparations
They act more slowly, so the treatment time increases.
If you need to quickly increase your iron level (surgery is coming up, severe anemia, etc.), at the beginning of treatment the doctor will most likely prescribe a ferrous iron supplement. In the future, he can transfer the patient to a ferric iron preparation if he does not tolerate divalent iron.
Let's look at the features of some popular drugs in this group.
Maltofer
Release forms for oral administration: drops, syrup, chewable tablets.
Main feature: iron hydroxide is combined with carbohydrates. This complex is called: “Iron hydroxide polymaltosate.” In articles and instructions it is referred to by the abbreviation HPC (hydroxide-polymaltose complex).
Its structure is similar to that of the natural iron compound ferritin. Thanks to this, it can connect with the transport protein, which delivers iron from the intestines to the blood.
GPC is stable. “pure” iron is not released into the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore there are significantly fewer adverse reactions when using it.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women can. Maltofer Fol will be optimal , which contains folic acid necessary for normal growth and development of the fetus.
Children: Maltofer drops, syrup - from birth, tablets - from 12 years.
Adverse reactions: nausea, constipation, diarrhea, dark stool, rash, itching, discoloration of tooth enamel.
Drug interactions - no.
There are no food interactions.
How to take: for the treatment of IDA, adults take 40-120 drops or 10-30 ml of syrup or 1-3 tablets per day. (100-300 mg pure iron) during or after meals. Chewable tablets can be swallowed as usual.
Maltofer in the form of drops or syrup can be mixed with fruit juice, vegetable puree, and milk mixture.
Totema
Release form: solution for oral administration. 1 ampoule - 50 mg of pure iron.
Why is the liquid form better?
The fact that the solution is more evenly distributed throughout the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, and the likelihood of irritation is reduced.
Secondly, this form is good for those who do not know how to swallow tablets, or for bedridden patients.
Another advantage of the drug Totema: it contains a safer iron salt - gluconate. The risk of side effects is less.
Fourthly, Totema contains copper and manganese, which improve iron absorption.
Children – from 3 months.
Pregnant women can.
Caution for patients with diabetes mellitus, because For taste, a lot of all sorts of chemical rubbish has been added to it. This is why I don't like liquid forms. In addition to the active and auxiliary substances necessary for stability, they contain all sorts of flavorings, dyes, sweeteners, etc., so the likelihood of allergic reactions is higher.
How to take: the contents of the ampoule should be dissolved in plain or sweetened water and drunk before meals. To treat IDA, take 1-2 ampoules 2 times a day. This is 100-200 mg of iron per day.
Ferrum Lek
Ferrum Lek used to be almost the only iron preparation for parenteral administration. There were no oral forms of it.
And now they are: syrup and chewable tablets.
Ferrum Lek is an analogue of the drug Maltofer in the form of syrup and chewable tablets. So, if something happens, they can replace Maltofer.
How to take: for adults to treat IDA, 10-30 ml of syrup (100-300 mg of iron) or 1-3 tablets per day during or after meals. After hemoglobin returns to normal, continue taking the drug 1 tablet until ferritin (iron reserves) normalizes.
Application
• In factories for the production of ferrites (ferri-gypsum, ferron), building boards, cement. • In the chemical industry - raw materials for the production of iron derivatives. • To obtain dyes, inks for pens. • In the textile industry - for dyeing fabrics. • In pharmacology to obtain iron-containing drugs against anemia. For example, it is used in the production of Ferroplex, Ferlatum, Hemofer, Tardiferon, Sorbifer Durules, etc. • In agriculture - a fungicide against fungal diseases, mosses; for spraying trees and shrubs, treating seeds against diseases and pests; means for treating the walls of vegetable stores; fertilizer for lawns, flowers, garden and vegetable crops, vineyards; soil pH regulator. • Ferrous sulfate monohydrate is used to produce animal feed additives. • Reagent in a chemical dosimeter for ionizing radiation. • In the food industry - a food additive for fortifying food products with iron. • For antibacterial impregnation of wood; to give maple boards a silver tint. • For the preparation of electrolytes for galvanizing. • Coagulant and reducing agent in water treatment. In demand for the removal of cyanide, phosphates and chromium salts from industrial and municipal wastewater; to prevent “blooming” of water bodies. • In laboratory analytics as a reagent. • In the energy industry - an anti-corrosion additive to the water circulating in the cooling tubes of turbine condensers. • To obtain high-purity gold from solutions.
Ferlatum
Release form: solution for oral administration. 1 bottle contains 40 mg of pure iron.
Features of the composition: this is also a complex, only iron is in a complex not with carbohydrates, as in the previous case, but with protein. This prevents damage to the gastric mucosa.
Iron from this complex enters the blood from the intestines only thanks to carrier proteins, so an overdose is impossible. This means that there will be significantly fewer side effects than with treatment with ferrous iron preparations.
Adverse reactions: rarely - diarrhea, constipation, nausea, epigastric pain.
Drug interactions
- Reduces the absorption of tetracyclines.
- The absorption of iron increases if the drug is taken simultaneously with 200 mg of ascorbic acid. Keep it up! They ask Ferlatum, and you ask the buyer: “Did your doctor recommend you take ascorbic acid with it?” To be more convincing, you can show the instructions.
- Antacids reduce iron absorption.
Children, pregnant and lactating women are allowed. But it is better for pregnant women to take Ferlatum Fol , which contains a folic acid compound in the dispenser cap.
You need to remove the white cap from the bottle, press the red dispenser cap with your finger, and the powder with folic acid will pour into the bottle, and now the drug is ready for use.
How to take: standard dosage: 1-2 bottles per day before or after meals. This is 40-80 mg of pure iron. In my opinion, not enough.
The manufacturer does not say anything about its dilution, which means it is usually taken: drink it and wash it down with water. Has a cherry taste.
Friends, I draw your attention: I have indicated here the MEDICAL dosages of drugs. But they will be different if the drug is prescribed for latent iron deficiency or for prophylactic purposes.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
Although different types of anemia have different causes, their symptoms are very similar. Here are the frequent complaints of patients with low hemoglobin, that is, with iron deficiency anemia: fatigue, weakness, fatigue, dizziness, pallor, headache, feeling of cold, numbness of the limbs, shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air, increased heart rate, chest pain.
Most often, anemia manifests itself as pale skin, often with moderate yellowness, weakness and fatigue, and sometimes with decreased concentration. Shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat appear. You can also notice external signs of anemia: a person looks pale and lethargic, he exhibits some “oddities” in behavior: a desire arises to eat chalk, he begins to like unpleasant odors.
In older people, angina attacks may occur and become more frequent, and in young women, menstrual irregularities may occur. The usual explanations for this are: “tired”, “stress in the family and at work”, “lack of sleep”, “overworked”. Meanwhile, quite often these are signs of anemia.
How to take ferrous sulfate
Ferrous sulfate supplements usually come in tablet form to take by mouth. You can also take them as liquid drops.
The tablets are often red, green or white.
If you choose to take ferrous sulfate specifically, it is important to look for the words “ferrous sulfate” on the label rather than choosing an iron supplement.
This is because iron supplements can contain different types of iron.
Most supplements clearly indicate the type of iron on the front label.
Many multivitamins also contain iron. However, there is no guarantee that the iron they contain is ferrous sulfate unless it is stated on the label.
Recommended dosage
In some cases, the required amount of ferrous sulfate is difficult to determine. To determine the right dosage for you, always consult your doctor.
There are no official recommendations regarding the amount of ferrous sulfate you should take each day. The amount will vary depending on factors such as your age, gender, health status and the reason you are taking the supplement.
Many multivitamins that contain iron provide about 18 mg or 100% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) for iron. However, one ferrous sulfate tablet typically contains about 65 mg of iron, or 360% of the RDI ().
The general recommendation for treating iron deficiency or anemia is to take one to three 65 mg tablets per day.
However, the total amount you should take each day may vary.
Some preliminary research suggests that taking iron supplements every other day, rather than every day, may be as effective, if not more effective, than taking a daily supplement (, ).
Your doctor will be able to provide more specific and personalized advice on how much ferrous sulfate you should take and how often, depending on your blood iron levels and personal circumstances.
When to take
Certain foods and nutrients, such as calcium, zinc, or magnesium, can interfere with iron absorption and vice versa. Therefore, for best absorption, some people try taking ferrous sulfate supplements on an empty stomach (, ,).
However, taking ferrous sulfate supplements—or any other iron supplement—on an empty stomach can cause stomach pain and discomfort.
Thus, doctors usually recommend taking ferrous sulfate supplements with meals.
Try taking ferrous sulfate supplements with low-calcium meals and avoid high-phytate drinks such as coffee and tea (,).
On the other hand, vitamin C can increase the amount of iron absorbed from ferrous sulfate supplements. Taking ferrous sulfate with a vitamin C-rich juice or food may help your body absorb more iron (, ,).
Summary:
There are many different forms of ferrous sulfate supplements on the market. Most are oral tablets, although liquid drops are also available. Before deciding to take ferrous sulfate, be sure to consult with your doctor.
The use of iron sulfate in the furniture industry
Wood etching not only serves as protection, but also gives it a new aesthetic appearance. The resulting color of a wood product depends on the type of wood species. So when etching with ferrous sulfate:
- in a concentration of 0.5% to 2%, oak wood turns dark, almost black;
- in a concentration of 2% to 4%, beech wood becomes brown;
- at a concentration of 4%, birch wood acquires a yellow-brown color;
- in concentrations of 2% to 4%, pine wood acquires a gray-brown color.
How do iron supplements affect teeth?
Iron supplements can cause darkening of tooth enamel. This applies mainly to liquid forms (drops, syrup, oral solution) and chewable tablets.
Even if the instructions say that this drug does not stain tooth enamel, judging by the reviews of those who have taken iron supplements, sometimes it does.
Apparently, this is due to some characteristics of the microflora of the oral cavity or tooth enamel, because this does not happen to everyone.
Is it possible to avoid darkening of teeth while taking iron supplements?
Can. To do this, you need to follow several rules:
- Do not bite, dissolve, coated tablets, or keep them in your mouth.
- If a person has difficulty swallowing tablets or capsules and purchases chewable tablets, they should thoroughly rinse their mouth and brush their teeth after each dose.
- It is better to take drops, syrup, or oral solution through a straw and rinse your mouth after taking it.
- It is impossible to accomplish the previous point in small children, therefore you need to let the child drink the drug, preferably with a large amount of water, and then wrap a bandage around his finger, moisten it with clean boiled water and wipe his teeth.
Some of you asked:
“How do you solve the problem of teeth staining in chewable tablets?”
Please note that only complex iron preparations have the form of chewable tablets, because They are less likely than ordinary iron salts to cause staining of tooth enamel. Most likely, it is due to the different structure of the active substance, when iron is surrounded by either polysaccharides or protein.
Reviews for all iron preparations that we are talking about today, and almost all liquid forms or chewable tablets, in some cases cause staining of tooth enamel, with the exception of Ferlatum. If you heard that it also caused darkening of teeth in some of your customers, write about it in the comments.
You may also be asked:
“Do iron supplements destroy teeth?”
Judging by the reviews, children’s teeth sometimes get damaged from them, but I haven’t found any scientific evidence for this.
Perhaps it's all about the sweeteners that are included in the liquid forms, and not about the iron itself.
Precautionary measures
Ferrous sulfate is moderately toxic (hazard class 3 for humans), upon contact it causes irritation to the mucous membranes of the respiratory system and eyes, as well as skin. Its aerosols and dust are especially dangerous. Therefore, when working with the reagent, you should use protective equipment: overalls and shoes, gloves, safety glasses and respirators with a dust filter. The workroom should be equipped with a ventilation system, and areas of possible intense dust should be provided with additional local ventilation.
Sulfate and its crystal hydrates are stored in polyethylene or multilayer (5-6 layers) paper, hermetically sealed bags, in covered warehouses. In laboratories - in glass or plastic containers with hermetically sealed lids.
Usage
- As a reagent for hydrometallurgical processing of copper ores.
- As a coagulant in the treatment of wastewater, municipal and industrial wastewater.
- As a mordant for dyeing fabrics.
- When tanning leather.
- For pickling of stainless austenitic steels, gold and aluminum alloys.
- As a flotation regulator to reduce the buoyancy of ores.
- In medicine it is used as an astringent and hemostatic agent.
- In the chemical industry as an oxidizer and catalyst.