general characteristics
Treponema pallidum has several antigens that cause the production of antibodies. One of them is similar to cardiolipin, which makes it possible to use the latter to detect immunity to Treponema pallidum. RPR is a screening anticardiolipin test (non-treponemal) for detecting antibodies (reagins) of the IgG and IgM class to lipoid and lipoprotein-like material released from damaged cells of a patient with syphilis. Antibodies are detected in 70 - 80% of people with primary syphilis and in almost 100% of patients with secondary and early latent syphilis. In most cases, a positive RPR reaction is observed 7 to 10 days after the appearance of the primary chancre or 3 to 5 weeks after infection, then titers decrease. About 30% of patients with late syphilis become non-reactive on the RPR test. A decrease in RPR titer by 4 or more times within 1 year after therapy confirms its effectiveness. In 90 - 98% of cases after treatment for syphilis, the RPR test result becomes negative. The test is not specific, so false-positive reactions may occur. Antilipoid antibodies can appear frequently in autoimmune diseases. If a positive result is obtained in the RPR test, the patient should be examined by a dermatovenerologist with an additional blood test - antibodies to Treponema pallidum IgG/IgM. These two studies are complementary; the combination of RPR and the IgG, IgM ELISA test represents the best screening test for detecting or excluding syphilis at all stages.
Syphilis. Enzyme immunoassay for the detection of total antibodies of class M and G to the causative agent of syphilis
What kind of analysis is this? This is the detection of total class M and G antibodies to the causative agent of syphilis, which can be used as an effective ultra-sensitive screening test for diagnosing early syphilis infection.
At the moment, the Wasserman reaction is considered outdated, and since 2006 it has hardly been used to diagnose syphilis. It has been replaced by more sensitive and modern tests. However, the forms still display the unchanged “RW”. The signature “RW” is a tribute to tradition, a small unspoken rule among doctors: leaving the old signature, they now have in mind new modern tests for syphilis.
What biomaterial can be used for research? Venous blood
Treponema pallidum (treponema pallidum) is a bacterium that causes syphilis, a chronic venereal infectious disease that is most often transmitted sexually, for example, through direct contact with a syphilitic ulcer (chancroid), intrauterine infection is also possible.
The source of infection is a sick person. Syphilis is easily curable, but can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. An infected mother can transmit the disease to her fetus, which may develop serious and irreversible changes.
Syphilis is classified as a classic sexually transmitted disease (sexually transmitted disease). The causative agent is Treponema pallidum. Syphilis is characterized by a slow progressive course. In later stages, it can lead to severe damage to the nervous system and internal organs
Symptoms of syphilis
The symptoms of syphilis are very varied. They vary depending on the stage of the disease. There are three stages of syphilis:
Primary syphilis occurs after the end of the incubation period. At the site of penetration of the pathogen into the body (genital organs, oral mucosa or rectum), a painless ulcer with a dense base (chancroid) appears. 1-2 weeks after the onset of the ulcer, the nearest lymph nodes enlarge (if the ulcer is localized in the mouth, the submandibular nodes enlarge; if the genital organs are affected, the inguinal ones become enlarged). The ulcer (chancroid) heals on its own within 3-6 weeks. after occurrence.
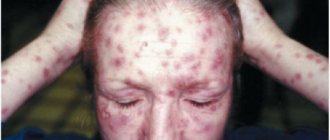
Secondary syphilis begins 4-10 weeks after the appearance of the ulcer (2-4 months after infection). It is characterized by a symmetrical, pale rash over the entire body, including the palms and soles. The appearance of a rash is often accompanied by headache, malaise, and fever (as with the flu). Lymph nodes throughout the body enlarge. Secondary syphilis occurs in the form of alternating exacerbations and remissions (asymptomatic periods). In this case, hair loss on the head is possible, as well as the appearance of flesh-colored growths on the genitals and in the anus (condylomas lata).
Tertiary syphilis occurs in the absence of treatment many years after infection. This affects the nervous system (including the brain and spinal cord), bones and internal organs (including the heart, liver, etc.).
If infected during pregnancy, the child may develop congenital syphilis.
Complications of syphilis
According to scientific research, in the absence of treatment, about a third of patients develop tertiary syphilis. About a quarter of patients die because of it. Congenital syphilis can cause severe damage or death to the child.
Treatment of syphilis
It is quite complex and requires further long-term observation. It is worth noting that treatment of syphilis in the early stages is not particularly difficult in terms of choosing drugs. The peculiarity of Treponema pallidum is that it still retains sensitivity to penicillin , which is the drug of choice for syphilis.
In case of an allergy to penicillin, antibiotics from a number of macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin) or cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, etc.) are prescribed. The drugs are prescribed intramuscularly or in tablets. Treatment of active forms of the disease takes place in an inpatient setting; patients with a latent form can receive outpatient therapy. The duration of treatment depends on the stage of the disease and can take from several weeks to several years.
Antibodies to the causative agent of syphilis
When a person comes into contact with T. pallidum, their immune system reacts by producing antibodies to the bacterium. Two types of antibodies to Treponema pallidum can be detected in the blood: IgM and IgG. In response to T. pallidum infection, IgM antibodies to T. pallidum are the first antibodies produced by the body. They are detected in most patients at the end of the second week of the disease and are present in them in the primary and secondary stages. Class G immunoglobulins to T. pallidum appear in detectable quantities in the blood 3-4 weeks after infection. Their concentration increases and in the 6th week begins to prevail over the concentration of IgM, reaching a maximum, and then remains at a certain level for a long time. Starting from the 4th week, the amount of both types of immunoglobulins in the blood increases, which leads to a positive test result for total antibodies to T. Pallidum. This allows this test to be used for early diagnosis of T. pallidum infection. After effective treatment, the concentration of immunoglobulins gradually decreases, but this happens slowly; in some cases, antibodies can be detected after a year or more. Syphilis can be treated with antibiotics, and it is preferable to use penicillin derivatives. At an early stage, the disease is treated easier and faster. Longer therapy may be needed for patients infected for more than a year.
Why is the analysis carried out?
Increasing and decreasing indicators
For the diagnosis of syphilis. For examination of all pregnant women for preventive purposes (preferably at the first appointment with a gynecologist, when registering).
When is the study scheduled? For symptoms of syphilis, such as chancroid on the genitals or throat. When a patient is being treated for another STD, such as gonorrhea. When managing pregnancy, because syphilis can be transmitted to the developing fetus and even kill it. When it is necessary to determine the exact cause of the disease if the patient has nonspecific symptoms that are similar to syphilis (neurosyphilis). If the patient is infected, they should repeat the syphilis test after 3, 6, 12 and 24 months to ensure that treatment has been successful.
Results/Normal/Transcript of analysis
Reference values (normal values)
Result: negative. S/CO ratio (signall/cutoff): 0 - 0.9.
A positive result means that the patient has a recently acquired infection. However, a negative result does not always mean that the patient does not have syphilis.
Positive result
A positive result in a previously seronegative patient, as well as a significant increase in titers in paired sera taken at an interval of 7 days, indicates a primary infection. Detection of antibodies to treponema in the blood of a newborn helps confirm the diagnosis of congenital syphilis. In addition, the cause of a positive result may be tertiary or latent syphilis.
Negative result
A negative test result may indicate the absence of infection or its early stage when an immune response has not developed. At the same time, the absence of antibodies in a baby born from an infected mother does not exclude a congenital disease, since antibodies may not yet have formed at the time of the study.
Preparing for the test
Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood
What can affect the result of the analysis?
False-positive results may occur with diseases such as HIV, Lyme disease, malaria, systemic lupus erythematosus, some types of pneumonia, as well as drug addiction and pregnancy. And many other somatic diseases.
Important Notes
- The examination for syphilis must be comprehensive and include taking into account the medical history, clinical picture and confirmation of the diagnosis by laboratory data.
- People who are sexually active should consult a doctor about any suspicious rashes or pain in the genital area.
- If a patient is diagnosed with infection, he/she needs to inform his/her sexual partner so that he/she can also undergo examination and, if necessary, treatment.
- With syphilis, the risk of contracting other sexually transmitted diseases increases, including the risk of contracting HIV, which leads to AIDS.
• Syphilis can also be transmitted through blood transfusion through contaminated medical instruments, so testing before hospital admission is very important.
Shapilova N.V.
Interpretation:
- If anticardiolipin antibodies are detected, a “positive” response is given with a titer value. At very low titers, the answer is “doubtful, it is recommended to repeat the study after 10 - 14 days.” Positive: RPR - primary seropositive syphilis (infection occurred 1 - 3 months ago); secondary seropositive syphilis (infection occurred more than 3 months ago); tertiary seropositive syphilis (infection occurred more than 3 - 4 years ago); the first year after treatment of syphilis; seroresistance after treatment of syphilis; APS is probable (if syphilis is excluded). False positive reaction (see interference).
- In the absence of anticardiolipin antibodies, the answer is “negative”. Negative: absence of infection, early primary (seronegative) syphilis cannot be excluded, late tertiary syphilis cannot be excluded.
Sample result (PDF)
Complexes with this research
Male infertility.
Extended examination Analysis of the state of male reproductive health 29,030 ₽ Composition Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure 23,020 ₽ Composition
Women's check-up No. 1 38 studies for annual preventive examination RUB 19,290 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Men's check-up No. 1 RUB 18,570
- Eight infections. Complex for women 5,310 ₽
- Preparation for IVF for a man 6,060 RUR
- Expanded hospital complex RUB 7,700
- Eight infections. Complex for men 5,310 ₽
What are the blood tests for syphilis?
Assessment of the suitability of serological tests, which are currently the basis for laboratory diagnosis of syphilis, is based on concepts such as sensitivity and specificity. The higher these indicators, the closer to ideal the test is considered.
In addition to diagnosis, a serological test should allow monitoring the effectiveness of treatment. Basically, serological diagnosis is based on testing patients with screening tests, followed by verification of the results with confirmatory tests. The latter are used to distinguish between false positive and false negative results obtained from screening.
All serological methods for diagnosing syphilis are based on the interaction of an indicator antigen with a bioassay, possibly containing antibodies to T. pallidum. The differences between the tests are determined by the nature of the antigen used (treponemal or non-treponemal tests), the principle of the serological test used (flocculation, complement fixation, immunofluorescence, etc.). When choosing a test, technical and economic considerations also play a role: technical simplicity, possibility of automation and financial cost. But if you are not a doctor, you don’t need all this in detail.
The main non-treponemal test remains the microprecipitation reaction with cardiolipin antigen (MP), which is a screening test for screening the population for syphilis. We also use foreign tests VDRL (VDRL), RPR (RPR) similar to MR both in the principle of setting the reaction and in sensitivity and specificity. This method is convenient, cheap and is used as a main screening test, as well as for monitoring cure.
MR often produces false-positive or false-negative results for syphilis. Therefore, to confirm the results of MR, treponemal tests are used, which detect specific antibodies formed in the patient’s body in response to T. pallidum infection. Most often in our country they use:
— enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA/ELISA);
— passive hemagglutination reaction (RPHA).
Another option for ELISA is immunoblotting, which is used in two variants to detect IgG and IgM antibodies to the causative agent of syphilis.
All of the above reactions have approximately the same sensitivity and specificity.
To indicate the degree of positivity of serological tests for syphilis, a system of four pluses is used: 4+ strongly positive reaction, 3+ positive reaction, 2+ weakly positive reaction, 1+ questionable reaction.
It is important to know! That in approximately 85% of patients after successful treatment of syphilis, treponemal tests remain positive for several years, and in some throughout their lives. The control of cure is a non-treponemal test - MR or its analogues.
What does blood mean for syphilis?
You can watch my video about the clinical manifestations of syphilis, so now I will not dwell on describing the signs of syphilis.
It is important to note that no matter what typical signs of syphilis are observed in a patient, the diagnosis of syphilis cannot be made without laboratory confirmation!
Simply put, in order to definitively diagnose syphilis, the patient needs to donate blood for syphilis. If the reactions are positive, then only then does the doctor have the right to make a diagnosis of syphilis. Based on clinical signs, the stage of the disease is determined, but the diagnosis of syphilis cannot be made only from the clinic. This is the law!
Thus, the basis for diagnosing syphilis in a patient is taking a blood test for specific tests or serodiagnostics (from the Latin serum - serum and diagnosis).
Why do some blood reactions to syphilis remain positive after full treatment?
There is no clear answer to this question; it is believed that this is some kind of immune memory.
Thus, after full treatment for syphilis, a person’s reactions to syphilis may remain positive for the rest of their life. This is normal. The patient does not have syphilis. The person is not dangerous, both sexually and in everyday life. He does not need additional treatment.
This rule is reflected in the orders of the Ministry of Health “On improving the serological diagnosis of syphilis” and every dermatovenerologist should know this and warn the patient about it.
That is why all persons who have been treated for syphilis must be under clinical and serological control for various periods (from three months to three years) depending on the stage of the disease at the time of treatment.
In fact, the vast majority of patients do not undergo clinical and serological control. The main reasons for this are increased population migration in recent years, as well as widespread unofficial treatment of syphilis.
As a result, a situation often arises when a person had syphilis several years ago, was treated and forgot about it. And then he needed to donate blood for syphilis, for example, for hospitalization in a hospital. He donated blood and it was positive. And a person has bewilderment and many questions.