Insulin is a vital hormone that is produced in the pancreas. Chemically, it is a protein that regulates blood glucose levels. The insulin level varies widely. If the hormone is not produced enough, a person begins to develop type 2 diabetes, which can lead to serious complications.
What is insulin
Insulin is one of the most important hormones that is directly involved in metabolism:
- stimulates the exchange of glucose from the bloodstream into the body's cells;
- removes excess glucose from the liver;
- converts excess glucose into glycogen or fatty acids.
The main role of insulin is that it utilizes excess amounts of glucose into other compounds and stimulates the saturation of cells with this vital substance - the main source of energy.
The hormone also performs a number of additional functions:
- activation of amino acid biosynthesis;
- ensuring normal muscle function;
- regulation of enzyme metabolism;
- restoration of damaged tissues.
Why is insulin resistance dangerous?
Even in people without serious changes in metabolism, insulin resistance triggers the processes of early aging; it is also known today that it is precisely it that is associated with severe cardiovascular pathologies and their dangerous complications (stroke, heart attack, acute cerebrovascular accidents, diabetic neuropathy, etc.).
Insulin resistance is very common. In 10-15% of adults (without chronic diseases and diagnoses) it can be detected by chance, during any examinations. This means that thousands of people not only do not know about it, but are also at risk of dangerous diseases!
It may seem that insulin resistance is a very insidious and hidden enemy of health, but in fact this disguise is very arbitrary, because a deviation can be suspected in the presence of specific problems in appearance and well-being.
For example, all women, especially middle-aged women, are familiar with the problem of being overweight. There comes a time when extra pounds literally become fused with the body, it is almost impossible to lose them, no diets help. Moreover, it feels like the excess weight is concentrated in the abdominal area - which is why many women dream of losing weight specifically at the waist, pumping up their abs, without attaching importance to other parts of the body. Meanwhile, age
and
the accumulation of adipose tissue in the abdominal area
(the so-called abdominal obesity, of the central type) are two of the most important factors that trigger the development of insulin resistance and support its strengthening.
Women over 35 years of age may experience various hormonal abnormalities.
, which at this age do not yet lead to the development of diseases, but create a “storm” in the body. Fluctuations in the content of estrogen and testosterone (and long before the onset of menopause), a decrease in the concentration of thyroid hormones and an increased release of stress hormones - adrenaline, cortisol - all this primarily affects physical health. Problems that are related to each other are gradually accumulating: excess weight, increased cholesterol levels in the blood, high blood pressure. Insulin resistance can be either a consequence of these changes in the body or their faithful companion.
Bad habits, lack of physical activity, and a diet based on fast food contribute to the development of insulin resistance.
and generally
poor quality of food
. By the way, strict diets and other food restrictions can also be attributed to poor quality of nutrition: the body does not get better from them, and the constant “swing” of losing and gaining weight only increases the tendency to insulin resistance.
If you think about it, in the lives of each of us there are at least a couple of the listed harmful factors, so if some problem has been bothering you for a long time and seriously (can’t lose weight, constantly high blood pressure, headaches and weakness), you should consult a doctor and describe him a complete picture of his symptoms. It’s not uncommon to dot all the points
i is assisted by an endocrinologist and carrying out several tests (glucose, glucose tolerance test, glycated hemoglobin, insulin resistance index, etc.).
Where is insulin produced: normal content
The hormone is produced in the pancreas in the so-called beta cells of the islets of Langerhans (the tail part of the organ). The synthesis proceeds continuously, i.e. throughout 24 hours a day. Therefore, insulin is produced in much larger quantities than any other hormone. This particular production process intensifies after a person eats.
From the pancreas, the hormone enters the bloodstream and provides a chain of processes as a result of which cells receive glucose in an easily digestible form. The body is saturated with the necessary energy, the person feels full and does not overeat.
Chemically, insulin is a protein consisting of 51 amino acids combined into 2 chains:
- A-chain (21 amino acids);
- B-chain (30 amino acids).
They are connected to each other by a special disulfide bridge - a sequence of 2 sulfur atoms S.
The level of insulin in the blood varies widely:
- 3-20 µU/ml for children;
- 5-25 µU/ml for adults.
At the same time, pregnant women and women over 60 years of age may produce more insulin - up to 36 µU/ml. Fluctuations are due to the fact that the synthesis of the hormone occurs continuously and increases sharply directly during food intake, as well as digestive processes. Along with this, the concentration depends on the age, gender, condition, and lifestyle of a person.
Insulin index of certain foods
The insulin index is an innovation in the science of proper nutrition and a detailed table with its exact value for various foods is still in an “open” state, is incomplete and is constantly being updated with new data.
But for the most popular food products, all the necessary calculations have already been carried out and we have quite accurate information that can be used by diabetics and ordinary citizens who want to lose excess weight.
Insulin index of greens and vegetables
Potato insulin index
Insulin index of berries, fruits and fruits
Insulin index of dairy products
Insulin index of sweets and treats
Insulin index of cereals and grains
Insulin index of bread, pastries and confectionery products
Insulin index of other common foods
Knowing the insulin index of foods is not enough. For the best result, it is important to take into account the compatibility of products. A great option is to combine vegetables with proteins and fats (vegetable salad with olive oil and a piece of poultry). Starchy foods (porridge, beans, potatoes, white rice, beets) are good to eat with leafy vegetables and oils.
Avoid combining fast carbohydrates with starchy, protein foods (a sandwich or burger is one of the typical combinations). It is not the best option to mix protein foods (fish, meat, poultry) with starchy foods (that is, with traditional side dishes - white rice or mashed potatoes).
We recommend
“Buckwheat tea: beneficial properties, contraindications and reviews” Read more
Here are some more simple tips to consider when planning a diet for diabetics:
and people suffering from prediabetic conditions.
- For a very long time, the thesis has flourished in dietetics that such “healthy” foods with a low glycemic index, such as cottage cheese, are best consumed at night; this, in theory, should promote weight loss and active “nighttime” fat burning. But with the advent of new research on the insulin index, the outdated postulates of nutrition science must be adjusted.
It has now become clear that cottage cheese has a very high AI and is not suitable for consumption in the afternoon by people with diabetes and those with insulin resistance.
- Products with an insulin index above average go very poorly with fatty foods.
- When drinking alcohol with a “bad” AI, it is better to avoid high-fat snacks.
- The first half of the day is a great time to refuel with something tasty with a high insulin index. It is best to have dinner with fish, vegetables, seafood and other “goodies” with a low insulin and glycemic index, in order to eliminate the possibility of sharp evening insulin surges and protect the body from gaining excess weight.
Insulin synthesis disorders and type 2 diabetes
Sometimes the pancreas stops producing insulin in the required quantities. If this is observed regularly, the patient develops type 2 diabetes. This is a metabolic disorder that manifests itself with a number of symptoms:
- excessive feeling of thirst;
- frequent acts of urination;
- excessive feeling of hunger;
- vision problems (blurred);
- feeling of lack of strength;
- increased fatigue;
- numbness, tingling in the upper and lower extremities;
- long-lasting wounds.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a dangerous disease that leads to a number of complications, including death:
- strokes of various types;
- nephropathy;
- polyneuropathy;
- dementia;
- diabetic foot and others.
"Passing Through"
Humanity approached the invention of insulin from afar.
People paid attention to a strange and insidious disease, accompanied by increased urination and, as a result, constant dehydration and increased thirst, even before our era. The most varied and unusual explanations for this phenomenon have been given. In particular, in 201, the Greek doctor Aratheus of Cappadocia stated that there was “melting of muscle tissue and bone and excretion in the urine.” He also owns the name of the disease - “dia-byno”, that is, “passing through”. This meant, of course, liquid rapidly passing through the body.
Over time, a connection was established between this disease and high sugar levels in the body. But no one knew what kind of connection this was and what to do with it. We followed a simple path: a strict and absolutely no-carbohydrate diet.
The word “diabetes” sounded scary. The life of the sick person was usually limited to a maximum of seven to eight years. After which he died - from complications of diabetes. And from exhaustion, which was partly caused by this seemingly life-saving diet.
However, these years were, to put it mildly, not the best. Moscow merchant Nikolai Varentsov wrote about the Kiev merchant Lazar Brodsky: “Brodsky was a diabetic... he, who had amassed enormous wealth, wanted to enjoy life, and the percentage of sugar in his body put him on a strict regime. He had to restrain himself in everything: go annually to the boring Liman sanatorium, live there for a month or more, follow all the doctor’s orders, and finally the sugar seemed to disappear. But as soon as he came home to Kyiv, where, as he said, he had an excellent French cook... the sugar percentage appeared again, increasing monthly. And Brodsky, who had achieved all his possibilities, was forced to deprive himself of everything.”
Ironically, Lazar Izrailevich was one of the largest sugar producers in the Russian Empire, from which he made his capital.
At the same time, the newspapers were full of messages that were not at all uplifting.
Jan Steen, The Doctor's Visit. Image from diapedia.org
“The other day, the artist N. Butze died, who was persuaded by one of the representatives ... of the sect to stop the very successful treatment of the rudiments of sugar disease and limit herself to her prayers.”
“Recently, diabetes (diabetes) has become widespread in Moscow, mainly among the intelligentsia. Even many doctors are getting sick. The disease is very difficult to treat conventionally and sometimes ends with a sad outcome before the age of 30.”
This surge in diseases was associated with the revolutionary events of 1905 and the corresponding stress.
In 1906, Chaliapin was diagnosed with the disease. Subsequently, it was diabetes that became one of the reasons for Fyodor Ivanovich’s non-return to the USSR - he allegedly needed treatment abroad.
The hero of Gorky’s novel “The Life of Klim Samgin” shares his medical knowledge: “Cognac is useful for diabetes, and blackcurrant for intestinal disorders.”
In 1915, the poet Alexander Tinyakov dedicated a terrible poem to his friend, critic Heinrich Tastaven, who died of diabetes at the age of 35:
Death is playing a fatal game with me, Crushing my throat with a merciless hand, And I know that in a month I will die: I will become wormy and stinking dirt.
Will there be heaven or hell? Will I be resurrected or not? All the same: equally stupid! I have diabetes, I have diabetes, - Hell and heaven are indifferent to a corpse!
Arkady Averchenko, on the contrary, allowed himself to mock the disease:
“Chugunov. I have diabetes.
Gendelman (changes a seat closer to Chugunov and, pushing his bowler hat to the back of his head, speaks enthusiastically). Look at him. He has diabetes, but he is silent! Do you have a lot of diabetes?
Chugunov. What do you mean - a lot? How much should it be!
And in the same 1915, the disease was suddenly completely defeated: “The Journal of Medical Sciences reports the discovery of a method of radical cure for sugar disease... The main medicine used in treatment is bicarbonate of soda with a small admixture of salt.”
Here, as they say, no comments.
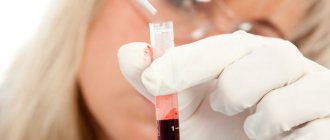
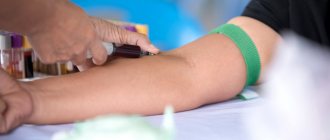
How to determine insulin levels
Insulin levels can be determined in a laboratory setting using a venous blood test. It is carried out for different purposes:
- detection of type 2 diabetes;
- identifying the need for artificial insulin intake;
- determining the causes of hypoglycemia (low blood glucose).
The analysis is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor. The main prerequisites are:
- sweating;
- blurred vision;
- cardiopalmus;
- frequent feeling of hunger;
- heart attacks;
- dizziness;
- to determine whether the insulinoma (pancreatic tumor) was successfully excised;
- for diagnosing relapses of insulinoma;
- to control the transplantation of Langerhans islet cells after the intervention.
Before conducting the study, certain preparation is required:
- do not eat food for at least 12 hours;
- do not take medications 24 hours in advance (check with your doctor);
- do not smoke at least 3 hours before the test.
Food for single-celled animals
For bacteria to multiply, they need a nutrient medium. It is produced in two tanks, they are called “kitchen” at the enterprise. The diet of unicellular organisms is balanced, and the quality of the future product depends on this. It takes no more than 12 hours to prepare.
“Our nutrient medium is plant-based. Was selected by our company. We developed it ourselves. These are mainly microelements and macroelements. And also plant extracts,” explains Sergei Salnikov, head of the insulin production workshop.
Almost all processes in the workshops are automated. People here only monitor instrument readings. Shift – several people. Most production facilities are behind glass. This ensures perfect cleanliness.
Single-celled organisms feed and reproduce in reactors with a volume of up to 2 tons. It is impossible to count the number of bacteria. There are several billion of them in just one milliliter of liquid.
What do the analysis results mean?
During the study, blood is drawn from a vein, after which the concentration of the hormone is determined using a chemical analysis. A value in the range from 2.6 to 24.9 µU/ml of blood is taken as normal.
If the norm is exceeded, the patient is sent for additional diagnostics to determine possible causes. The most common ones are:
- acromegaly;
- insulinoma;
- pancreas cancer;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- obesity of varying degrees;
- intolerance to simple carbohydrates (glucose, galactose, fructose).
Final stage
Then the powder is sent to a plant in Obolensk near Moscow. There it is dissolved and poured into containers. Insulin is filled into vials, cartridges, and syringe pens.
Then there is the mandatory quarantine stage. Samples are taken from each batch to ensure compliance with quality standards. Only after this the labels are applied. Here we must be confident in every ampoule, because people’s lives depend on the products.
Today the plant produces a third of all insulin in Russia. In a few years, production will be able to provide medicine to the entire country. The products of this enterprise are already being supplied to the CIS countries, and soon the first batches will be sent to Venezuela.
What to do if insulin is low
If the pancreas produces little insulin or does not synthesize it at all, urgent administration of the hormone artificially is required. To do this, they give injections or take tablets. The latter option is more convenient, since you do not need to give an injection, and it is also easier to take the package of tablets with you.
The dosage, frequency, and time of administration are determined by the doctor. Depending on the characteristics of administration, there are several types of insulin:
- fast acting - it starts working within 15-20 minutes after administration;
- short-acting – after 40-60 minutes;
- intermediate action – after 1-2 hours;
- long-acting - after 2-4 hours.
Filtration
The final push is cleaning. The liquid containing insulin is placed in a chromatograph. There they get rid of excess impurities and collect proteins together.
“The insulin is charged, and we take on another charge, and they attract each other. Everything that is not attracted goes away. We pour it out, well, relatively speaking, we dispose of it,” says Roman Dry, director of the research center.
The output is 99% insulin. Then it is crystallized, dried and turned into powder. Three tons of liquid turn into five kilograms of concentrate in 12 days. This is enough to provide injections to hundreds of thousands of people.