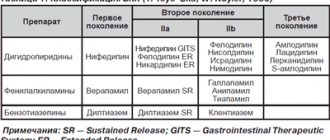
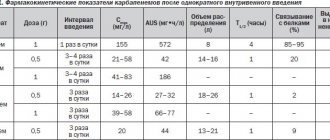
Indications
Ministry of Health of Russia
- E23.2 Diabetes insipidus
- F10.3 Withdrawal state
- F30 Manic episode
- F31 Bipolar affective disorder
- G35 Multiple sclerosis
- G40 Epilepsy
- G40.1 Localized (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with simple partial seizures
- G40.2 Localized (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with complex partial seizures
- G40.3 Generalized idiopathic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes
- G50.0 Trigeminal neuralgia
- G52.1 Lesions of the glossopharyngeal nerve
- G63.2 Diabetic polyneuropathy (E10-E14+ with common fourth character .4)
- R35 Polyuria
- R52.9 Pain, unspecified
- R63.1 Polydipsia
FDA recommendations
- Partial seizures with complex symptoms
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal)
- Mixed seizures
- Trigeminal neuralgia pain
- Acute episode of mania/mixed mania
UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency guidelines
- Generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures
- Trigeminal neuralgia pain
- Prevention of manic-depressive psychosis in patients not responding to lithium treatment
Proprothene-100
To date, the most studied of the antibody drugs is Proproten-100, which contains potentiated antibodies to the brain-specific protein S-100 (AS-100). The drug Proproten has been studied at all levels of organization of neuronal structures: cellular, intercellular (synaptic), structural, systemic. The most specific of the studied effects can be considered the sensitizing effect of AS-100 on the cell membrane of neurons. The unusual biological effect at the clinical level is manifested by a balanced effect on the mental status of patients. Depending on the initial condition of the patients, the drug has both a sedative and a stimulating effect.
Treatment regimen
Dosage and dose selection
- 400-1200 mg/day
- Children under 6 years: 10-20 mg/kg per day
Bipolar disorder, seizures (adults, children over 13): Start with 200 mg twice daily; increase every week by 200 mg/day in several doses; maximum for adults 1200 mg/day; maximum for children 13-15 years old – 1000 mg/day; some patients may require doses up to 1600 mg/day.
Trigeminal neuralgia pain: start with 100 mg twice daily; increase every week by 200 mg/day in divided doses.
- Best taken with food
- Slowly increasing the dose delays the onset of the therapeutic effect, but increases tolerance to sedative side effects
- If other sedatives are being taken, increase the dose slowly
- Over time, after several weeks of treatment, dose adjustment is required
How quickly does it work?
Response to acute mania may occur within a few weeks.
It may take several months for your mood to stabilize.
Cramps should stop after 2 weeks.
Expected Result
Disappearance of symptoms.
Treatment can be continued indefinitely to prevent mania or seizures.
If it doesn't work
(for bipolar disorder)
Increase the dose;
Switch to another drug or add another drug;
Connect psychotherapy;
Determine if there is a comorbid condition
How to stop taking it
Reduce the dose gradually. Abruptly stopping use increases the risk of bipolar disorder relapse. In epilepsy, abrupt cessation can trigger seizures [1].
Treatment combinations
- Lithium
- Valproic acid
- Atypical antipsychotics
- Lamotrigine
- Antidepressants (with caution, as there is a risk of mood destabilization) [1].
Mechanism of action of carbamazepine
According to its chemical structure, carbamazepine belongs to the group of tricyclic antidepressants.
In clinical practice, it is used as a sedative, normothymic and anticonvulsant substance. Pharmaceutical preparations based on it are characterized by low toxicity and low potential for addiction. Unfortunately, the mechanism of action of the substance is still not fully understood. It has been established that its administration makes it possible to stabilize the cell membranes (membranes) of hyperstimulated cells of the nervous system, for example, in epilepsy or acute psychosis with convulsive syndrome. At the same time, it suppresses the development of repeated excitation and inhibits the conduction of neuronal impulses.
Cautions and contraindications
- You need to watch for bleeding, bruising, mouth ulcers, infections, and fever. Taking carbamazepine increases the risk of aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis by 5-8 times.
- Use cautiously with MAOIs.
- May cause exacerbation of angle-closure glaucoma.
- Reduces the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives.
- Restriction of fluid intake may be necessary due to the risk of interfering with antidiuretic hormone production.
- Cannot be used if the patient has a history of bone marrow suppression.
- Do not use if the patient is allergic to any tricyclic compounds.
CARBAMAZEPINE (tablets)
also applies to the treatment of alcoholism.
Carbamazepine blocks Na channels, which leads to stabilization of the neuronal membrane and a decrease in synaptic conduction of impulses. I didn't quite understand what he was talking about. I paid the doctor 7,300 rubles and we said goodbye. The husband slept until the morning. And when he woke up, he again ran to the store for beer. That is, the drip improved his condition, but did not bring him out of the binge. I bought Carbamazepine and B vitamins for the brain at the pharmacy. First I gave him two Carbamazepine tablets. But the husband did not calm down. I had to close the doors and hide the keys so that I wouldn’t run for beer again. Then she gave him 4 more tablets. Finally the medicine worked and the husband fell asleep. I slept for about three hours. When I woke up, I couldn’t get to my feet, I couldn’t even speak. I realized that his lack of coordination was due to the medication. But it’s better than binge drinking. In the morning he told about the horror he experienced. I thought it was a stroke. I felt absolutely sober, I understood everything, but I could not move or speak. It was an overdose combined with alcohol. By morning, the lack of coordination had almost disappeared. He felt slow and spoke slowly. I realized that he had forgotten to take his medication, and I encouraged him to think that it was the effects of alcohol and possibly a stroke. His desire to drink had passed. The next day, the lethargy and lack of coordination also disappeared.
After 3 months, I saw him drunk in the yard. I took her home. I crushed 4 Carbamazepine tablets in a mortar. Then she poured half a glass of fermented baked milk and added crushed Carbamazepine to it. I gave this to my husband to drink. He quickly fell asleep. Slept all night. In the morning I woke up completely sober. There was no miscoordination. The speech was normal. There was no desire to drink. In general, you need to prevent binge drinking as quickly as possible, use Carbamazepine in small doses so that there is no miscoordination.
Now we sometimes even drink dry wine on holidays. You cannot drink strong alcoholic drinks or beer. They make you want to drink more. I don't keep a tight rein on my husband. I know that prohibitions can provoke breakdowns. And dry or semi-sweet wine does not make him want to drink more and more. Drinks no more than one glass. Life has changed dramatically. No binge drinking. We don’t go to drug addiction specialists anymore. We don't spend a lot of money on them. I got rid of anxiety. Now I always have Carbamazepine in my medicine cabinet. It’s only a pity that not a single narcologist told me about this medicine earlier.
Special patient groups
Patients with kidney problems
The dose needs to be reduced [1].
Patients with liver disease
Use with caution [1].
Patients with heart disease
Use with caution [1].
Elderly patients
In older people, side effects are more pronounced.
Children and teenagers
- Approved for use in epilepsy.
- Children 6-12 years: initial dose 100 mg twice daily; increase every week by 100 mg/day in several doses; maximum dose 1000 mg/day; maintenance dose 400-800 mg/day.
- Children 5 years and younger: initial dose 10-20 mg/kg per day 2-3 times daily; increase every week if there is a need; maximum dose 35 mg/kg/day.
Pregnant
- In the first trimester, it increases the risk of fetal developmental abnormalities. If treatment continues, tests should be performed to identify pregnancy pathologies. To reduce the risk, you should start taking folic acid (1 mg/day) earlier than usual.
- For bipolar disorder, carbamazepine should be discontinued until pregnancy occurs. During pregnancy, atypical antipsychotics are preferred.
Breast-feeding
- It is recommended that you stop taking carbamazepine or stop breastfeeding.
Carbamazepine
It is effective against all symptoms when withdrawing from binge drinking and can be the drug of choice when interrupting mild to moderate binge drinking. The lack of interaction with alcohol allows the drug to be used even if it is present in the blood. It has been established that Carbamazepine affects the neuronal transmission of GABA, glutamate, norepinephrine, acetylcholine and dopamine. Monotherapy with carbamazepine is effective for mild to moderate withdrawal syndrome; for severe withdrawal, benzodiazepines are recommended. The undoubted advantage of carbamazepine is the absence of a euphoric effect and the risk of dependence on the drug.
Side effects and other risks
Mechanism of side effects
The causes of side effects of carbamazepine are theoretically associated with excessive effects on voltage-gated sodium channels.
Major metabolites may cause side effects.
Side effects
- Sedation, dizziness, confusion, unsteadiness, headache.
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
- Leukopenia
- Rash
- Dangerous side effects: aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, purpura, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Parhon syndrome with hyponatremia.
- Weight gain: yes, but infrequently
- Sedation: yes, and may be significant and, for some patients, excessively strong
What to do about side effects
- Wait;
- Take in the evening to avoid sedation;
- To avoid irritation to the stomach, take with food;
- Switch to another drug [1].
Long term use
Reduces libido;
Monitoring the functioning of the liver, kidneys, and thyroid gland is required, as well as regular general blood tests and sodium level measurements.
addictive
No.
Overdose
May be fatal; nausea, vomiting, involuntary movements, cardiac arrhythmias, difficulty breathing, sedation, coma.
Use for alcoholism
In the treatment of any pathological conditions associated with long-term alcohol abuse, one-size-fits-all medications are never used. The choice of each medicine is approached with the utmost rigor, since in some cases it can only worsen the situation. The patient is thoroughly examined, after which the benefit/risk factor is assessed.
Indications
The main spectrum of action of the drug is the relief of seizures; to a lesser extent, the emotional background is normalized. Carbamazepine is used for alcoholism if the following indications exist:
- The structure of the syndrome of pathological craving for alcohol contains affective (psycho-emotional) disorders.
- Relief of withdrawal symptoms - “withdrawal” during the period of cessation of abuse in fully formed true binge drinking.
- Prevention of the development of convulsive attacks in cases of aggravated medical history.
- The patient is not suitable for other antidepressants or antiepileptic drugs.
Carbamazepine has been shown to be as effective as or superior to barbital, tiapride, clomethiazole, oxazepam, and placebo in open-label and double-blind studies. A double-blind study conducted by Malcolm et al. and repeated by Stuppaeck et al. demonstrated equal effectiveness of carbamazepine and oxazepam in relieving alcohol withdrawal. However, no differences were found in laboratory testing of liver and blood function, although carbamazepine may worsen these indicators. In addition to relieving withdrawal symptoms, carbamazepine, compared to oxazepam, more effectively improves the general condition of the patient, assessed according to the SCL-90-R criteria.”
Portal about medicines Medi Ru
Carbamazepine also enhances the positive effects of other neurotropic drugs that are used during the period of active anti-relapse treatment. In small dosages, it improves the emotional background, eliminates dysphoric symptoms (anxiety, depression, apathy) and reduces convulsive readiness. At the same time, the craving for drinking alcohol is suppressed.
Side effects and contraindications
The dose of the anticonvulsant is selected individually; the drug is usually well tolerated. Carbamazepine is contraindicated in case of clinically significant cardiac rhythm and conduction disturbances, hypersensitivity to tricyclic antidepressants, acute porphyria and a history of myelosuppression. The following side effects are possible:
- disturbance of taste and speech
- headache
- relapse of psychosis
- depression
- appearance of hallucinations
- dizziness
- excessive psychomotor agitation
- nystagmus – multi-frequency involuntary eye movements
- diplopia - double vision
- noise in ears
- conjunctivitis
- peripheral neuropathy
- muscle weakness up to paresis
- atrioventricular block
- worsening heart failure, including due to hemodynamic disorders (hypo- or hypertension)
- kidney damage
- nausea
- vomit
- toxic hepatitis
- thromboembolic complications if there is a predisposition
- electrolyte disorders
- allergic reactions