Gastric acidity is a characteristic of the concentration of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. This acid is produced by special parietal cells from the glands of the stomach. The main functions of hydrochloric acid are the digestion of protein foods, antibacterial action, stimulation of the pancreas, activation of digestive enzymes. And most importantly, hydrochloric acid contributes to the normal processing of food and its further movement into the duodenum.
Low acidity, as well as high acidity, absolutely equally causes the body a feeling of discomfort in the stomach area and leads to serious chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Liquids with respect to their acidity are considered: neutral at pH = 7, acidic at pH < 7, alkaline at pH > 7.
The maximum theoretically possible acidity in the stomach is 0.86 pH.
The minimum theoretically possible acidity in the stomach is 8.3 pH. Normal acidity in the lumen of the body of the stomach on an empty stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH.
In addition, at different times of the day and in different parts of the stomach, acidity levels vary.
1.General information
Every adult has heard about such a functional indicator of the digestive system as acidity. And not only adults: a school chemistry course includes information about the pH value, acid-base balance, as well as litmus paper and phenolphthalein as indicators of acidity.
The pH value of the gastric environment should normally be significantly shifted to the acidic side: if approximately seven is considered a neutral value, then the pH of gastric juice is 1.5-2.5. This is one of the evolutionary protective measures that, to some extent, prevents the introduction and reproduction of numerous infectious pathogens that enter the body in large quantities with food. In addition, a strongly acidic environment is provided as a normative condition for food processing in such a complex biochemical synthesizer as our digestive (digestive) system.
However, acid has an aggressive and destructive effect not only on pathogenic microorganisms and food products; it can also corrode its own mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the stomach. Therefore, it is necessary, firstly, precise control and constant “adjustment” of the acidity level, and secondly, physicochemical protection of one’s own tissues. The regulatory function is ensured by the fact that the stomach produces, along with hydrochloric acid, special mucus with an alkaline pH reaction, which, as necessary, neutralizes excess acid and acts as a surface protector for the gastric walls.
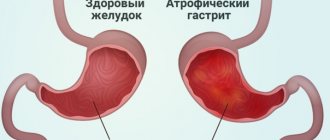
Any deviations from the natural pH level for the stomach, if they are persistent or chronic, are dangerous. So, low acidity, i.e. рh>5, leads to the development of antacid gastritis and is considered a precancerous condition. Increased acidity in recent decades has become a real scourge of modern man.
Excessive “acidification” of the gastric environment (acidosis, ph
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
How to treat gastritis with high acidity
Knowing the exact clinical picture of the patient’s stomach condition, the type, stage, form of gastritis, the treatment will be determined by the doctor based on these detailed data for each specific patient:
- Before starting treatment, the doctor must carefully examine the patient’s medical history, his general health, concomitant diseases, including the gastrointestinal tract, in order to clarify possible contraindications for taking certain medications.
- According to FGSD, the doctor determines the type, stage and form of gastritis, the acidity of gastric juice and finds out the causes of the disease.
- The effectiveness of treating gastritis with high acidity depends on the severity of the inflammatory process, its type and on the discipline and responsibility of the patient himself, since with any treatment, medication, folk remedies - without following a diet and eradicating bad habits, it is impossible to cure gastritis.
Today, when selecting therapy, gastroenterologists rely not on the acidity of the stomach, but on the condition of the mucous membrane according to FGDS. In case of acute gastritis, symptomatic therapy is first prescribed, since at the beginning it is necessary to reduce pain and reduce inflammation, and this is possible by reducing the production of hydrochloric acid, that is, with the help of drugs that neutralize acidity, and of course, following a diet.
2. Reasons
There are so many possible reasons for a persistent increase in acidity that they are usually divided into two large groups: endogenous and exogenous (internal and external, respectively).
The most common endogenous factors include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- chronic infections and/or presence of parasites;
- persistent hypoxia (lack of oxygen supply to tissues and organs);
- metabolic (metabolic) disorders;
- hypovitaminosis, deficiency of microelements, amino acids, etc.
Main exogenous factors:
- smoking and drinking alcohol, especially strong drinks;
- distortions in the daily diet (infatuation with spicy, fatty, spicy, over-salted, too hot and other dishes that irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract);
- long-term or amateur use of medications without prior consultation and supervision of a gastroenterologist;
- work in some hazardous industries, which involve, in particular, constant contact with nitrates;
- physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, haphazard eating with long breaks and a predominance of sandwiches, fast food, sour juices, coffee, carbonated drinks and similar “stomach killers.”
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Prevention
The main preventive measure for gastritis with high acidity is measures to normalize the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
- Refusal of hot, cold, spicy, fatty, heavy, fried foods.
- Avoiding overeating, fasting, dry food, “on the go.”
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- A balanced diet - a sufficient amount of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins.
- Compliance with the terms and conditions of food storage - most gastrointestinal diseases begin with the words “what will happen to them in the refrigerator.”
- Compliance with the meal schedule - dinner no later than 4 hours before bedtime.
- Compliance with food preparation technology.
- Take medications only under the supervision of a doctor.
- Control of your psycho-emotional state.
- Compliance with the requirements of personal hygiene and sanitation - washing hands before eating, visiting the toilet, regular wet cleaning of premises.
- Timely sanitation of the oral cavity, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of other body systems.
These rules are very important; they must be followed not only during the period of peak exacerbation of the disease, but also in everyday life. This will preserve the health of not only the stomach, but also all organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
A classic companion to high acidity is a specific baking, burning sensation in the esophagus, which we call heartburn. Heartburn can be so intense that the attack ends in vomiting. Most often, heartburn is caused by the so-called. reflux, i.e. reverse reflux of stomach contents up the esophagus, which should not happen under any circumstances with normal peristalsis, secretory activity and sphincter function: the walls of the esophagus do not have the same mucous-alkaline protection against acid that the stomach is equipped with.
In addition to heartburn, almost all patients complain of heaviness, abdominal pain of various types (dull, aching, pulling, “twisting”) and with various irradiations. Painful discomfort is usually associated with eating: when the stomach is full, the acid, so to speak, finds a new field of activity, but after 1-2 hours the pain returns.
It should be understood that a violation of the acid-base balance is a guarantee of complex, multifactorial digestive disorders (dyspepsia inevitably develops: constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, appetite disorders) and, therefore, metabolism. The walls of the stomach and the duodenum closest to it, from constant contact with an aggressive acidic environment, are covered first with superficial erosions, and then with ulcers that corrode the submucosal, deeper and therefore unprotected cell layers. A special “ulcerative type” of a patient suffering from gastroduodenitis or peptic ulcer disease itself is a thin, emaciated person with unhealthy skin and problem hair, a sallow complexion, dull and ever-tired eyes, a sarcastic, doomed mood (though many of them do not consider necessary to make at least some adjustments to your lifestyle). However, if the syndrome of high acidity and the associated erosive gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, peptic ulcer continue to remain, as they say in medicine, untreated, the situation can quickly become life-threatening: massive bleeding can begin at any moment or a perforation of the walls of the stomach or intestines can occur. , which leads to peritonitis, sepsis and other deadly complications.
The diagnostic standard in modern gastroenterology is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) - examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract from the inside. For this purpose, today we use not the ever-memorable “hoses” or “rubber tubes”, which served as a nightmare for many generations of patients, but high-tech, thin, flexible and very “smart” endoscopes, interfaced with a computer, equipped with a backlit video camera and the necessary manipulators (which allows “on the spot” to select material for biopsy, deliver the necessary treatment solutions, measure the pH level in various zones, etc.). The discomfort from such a procedure today is, perhaps, more of a psychological nature than physiological: the sensitivity of the pharynx and the gag reflex are suppressed by reliable irrigating anesthetics, and the procedure itself lasts only a few minutes - but the whole “picture” from the upper parts of the esophagus to the internal space of the duodenum is displayed in high resolution, stored on disk and provides invaluable information about the real state of affairs.
If necessary, radiography, tomographic and ultrasound examinations, and a set of laboratory tests are also prescribed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Gastritis type C
Reflux gastritis, chemical gastritis type C with high acidity is characterized by focal lesions of the fundamental part of the stomach with the contents of the duodenum. With small intestinal reflux (movement in the opposite direction), gastritis C develops after gastric resection.
This type of gastritis with high acidity can also be caused by drug, chemical or alcohol poisoning. It is also possible to have a course without pronounced symptoms, or the following signs are observed:
- feeling of heaviness and pain immediately after eating or during sleep;
- nausea, heartburn, vomiting.
4.Treatment
To a certain extent (and only with the agreement of a gastroenterologist!) acidity can be controlled by yourself by drinking, for example, bicarbonate mineral waters. However, self-medication, in particular, “quenching acid with soda” still practiced by the population, is in itself dangerous, since a violent acid-base reaction with the formation of salt and water occurs in vivo in a somewhat more complex manner and differs from school chemical experiments in vitro.
The therapeutic regimen, of course, is selected on a strictly individual basis, taking into account diagnostic examination data and a number of other factors. The main directions, as a rule, are the prescription of antacids (acid-neutralizing) and coating agents, antihistamines, proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, etc.); sometimes, strictly according to indications, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and/or antibiotic drugs are prescribed. You will need a special diet and the maximum possible elimination of all the factors of increased acidity described above (it is unnecessary to even discuss the need for immediate and complete abandonment of suicidal habits). At the first signs of a persistent increase in acidity, it is very important to contact a gastroenterologist for consultation, examination and treatment as quickly as possible, without waiting for the development of truly severe complications and without wasting time on all sorts of “proven old-fashioned methods”, which are sometimes more dangerous than the disease itself.
Drugs
Drug treatment slows down the spread of the inflammatory process and normalizes the activity of the glands. Doctors prescribe:
- Antacids. Reduce the acidity level of gastric juice: Rutacid, Phosphalugel, Almagel, Maalox.
- Antibacterial agents (according to indications): Metronidazole, Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin.
- Blockers of hydrochloric acid production: Lanzoprazole, Omeprazole, Ranitidine.
- In case of severe pain, injections of antispasmodics and medications that reduce gastric secretion are necessary.
- You cannot do without Smecta, which envelops the walls of the stomach. Enzymes are needed to improve the digestion process. They contain drugs: Mezim, Creon, Digestal.
The above list of tablets for gastritis and stomach ulcers can only be used after consulting a doctor. This is important to remember, since different forms of gastritis require an individual approach. Otherwise, you risk making things worse with the wrong treatment.