- General information
- Historical facts
- Effect on the body
- How to recognize a drug addict
- Tests for morphine
- How long does it stay in the body?
- In blood
- In urine
- In the hair
- How long do drug addicts live?
- Morphine analogues
- How addiction is formed
- How to speed up drug withdrawal at home
- Detoxification in hospital
- Overdose
- How to recognize
- What to do
- Rehabilitation
- Coding
- Why you can’t undergo rehabilitation at home or on an outpatient basis
- Working with codependents
- Treatment in hospital
- How to quit on your own
- Resocialization
Attention! Drug use causes irreparable harm to health and poses a danger to life!
General information
Morphine is an alkaloid that is extracted from a special type of sleeping pill poppy. Small amounts of morphine can also be obtained from other plants:
- Stephanie;
- moonseed;
- ocotea;
- croton
After purification of the milk of the sleeping poppy, raw opium is obtained, from which morphine is subsequently extracted. It is believed that for 100 grams of opium there are from 10 to 20 grams of morphine or morphine.
Morphine is still used in medical practice. It has a pronounced analgesic effect. Therefore, it is prescribed in the postoperative period or to alleviate the condition of patients with terminal stages of cancer.
You cannot buy a morphine-based drug at a pharmacy without a prescription. Distribution of morphine is a criminal offense. All morphine drugs in the hospital are subject to strict controls. Each ampoule is retained for reporting purposes after use.
Morphine addiction is less common than heroin addiction. But the principle of action of both drugs is identical, the only difference is the strength of the effect and toxicity.
The main mechanism for the effects of opium alkaloid is the effect on opiate receptors. The pain threshold decreases, the mind becomes clouded, drowsiness increases (that’s why the poppy from which opium and morphine is extracted is called sleepy), heartbeat and breathing are disrupted.
Historical facts
Morphine was first extracted from opium in the early 19th century, but it did not become popular until mid-century. He gained general fame after the appearance of injection needles.
The scientist who studied morphine conducted tests on dogs. After they ate a portion of the drug, the dogs fell into deep sleep.
In the second half of the 19th and early 20th centuries, morphine was freely available to doctors and soldiers. This all led to the development of morphinism (morphine addiction).
In America, during the Civil War, more than 400 thousand soldiers who regularly used the drug fell ill with morphinism.
The emergence of rapid addiction and mental disorders under the influence of dope forced countries to introduce measures in the form of restricting access to morphine, banning its use and prescribing it unnecessarily.
Morphine is rarely used as a narcotic drug. It is more difficult to find on the market, and the effect is not as strong as its analogues.
Morphine is the main alkaloid of opium; it is found in opium about 10%.
Morphine was named this way by mistake; in fact, it does not have the properties of morphine. In 1804, it was obtained from plant materials (it was the first pure plant alkaloid). After morphine was obtained, it was practically forgotten and was not used in medicine as a medicine, but in 1835 an injection needle was created, after which morphine began to be used in intravenous injections.
It was not until the middle of the last century that morphine was fully synthesized, during which it was concluded that it should not be put up for wide sale. Today, natural morphine costs much less than synthetic morphine.
Morphine is used in medicine to relieve pain, and not so long ago it was used to replace alcohol or opium in cases of addiction to these substances. Now they are being replaced by codeine.
What does morphine look like?
Morphine is obtained from the plant's milky white matter. When finished, it looks like white crystals in the shape of needles. If the drug is stored, it may change color slightly over time and become grayish or yellowish. Morphine crystals cannot be dissolved in alcohol and water; they do not combine with alkali.
How does morphine affect the body?
Effect on the body
Morphine destroys the nervous system. First of all, it inhibits all natural processes that occur in the central nervous system. Morphine has the strongest effect on the brain stem, depressing the respiratory and cardiovascular centers.
Impulses going to the center of the cough are blocked. This allowed the use of morphine and its analogues to reduce cough symptoms. The effect was considered especially beneficial for patients with whooping cough.
Morphine greatly inhibits the processes of excitation, this leads to a decrease in reaction, a drop in visual acuity (the pupils become very narrow after taking morphine). A person who takes this drug experiences a feeling of disorientation and impaired perception of time.
Morphine increases the tone of all sphincters in the gastrointestinal tract. Because of this, there is a disruption in the secretion of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum. Under such conditions, digestion cannot take place and the patient's glucose levels gradually drop.
Due to a drop in glucose levels, morphine addicts always have suppressed appetite, they are thin and emaciated. The drug is the only thing they want: neither food, nor sex, nor social significance bothers them.
Against the background of sphincter spasm, intestinal atony, and infrequent meals, constipation develops. This is a common problem among morphine addicts. In addition, the drug disrupts the secretion of antidiuretic hormone. This leads to anuria or oliguria in the first 2-5 hours after drug use.
Morphine has a selective analgesic effect that has not yet been studied in detail. The mechanism of blocking pain receptors is unclear, while other types of sensitivity are not impaired.
Morphine can lower body temperature. At small doses it is almost unnoticeable (up to 1-0.5 degrees). But with an overdose or high doses, the temperature can drop by 2-3 degrees, which increases the risk of hypothermia, disrupts metabolic processes, causes blood stagnation and exacerbation of chronic diseases.
When using morphine, the following complications always develop:
- decreased activity of the respiratory center, which leads to a decrease in oxidative processes and the accumulation of toxic products;
- disruption of the heart and a decrease in the amount of blood pumped in 1 minute;
- disorientation, drowsiness, disruption of excitation processes, inhibition of the functioning of all organs and systems;
- development of persistent physical dependence of human opiate receptors on the drug;
- destruction of the liver and kidneys;
- destruction and dystrophy of brain neurons.
Each of these points is dangerous. But most of all, morphine affects a person as an individual. It completely destroys his social role, disrupts his perception of life, and makes him a “slave to the dose” of the drug.
The effect of the drug when taken orally appears within 20-25 minutes. When administered intramuscularly after 10-15 minutes, when administered intravenously after 1 minute.
Taken from: Bulletin of KazNMU No. 3 (2) 2013. Author: Yu.S. Ismailova
To receive a dose, a person is ready to commit crimes and, thereby, he becomes dangerous. Because of this, drug addicts very often end up in prison, committing crimes under the influence of morphine.
It is very difficult to get rid of addiction on your own. Less than 15% of patients who use morphine are cured of opiate drug addiction without professional help.
How to recognize a drug addict
The main route of morphine use is parenteral (by injection). Morphine is administered intramuscularly and intravenously, and in the second case, injection marks can always be found on the drug addict’s body.
Often people try to hide the fact that they have an addiction. So they inject the drug into the veins in the legs or the groin.
One of the effects of morphine is itching. Morphin addicts constantly scratch their skin; scratch marks and sometimes even wounds are visible. This is due to the fact that the genesis of itching is not skin problems, but pathological impulses coming from the central nervous system.
Morphine addicts do not recognize social standards. They leave the family or constantly conflict with it. They stop going to work and constantly disappear somewhere. If an addicted person is a student, he begins to skip school for no apparent reason.
Such people spend a lot of money on drugs, lose weight, are constantly sleepy and lethargic. To obtain morphine, a person is capable of the most cynical deception. They often steal jewelry and household appliances from the house.
Opiate drugs completely disrupt behavioral instincts. A morphine addict has no interests or aspirations.
In order to know for sure whether a person is using opiates or not, tests need to be done. There are no other reliable ways to confirm or refute guesses.
Tests for morphine
In the body, morphine is gradually metabolized in the liver. Bioavailability of the drug is from 25 to 30%. 10-15 minutes after intravenous administration, the concentration of morphine drops sharply.
The simplest way to determine morphine in the blood is rapid testing using disposable plates. The advantage of these plates is that they can test for the presence of several drugs in the blood at once. In addition, they have high accuracy: up to 99.5%. They are fast and easy to use, and you can try them at home.
The disadvantage of such testing is that the tests are easy to fool. They do not show the amount of the substance and the time of last use.
The average price of the test is from 65 to 450 rubles. The test system can be purchased at a pharmacy or online. Most often, specialized institutions use the following test systems:
- tablets "ImmunoChrom";
- testing from ;
- test systems "Boson" and "Wondfo";
- Narcoscreen test strips.
Rapid tests are not included in the legislative framework. That is, any result of such a test will not have legal force. To document episodes of drug use, a biochemical test of urine, hair, or blood must be performed.
Laboratories use new methods of immunochromatography and enzyme immunoassays. Our body releases antibodies in response to morphine. With the help of immune reactions they can be found in the blood. This is evidence that the person used morphine at least 2 weeks ago.
Most often, urine is tested. It's simple and inexpensive. Hair testing is more expensive and is used only in judicial practice.
A blood test may not always be informative, since the content of morphine in the blood decreases very quickly and half a day after taking it it can already be detected there.
The advantage of all tests is that they cannot be fooled. When testing body fluids, the test always analyzes the actual data. The only weak point of testing is the human factor.
The accuracy of the test depends on what time after administration the reagents are taken. Therefore, you need to know which liquid can contain morphine metabolites for how long.
How long does morphine stay in the body?
In the body, morphine is immediately metabolized to simpler compounds. First, these compounds enter the blood, then into the urine. As metabolic processes progress, morphine metabolites accumulate in the hair.
Some metabolites can be found in saliva, but such an analysis is rarely used, since it is less informative than a urine or blood test.
Drugs remain in each biological fluid for a different time.
In blood
The average residence time of morphine metabolites in the blood is from 12 hours to several days. This “corridor” appears due to the individual characteristics of the body in the form of weight, liver and kidney functionality. The dosage of morphine and duration of use also influences.
In urine
Metabolites of the drug begin to be excreted in the urine after 10-15 hours. After this, drugs can be found in the blood for another 2-4 days after the last dose. If at this time a person drinks a lot of fluid and performs light physical activity, the drug is eliminated from the urine faster.
In the hair
Drug metabolism products can remain in hair for up to 1 year. This is good material for research, since the accumulation of morphine in the hair can determine how many months ago the last doses were taken.
There is evidence that the hair of dead people was sometimes examined in court cases because it continues to grow for some time after death.
How long do drug addicts live?
On average, morphine addicts live from 5 to 8 years from the moment they begin regular use, provided they actively use the drug. First of all, death occurs due to “wear and tear” of internal organs (liver, kidneys). The functioning of the central nervous system is disrupted. The nervous system is not able to adequately innervate organs, and this leads to premature atrophy and a complete decrease in organ function.
Another cause of death for morphine addicts is drug overdose.
Morphine addicts die of natural causes very rarely. The cause of death may be injury during drug intoxication.
Injecting drugs through a needle can transmit hepatitis C, hepatitis B, and HIV/AIDS to a person. Constant suppression of the immune system leads to the development of tuberculosis, which progresses rapidly and often causes exhaustion and death.
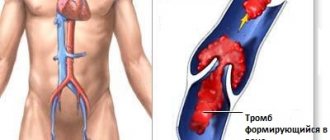
Due to injections, purulent complications appear at the injection sites. Due to the irritating effect of morphine, inflammation of the veins appears, against which thrombophlebitis and thrombosis develop, followed by the development of pulmonary embolism.
Opiates are toxic drugs. Affects the heart and liver. The average life of a drug addict is only 5-8 years. Addiction and physical dependence develop at lightning speed.
Taken from the scientific article: “Toxic depression of hematopoiesis in an opium addict.” Author A.V. Kosterina.
Get help now
Do any of your relatives or friends have an addiction? Have you tried in every possible way to help, but as a result the person still returned to his past life?
You are not the first to encounter this problem, and we can help you.
We guarantee anonymity, we will persuade you to undergo treatment, and we will help you choose a center.
Call us
8
or
Call me
Consequences
Complications develop during the first year of regular use of morphine, which progress as the experience increases. The most common side effects of opiates are:
- dementia - under the influence of the drug, memory, attention, thinking deteriorate, the person is no longer able to think;
- stroke, heart attack, thrombophlebitis, coronary heart disease, heart failure;
- renal and liver failure;
- psychoses, schizophrenia-like disorders;
- respiratory failure.
Morphine analogues
In medical practice, synthetic and semi-synthetic analogues of morphine are used. A group of such drugs is called narcotic analgesics or opiate analgesics.
List of popular drugs, morphine analogues:
- Promedol;
- Methadone;
- Traumadol;
- Nalbuphine;
- Buprenorphine;
- Butorphanol;
- Tepentadol;
- Omnopon;
- Thebaine;
- Remifentanil;
- Tapentadol;
- Piritramide.
An analogue of morphine that is sold to combat coughs is codeine. After taking any of the opiate analgesics, rapid tests may give a positive result.
All drugs belong to the list of group A. They are under strict control and are sold in pharmacies only with a doctor’s prescription.
On the black market, the composition closest to morphine is opium, which consists of 10% morphine. Analogues are heroin, khanka, shirk. Unlike purified morphine, other drugs have more pronounced toxicity and more pronounced effects on the body. But this does not negate the fact that morphine also depresses the central nervous system and can cause an overdose. It is important to understand that there is no safe drug. All of them are dangerous to the life of a particular individual and society as a whole.
Similar drugs:
- Katadolon Capsule
- Ibuprom Max Oral tablets
- Solpadeine Effervescent tablets
- Milgamma compositum Dragee
- Mesipol Solution for intramuscular administration
- Xefocam (Xefocam) Lyophilisate for the preparation of solution for injection
- Melbek Solution for injection
- Efferalgan Rectal suppositories
- Mesulide Oral tablets
- Amidopyrinum Oral tablets
** The Drug Directory is intended for informational purposes only. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions. Do not self-medicate; Before you start using Morphine, you should consult a doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal. Any information on the site does not replace medical advice and cannot serve as a guarantee of the positive effect of the drug.
Are you interested in the drug Morphine? Do you want to know more detailed information or do you need a doctor's examination? Or do you need an inspection? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Euro lab is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home . Euro lab clinic is open for you around the clock.
** Attention! The information presented in this medication guide is intended for medical professionals and should not be used as a basis for self-medication. The description of the drug Morphine is provided for informational purposes and is not intended for prescribing treatment without the participation of a doctor. Patients need to consult a specialist!
If you are interested in any other drugs and medications, their descriptions and instructions for use, information about the composition and form of release, indications for use and side effects, methods of use, prices and reviews of drugs, or you have any other questions and suggestions - write to us, we will definitely try to help you.
How addiction is formed
Opiate drugs cause the most persistent addiction, and from the very first doses. The basis for the formation of such persistent addiction is that the body gets used to the flow of exogenous opiates and stops producing its own. And they are needed to reduce pain and are produced in small quantities constantly, even at rest. If such mediators did not exist, then a person would constantly live with a feeling of pain.
The main stages of morphine addiction include:
- drug entry into the body;
- binding to opioid receptors;
- depletion of opioid receptors;
- the appearance of resistance of opiate receptors to opiates;
- the need to increase the amount of drug taken;
- the body’s inability to produce its own opiates and their analogues;
- the onset of physical dependence with mental disorders;
- the emergence of psychological stigma for morphine addicts;
- changes in behavioral instincts and constant search for a new dose of the drug.
Physical dependence is the depletion of substances that are able to bind to opiate receptors in the body. Therefore, a person needs a constant supply of these substances from the external environment.
Without the supply of morphine or its analogues, withdrawal begins to develop, which is very difficult to survive on your own.
The rate of addiction formation is directly related to the frequency of drug use and the single dose. Metabolic rate and individual characteristics of opiate receptors are less significant.
Withdrawal syndrome
Withdrawal is a syndrome with symptoms of varying severity that occur as the body cleanses itself of the drug. At the first stage of morphine addiction, vegetative-asthenic disorders occur, namely increased sweating, dry mouth, tachycardia, dizziness. Taking a new dose allows you to cope with these manifestations and return to active life.
At the second stage of drug addiction, vegetative-somatic and neurological disorders appear:
- facial redness;
- constriction of the pupils;
- tachycardia, decreased blood pressure;
- heaviness in the head, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- hand trembling;
- impaired coordination of movements.
During abstinence in the second stage of drug addiction, there is practically no possibility of self-control - the drug addict, in order to relieve symptoms, takes a new dose of the drug, which does not alleviate the condition to the desired extent.
At the third stage, physical disorders are joined by a severe clinical picture of mental disorders. A drug addict cannot exist without morphine, and its use does not bring relief, but only provokes the following manifestations:
- anxious mood;
- superficial sleep with nightmares;
- fear, anxiety, panic;
- irritability, aggressive attitude towards others;
- delirium, hallucinations.
How to speed up drug withdrawal at home
It is not possible to quickly remove morphine from the body at home. Moreover, this practice is life-threatening. Using opioid receptor antagonists without the correct dosage can only make the situation worse. Therefore, these drugs are contraindicated for independent use.
At home, to speed up the release of morphine, you can do the following:
- increase water consumption to 2.5 - 3 liters per day;
- perform dosed physical activity for 10-15 minutes at intervals of 30 minutes;
- do breathing exercises 10-15 times every hour.
You should not abuse water. If you drink more than three liters, the risk of reducing the level of potassium in the blood plasma increases, and this is dangerous for the cardiovascular system.
Dosed exercise should be performed only under the control of pulse and blood pressure. If the pulse is more than 140 or less than 55, you should stop exercising. During exercise, metabolic processes in the liver accelerate, diuresis and minute volume of the lungs increase. All this accelerates the elimination of the drug and its metabolites.
For detoxification purposes, people can drink sorbents, but this is ineffective (except when drugs enter the gastrointestinal tract). Sorbents have nothing to bind, since the drug circulates in the blood, enters the liver and kidneys, and sorbents are active only in the stomach and intestines.
To improve liver function, you can drink special herbal infusions or do tubage. Tubage is a technique used to relieve spasm from the bile ducts. Its essence is to drink warm water with honey or 1 raw egg yolk in the morning on an empty stomach. Afterwards you need to turn on your left side and put a heating pad on your liver. You need to stay in this position for 10-20 minutes. Due to heat and honey or yolk, the functioning of the biliary tract is normalized.
Other methods and pharmacological therapy at home aggravate the situation. Always seek professional help to avoid harming yourself or your loved ones.
Physicochemical characteristics
Morphine belongs to the group of morphinan alkaloids, to the group of isoquinoline alkaloids. Chemical formula: C 17 H 19 NO 3
IUPAC nomenclature 7,8-didehydro-4, 5-epoxy-17-methylmorphinan-3, 6-diol
57-27-2
The morphine molecule has 5 asymmetric carbon atoms. Therefore, morphine has many isomers, including α, β and γ isomers. The physical properties of the isomers differ somewhat, especially the optical rotation indicators.
Molecular weight: 285.4 amu
Solubility:
- water (20 ° C) – 1: 5000
- water (100 ° C) – 1: 500
- diethyl ether - 1: 7630
- diethyl ether, saturated with water - 1: 10600
- benzene - 1: 1,600
- chloroform - 1: 1,500
- ethanol (20 ° C) – 1: 250
- ethanol (100°C) – 1:13
Morphine derivatives that are widely used
- CAS registration number 6009-81-0 - morphine monohydrate
- CAS 52-26-6 - morphine hydrochloride (anhydrous morphine HCl), its aqueous solutions are used under the name "morphine"
- CAS 6055-06-7 - morphine hydrochloride trihydrate
- CAS 64-31-3 - morphine sulfate (anhydrous morphine SO4)
- CAS 6211-15-0 - morphine SO4 hydrate
- CAS 302-31-8 - morphine tartrate (anhydrous morphine tartrate)
- CAS 6032-59-3 - morphine tartrate trihydrate
- CAS 41372-20-7 - apomorphine
- CAS 76-58-4 - ethylmorphine, or dionin (ethylmorphine)
- CAS 76-57-3 - methylmorphine, or codeine (methylmorphine)
- CAS 561-27-3 - diacetylmorphine, or heroin (diacetylmorphine)
- Dilaudid
- Antorphine
Morphine oxidizes quite easily, forming the so-called ψ-morphine.
Properties of morphine monohydrate
Colorless prismatic crystals, bitter taste.
Chemical formula: C 17 H 21 NO 4 (according to the Hill system)
Molecular weight: 303.37 amu
Melting point 254°C
Density: 1.317 (20°C, g/cm3)
Solubility:
- benzene (20°C) – 1: 1600
- water (20 °C) - 1: 4000 (0.03 g / 100 g water)
- water (100 ° C) – 1: 500
- diethyl ether (20 ° C) - 1: 10000
- chloroform (20 ° C) – 1: 1500
- ethanol (20 ° C) – 1: 250
- ethanol (25 ° C) – 1: 160
Physical properties of morphine hydrochloride
- White needle-shaped crystals or white crystalline powder, slightly yellowing or graying during storage.
- Slowly soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol (1:50). Incompatible with alkalis. Solutions are sterilized at 100 ° C for 30 minutes, 0.1 N is added to stabilize. hydrochloric acid solution to pH 3.0-3.5.
- Optical rotation of the aqueous solution -97 ... -99 (2%).
Synthesis
The total synthesis of morphine was accomplished only in 1952 by Robert Woodward, but its length and complexity (17 steps were initially included) make it impractical for commercialization. Currently, several different synthesis methods have been proposed, but natural morphine is still cheaper than synthetic morphine.
Identification of morphine
Reactions with reagents for group precipitation of alkaloids.
Morphine gives a precipitate with reagents for the group precipitation of alkaloids (Bouchard's, Dragendorff's, Mayer's, Sonnenschein's reagents, etc.)
Color reactions. Morphine reacts with concentrated nitric acid (blood red turning to orange-yellow). With Erdmann's reagent (concentrated sulfuric acid with concentrated nitric acid) it gives a red-yellow color. With Fred's reagent (concentrated sulfuric acid with molybdic acid) it gives a purple color. With Mandelin's reagent (concentrated sulfuric acid with vanadic acid) it gives a purple color. With Marqui's reagent (concentrated sulfuric acid and formaldehyde) it gives a purple color.
Pellagra reaction. When morphine is heated with concentrated hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, it turns into apomorphine, which gives a positive pellagra reaction. Performing the pellagra reaction on morphine is somewhat different from the way it is performed on apomorphine. When performing the pellagra reaction on morphine and codeine, they are converted to apomorphine by heating with concentrated hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, and then the remaining reagents necessary for this reaction are added.
Executing the reaction. A few drops of chloroform extract are added to the test tube and evaporated to dryness. Add 1-2 drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid to the dry residue. After dissolving the dry residue in this acid, 1-2 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid are added to the test tube and the mixture is heated in a water bath until the hydrochloric acid evaporates completely. After this, the liquid is heated for another 15 minutes, then cooled and 2-3 ml of water are added. If a precipitate is formed, then it is dissolved in several milliliters of dilute hydrochloric acid. The resulting solution is neutralized with a 10% sodium carbonate solution and 2-3 drops of an alcohol solution of iodine are added. In this case, a green color appears. After adding 0.5-1.0 ml of diethyl ether and shaking, the aqueous layer remains green in color, and the ether layer becomes purple-red. Excess iodine interferes with this reaction because its color masks the color of the final reaction product. Other substances also react with pellagra (codeine, ethylmorphine, diacetyl morphine, apomorphine, etc.)
Reaction with iron (III) chloride. A few drops of chloroform extract are added to a porcelain cup, which is evaporated to dryness at room temperature. Add 1-2 drops of a freshly prepared 2% solution of iron (III) chloride to the dry residue. In the presence of morphine, a blue color appears.
Reaction with iodic acid (HIO 3). When shaking a solution of morphine, slightly acidified with sulfuric acid, with a solution of iodic acid or a solution of potassium iodate (KIO 3), which does not contain iodides, free iodine is released, which, when shaken with chloroform, passes into the chloroform layer, coloring it purple.
This reaction also produces some impurities that pass into the chloroform extract when morphine is isolated from biological material. Therefore, the reaction with HIO 3 can be used to detect morphine in drugs and mixtures of medicinal substances, as well as in well-purified extracts from biological material.
Reaction with potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) and iron(III) chloride. This reaction is based on the fact that potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) oxidizes morphine and turns into potassium hexacyanoferrate(II), which reacts with iron(III) chloride. This produces Prussian blue, which is blue. The reaction with potassium hexacyanoferrates (III) is performed as follows: a few drops of a mixture of solutions of potassium hexacyanoferrates (III) and iron chloride (III) are added to an aqueous solution of the test substance. In the presence of morphine, a blue color or a precipitate of the same color appears.
This reaction also produces some impurities that turn from biological material into alkaloid extracts. Therefore, the reaction with potassium hexacyanoferrates (III) is used to detect morphine in medicinal mixtures and in well-purified extracts from biological material.
Chromatography method. Apply 1-2 drops of chloroform extract to the starting line on the chromatographic plate. To the right, at a distance of 2-3 cm, a drop of the “witness” solution (0.01% solution of morphine in chloroform) is applied to the start line. The stains on the plate are dried in air. Then the plate is introduced into a chromatography chamber saturated with solvent vapors (ether - acetone - 25% ammonia in a ratio of 40: 20: 2). The chamber is tightly closed with a lid. After the solvent system rises 10 cm above the starting line, the plate is removed from the chamber, dried in air and sprayed with Dragendorff's reagent modified by Mounier.
In the presence of morphine, spots of this alkaloid on the chromatographic plate acquire a pinkish-brown color (Rf = 0.18 ± 0.01).
Detection of morphine by UV and IR spectra. A solution of morphine in ethyl alcohol has an absorption maximum at 287 nm. At 0.1 n. in sodium hydroxide solution, the absorption maxima of morphine are observed at wavelengths equal to 250 and 296 nm. At 0.1 n. In a solution of sulfuric acid, morphine has an absorption maximum at 284 nm. Aqueous solutions of morphine hydrochloride and sulfate have an absorption maximum at 285 nm.
In the IR region of the spectrum, the base of morphine (disc with potassium bromide) has main peaks at 805, 1243, 1448, and 945 cm When it is impossible to get heroin, the first thing heroin addicts look for is morphine.
Acute morphine toxicity
Lethal dose of morphine for some routes of administration
| Animal | Method of administration | LD 50 mg/kg |
| Rats | internally | 270 |
| intravenously | 46 | |
| Mice | internally | 670 |
| intra-suture | 200 | |
| Dogs | intravenously | 316 |
Actions for morphine poisoning
In case of morphine poisoning, opioid receptor antagonists are used, in particular nalorphine (agonist-antagonist) and naloxone (antagonist). Thanks to competition for receptors, nalorphine reduces the manifestations of all the effects of morphine - euphoria, nausea, dizziness, and restores normal breathing.
Detoxification in hospital
It is easier to do this in a hospital, since there you can carry out infusion therapy and monitor the level of microelements in the blood plasma. The main method of inpatient detoxification from morphine is a 5% glucose infusion. This allows you to speed up filtration in the kidneys and remove drug metabolites.
In the hospital, symptomatic therapy is often used in the event of withdrawal syndrome or disorders of the internal organs.
Even in a hospital, Naloxone or its analogues are not administered to speed up the release of morphine from the blood. Such drugs only relieve the main symptoms of an opiate overdose, but do not reduce the amount of drug in the body.
Treatment of morphine addiction
Therapy takes place strictly in a hospital. There is no outpatient treatment for opioid addiction. Shown:
- Detoxification.
- Coding.
- Psychotherapy.
- Rehabilitation.
Initial treatment takes approximately 2-4 weeks. Even before a year, a person works on himself under the supervision of narcologists.
CONSULTATION WITH A NARCOLOGIST free of charge
Leave your phone number and we will call you back in 1 minute
or click on the number to call
8
Overdose
Overdose occurs in 99% of opiate addicts. This is due to the development of receptor resistance to morphine.
How does this happen:
- the receptor does not cause the expected response due to prolonged use of morphine;
- the person injects morphine again, wanting to get the expected sensations;
- the drug has a toxic effect on the central nervous system and internal organs, but still does not give the expected results;
- additional administration of morphine provokes disruption of organ function and complete depression of the central nervous system.
Thus, a gradual increase in dose leads to toxic damage to organs and the central nervous system. By inhibiting the centers of breathing and heartbeat, a person falls into a comatose or soporous state.
One of the causes of death in case of overdose is asphyxia by vomit.
Under the influence of morphine, all sphincters spasm, leading to stagnation of food in the stomach. Against this background, vomiting appears - a reaction of the body that occurs due to exposure to toxic substances, even if they did not enter through the “mouth”. Even if a drug addict eats once a day, he may vomit with particles of undigested food. Vomit can enter the airways and block them.
How to recognize
An overdose of morphine is always accompanied by constricted pupils, a weakened heartbeat and a pulse that is difficult to palpate. The pulse wave frequency is 40-50 times per minute (sometimes less), the respiratory rate is below 10.
Consciousness may not be completely impaired, but the person does not make contact. He looks lost, does not understand what is happening around him.
After giving up morphine, a person is ready to solve his social problems. He can have healthy relationships with other people. If this does not happen, new reasons for failure will appear.
Taken from the dissertation: “Resocialization of drug addicts: socio-psychological aspects” by Kutyanova I. P.
What to do
If you see someone with symptoms similar to an overdose of morphine or other opiates, look around to see if you are at risk before calling emergency services. Only after this you can dial 112, 911 or 103.
A lying person needs to be turned on his side in any direction, this way you will ensure the prevention of asphyxia with vomit. If vomiting occurs, you need to wrap gauze, a handkerchief or other cloth around your finger and wipe the patient’s mouth with it.
If there is no breathing and the pulse in the carotid artery cannot be felt, proceed to emergency care. To do this, place the patient on a hard surface with his back down. With folded hands, press on the chest slightly above the solar plexus with an intensity of 100-120 times every 60 seconds.
According to the rules, after every 15 seconds (or 30 presses), it is necessary to inhale air into the patient using the mouth-to-mouth technique. Considering that people who use drugs often have tuberculosis, hepatitis or HIV, this should only be done through gauze or a cloth. In practice, if there is a high risk of infection, it is better not to do such manipulation. Ideally, artificial respiration is done using an Ambu bag, which is available in emergency first aid kits.
In severe cases, an antidote to morphine can be given, the classic example being Naloxone. Please note that incorrect dosage calculation will worsen the situation.
Morphine affects the thermoregulation center, so in cold rooms or outdoors it is necessary to cover the patient to prevent him from freezing. In addition, enzymes in the body work worse in the cold, which slows down the inactivation of morphine in the liver.
Rehabilitation
Treatment of opioid addiction is one of the most difficult problems in modern addiction medicine. The essence of the problem is that such patients require constant care and monitoring. It is necessary to work with codependent people and restore the social role of the patient.
In addition, “withdrawal” always occurs, which not every patient can survive without breakdowns.
Rehabilitation from morphine should always be comprehensive. There are no single methods that cure; only a combination of techniques and the patient’s desire.
The complex of treatment for morphine addiction includes the following measures:
- detoxification of the patient using infusion;
- elimination of symptoms of organ dysfunction;
- managing the patient during withdrawal;
- work with a psychologist and psychiatrist;
- restoration of role in society;
- training and psychological preparation of codependent people.
Every person who begins treatment and his relatives must understand that it is impossible to recover from addiction. A person will periodically have desires to use the drug again. The task of specialists is to make sure that these desires appear extremely rarely and that it is easier to overcome them.
For independent rehabilitation, strong motivation and a developed volitional sphere are required; otherwise, “getting off the needle” will not work.
Coding
There is not a single case in evidence-based medicine where coding helps with drug addiction or any other addiction.
The body requires a new dose at the level of receptors and synapses. In such matters, psychology plays a secondary role. Therefore, coding is not efficient.
There are no described techniques or methods for coding drug addicts. Only long-term rehabilitation with psychological work to restore personality and self lead to long-term and stable remission.
Literature:
- Drugs: properties, action, pharmacokinetics, metabolism: textbook / N.V. Veselovskaya [etc.]. — 3rd ed., revised, corrected. and additional - Moscow: Narkonet, 2008. - 262 p.
- Opium addiction and combating drug trafficking: Social, legal, medical. aspects / Solodun Yu.V., Lavdarenko L.N., Soktoev Z.B. ; Prosecutor General of Russia. Federation [and others]. - Irkutsk: Irkut Publishing House. legal Institute, 2003 (PE Plyukhin R.A.). — 133 p.
- A manual on narcology for doctors and paramedics of primary medical care / A. A. Churkin, T. V. Klimenko. - Moscow ; Khanty-Mansiysk: Health and Society, 2006 (Cheboksary: IPK Chuvashia). — 173 p.
Why you can’t undergo rehabilitation at home or on an outpatient basis
Patients dependent on opiates require constant monitoring. First of all, because such a person can break down at any moment.
It is necessary to carry out psychological work with patients every day, to show that he is not alone, and there are people who are ready to help.
At home, there are many trigger factors due to which a person may look for an excuse for new use.
The main factor that does not allow quality treatment of such patients on an outpatient basis is withdrawal symptoms. It is very difficult to go through withdrawal. And in special institutions, at the moment of withdrawal, the patient is put into an artificial coma and thereby helped to survive a difficult period. After this, going into remission becomes easier.
Throughout the treatment, you need to constantly take blood tests, check the functioning of your heart and kidneys. Without this, you may miss illnesses associated with morphine use.
Use of high doses
If a large dose of morphine is administered, severe drowsiness will occur. Therefore, the drug is prescribed to people who cannot sleep normally due to severe pain. High dosages also contribute to:
- inhibition of conditioned reflexes;
- blocking the cough and respiratory centers;
- the occurrence of bradycardia;
- severe constriction of the pupils;
- overexcitation of cranial nerves.
Taking high doses of the drug results in bronze spasm and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. There is a weakening of intestinal peristalsis, and in the stomach, peristalsis, on the contrary, increases. Thanks to this, the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract is quickly cleared (doctors use this effect if they need to conduct an examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract).
Working with codependents
People who live with a drug addict or are members of his family, having any physical or mental connection, are called codependent.
Such people can be the mainstay of recovery even for an opioid addict. But if the connection is too strong, any conflict leads to a new breakdown.
Working with such people is an important part of rehabilitation. They need to be taught how to help a patient go into remission, and taught the rules of communication and behavior with addicted people.
Codependent people at first must seek a compromise, provide physical and mental support. Such care should continue until the patient regains his social consciousness and until the drugs fade into the background.
Correct prioritization leads to more stable remission and improved relationships in the patient’s family.
Increasing dosages
If after a day there is no good therapeutic effect, the patient still feels pain, but there are no signs of overdose, it is allowed to increase the dosage by one and a half times. This step is repeated every day until the analgesic effect is achieved or the first signs of drug poisoning are achieved. An alternative option is to add additional injections to the basic treatment.
It is important to clarify with the patient how effective the intermediate dose was. Sometimes there is a need to re-evaluate pain because in some cases morphine may not work for a particular patient.
Another important point when prescribing this substance is that there is no maximum permissible dosage of morphine. The more pain a patient experiences, the higher the likely amount of drug they can tolerate.
The correct dosage is one that completely relieves the pain syndrome, while it does not provoke acute drug poisoning, and also does not cause any side effects.
In most CIS countries, the daily dose of morphine is estimated based on the amount of injection administration with a modified release tablet form. This is due to the fact that in many post-Soviet republics there are no normal release oral forms.
Treatment in hospital
Pharmacological support is always used in the hospital. Otherwise, it is impossible to make rehabilitation reliable and safe. In addition, psychological work must be carried out with each patient.
During the first period of up to 14 days, patients undergo cleansing of the body from morphine metabolites. They are prescribed an infusion, tests are carried out, and treatment for pain and dyspeptic syndromes is prescribed.
During withdrawal, the patient is placed in an artificial coma. At this time, it is fed with infusion therapy. All this allows you to survive withdrawal without pain or harm to the body.
Every day, patients can come to group classes or, if desired, to individual ones. Such trainings make it possible to restore the social significance of the patient. This way you can show his importance to people from the group, show that he is not the only one in the world, that everyone makes mistakes, but is ready to correct them.
According to scientific reports, the study of religion or rehabilitation methods with a religious bias are more likely to produce positive results.
The confessional (with a religious bias) approach has proven itself better than similar methods, but without a religious component.
Taken from the dissertation: “Resocialization of drug addicts: socio-psychological aspects” by Kutyanova I.P.
One of the ways to distract the patient from the desire to use “dope” is a constant change of activity. Therefore, occupational therapy is recommended for drug addicts. This is a reason to train your willpower, communicate with other people, and improve your physical health.
Due to opiates, patients become exhausted and lose weight. In specialized rehabilitation centers for drug addicts, they create a special high-calorie menu that helps to gain weight. The most delicious and healthy food always lifts the mood and morale of people who want to quit drugs.
How to quit on your own
Doing this is more difficult than it might seem. You need to quit immediately, and not postpone the event for any other time.
It is important to completely renounce connections with all people who take drugs (even if other drugs, not morphine). Replacing one substance with another will not restore mental health, nor will the risk of new opiate use decrease.
Then the person must be prepared to experience withdrawal. This is one of the most difficult tests that await a drug addict after quitting.
For long-term remission, you need to find a new area of activity that is not related to drugs. Constant distraction and communication with new people is the key to long-term abstinence.