Many physiological processes occurring in the human body cannot be carried out without the presence of amino acids. These are broken down proteins that are absorbed into the blood. The human body needs all types of amino acids.
Amino acids can be replaceable (their synthesis occurs in the human body) and essential (we get them with food). Ordinary people do not need to monitor the presence of certain amino acids in the body, but athletes and sportsmen should do this, because The need for various types of digested proteins increases significantly. Therefore, they should be taken in the form of sports nutrition.
One of the most important amino acids is ornithine, which has many functions.
Ornithine (L-ornithine)[edit | edit code]
Ornithine cycle (urea cycle, Krebs-Henseleit cycle)
Ornithine
(English: Ornithine) is an amino acid that is used in bodybuilding to improve athletic performance. Ornithine is not part of the body's proteins, but is present in the body as a natural component. Ornithine can be converted into arginine, proline and polyamines.
Ornithine is used in sports nutrition because it is believed to have an anti-catabolic effect and anabolic activity, but this does not have a clear scientific basis.
Sports supplements often contain Ornithine alpha-ketoglutarate
. This is a molecule of alpha-ketoglutarate and two molecules of ornithine.
Claimed effects[edit | edit code]
- Increased insulin secretion. However, this claim has been refuted by research. [1]
- Immunomodulatory effect[2]
- Suppression of catabolism[3]
- Increased secretion of growth hormone[4]
Functions of ornithine
The main properties of ornithine include:
- Stimulation of somatotropin (growth hormone) production. The synthesis of somatotropin occurs in the pituitary gland (it is generally accepted that during sleep). Intense loads help its production. Due to the production of somatotropin, an increase in muscle tissue and fat burning is observed. Ornithine has a similar effect to arginine, so it is recommended to take it before bed.
- Manifestation of hepatoprotective properties. Ornithine protects the liver from the negative effects of all kinds of toxins contained in medications and food. The amino acid helps in the processes of restoration of liver cells, which is extremely important for all people suffering from various liver pathologies. Research shows that regular use of ornithine can significantly improve blood flow through the liver vessels.
- Stimulation of insulin synthesis. An important property of ornithine is the possibility of its use in bodybuilding by stimulating the synthesis of insulin, which is a powerful anabolic hormone (the most important hormone if weight training is carried out).
- Participation in the processes of urine formation. Ornithine is involved in the processes of formation and excretion of urine, thereby promoting the elimination of toxins (in particular ammonia, a toxic substance formed during the process of protein breakdown). This happens thanks to the ornithine cycle, during which ammonia is converted in the liver into urea and its further removal from the body by the kidneys.
- Participation in the breakdown of fatty acids. Ornithine is able to break down fatty acids, which allows you to obtain additional energy (extremely important for those who are “dry” or losing weight). Also, ornithine, as noted earlier, improves the production of somatotropin, which itself burns fat well even at night.
Ornithine also has a lot of positive characteristics, due to which this amino acid is often used in the treatment of the immune system:
- Strengthening tendons and ligaments.
- Accelerating the healing processes of connective tissue (for cuts, wounds).
- Improving the functioning of the immune system by enhancing the synthesis of glutamine.
- Normalization of acid-base balance.
400 mg L-Ornithine improves sleep[edit | edit code]
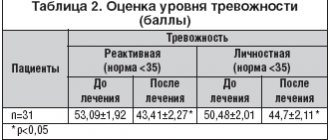
In Japan, a study was conducted on a group of healthy men aged 30-60 years, with complaints of mild stress and moderate asthenia (in other words, chronic fatigue syndrome). There was also a placebo group.
Before bed, for 8 weeks, they received 400 mg of pure L-ornithine. The subjects showed improved sleep quality and better falling asleep than those in the placebo group. In addition, subjects in the Ornithine group slept longer.
As indicated in studies, L-Ornithine may be beneficial for people who live under constant stress.
Doses and use
Ornithine is an extremely relevant supplement in the field of modern fitness and bodybuilding. It is used for the following purposes:
- Breakdown of fatty acids (during “drying”).
- Acceleration of oxidation.
- Increased muscle mass.
- Supports normal functioning of the immune system.
The recommended daily dose for athletes ranges from 500 to 2000 mg (depending on a number of factors). You should take ornithine on an empty stomach and before going to bed.
Often, in order to achieve a greater effect, a combined intake of ornithine and arginine occurs. On the modern market you can find many products that contain ornithine and arginine simultaneously in different ratios. Vivid examples of such drugs are:
- Dynamic Development Night Amino. Ideal for use before bedtime. Contains lysine, ornithine, arginine, vitamin B6. The concentration of all substances is maximum.
- Maxler Arginine/Ornithine/Lysine. Lysine, ornithine and arginine in this product are presented in a 1:1:1 ratio.
- Twinlab L-Arginine L-Ornithine. Ornithine and arginine in a ratio of 1:2.
- NOW: L-Ornithine 500 mg. The product contains ornithine in its pure form without additives.
Ornithine is not recommended for pregnant women (intestinal spasms and nausea occur). The amino acid has no other contraindications.
Admission rules
The usual prophylactic dose is 1-2 capsules per day of 500 mg. It is not recommended to take doses over 20-30 grams per day for a long time. Long-term use (over several weeks) of very large doses of arginine can cause reversible thickening of the skin, which disappears when the dose is reduced.
Most bodybuilders need 3-5 g of arginine (one-time dose). Experts advise calculating the dosage based on the following indicator: per kilogram of body weight there should be 115 mg of arginine.
Arginine is not recommended for pregnant and breastfeeding women. Arginine should not be used for schizophrenia and other mental illnesses. Arginine is contraindicated in cases of active herpes virus disease (simplex, zoster and genital), since viruses use this amino acid for their replication. Arginine is not recommended for children during periods of active growth (as it can cause gigantism by affecting growth hormone). Arginine should not be combined with nitroglycerin and Viagra.
Arginine improves mood, makes a person more active, proactive and resilient, and improves sexual function.
Buy Twinlab L-Arginine 500mg.
Study
Fatigue from exercise
L-Ornithine supplementation reduced fatigue in subjects in a placebo-controlled bicycle ergometer study. Results showed that L-ornithine has anti-fatigue effects by increasing energy efficiency and promoting ammonia excretion.[4][5]
Weightlifting Supplement
Amino acid supplements, including L-ornithine, are often marketed to bodybuilders and weightlifters with claims of increasing human growth hormone (HGH) levels, muscle mass and strength. A clinical study showed that L-ornithine at a dose of 2 g/day did not increase growth hormone.[6] A review on this topic concluded: “The use of certain amino acids to stimulate growth hormone production in athletes is not recommended.”[7]
Cirrhosis
L-Ornithine L-aspartate (LOLA), a stable salt of ornithine and aspartic acid, has been used to treat cirrhosis.[8]
How to take ornithine
Features of use are dictated by the specifics of the produced form of the dietary supplement. You should first consult with a specialist.
Capsules and tablets with ornithine are taken 3-6 g after meals. These forms should be taken with water or juice.
For parenteral administration, 2-6 g of the active substance is usually used:
- intramuscularly - the daily dose ranges from 4 to 14 g (for 2 injections);
- intravenous bolus – 4 g per day are used (for 1 injection);
- infusion – 20 g of amino acid are dissolved in 500 ml, the rate of administration is 5 g/hour (the maximum daily dosage should not exceed 40 g).
Instructions for use, in this regard, are mandatory for preliminary study. The average course duration is 2-3 weeks.
Ornithine in products
The amino acid is found in royal jelly of bees, bee drone brood, pumpkin seeds, hazelnuts and walnuts. Ornithine is formed as a result of endogenous reactions from arginine, which is found in eggs, meat and fish products.
© Michelle - stock.adobe.com
Therapeutic effect of arginine
Arginine belongs to the category of amino acids that are produced in the body only under certain conditions. With the slightest pathology, the body does not have time to cope with the production of arginine. And then it must be taken in the form of dietary supplements.
The process of protein synthesis in the body is constant, but in the case when at least one essential amino acid is missing, their formation is suspended, and due to the impossibility of implementing many biochemical processes, this leads to the development of various diseases.
In addition, the body’s ability to synthesize arginine decreases with age; from the age of 35 it is necessary to purposefully replenish its amount in the body.
With arginine deficiency, nervous and mental disorders occur, weakened immunity, persistent hypertension, weakened memory, diabetes mellitus, malignant neoplasms, functional disorders of the reproductive system including impotence, diseases of internal organs, fatty infiltration of the liver, slow growth and puberty, obesity.
Arginine relaxes the smooth muscles of all blood vessels, ensures normal blood flow and oxygen delivery to the heart muscle, brain, and limbs.
It dilates blood vessels and increases their blood flow. It is not without reason that in Japan, Greece and Israel, cardiologists inject arginine directly into the coronary artery of patients with angina pectoris, which dramatically restores blood circulation.
Arginine strengthens the immune system, as nitric oxide stimulates the production of macrophages and necrophil cells that absorb low-quality, dead cells and remove them from the body. Arginine contributes to a sharp increase in the activity of cells in the defense system of our body.
Arginine helps with cancer by slowing down the growth of benign and malignant tumors. Thanks to the normalization of hormonal levels, the development and resorption of hormone-dependent tumors (fibroids, fibroids, mastopathy, etc.) and thyroid nodules is inhibited.
Arginine performs detoxifying functions, removing toxins from the body and preventing them from accumulating. In fact, this amino acid is a biological assistant for the kidneys, improving blood purification.
Arginine accelerates the healing of wounds, tendon sprains, and bone fractures.
Arginine has a remarkable psychotropic effect. Arginine can heal and regenerate nerves.
Arginine increases libido, increases potency and stimulates spermatogenesis.
This amino acid is necessary for the normal functioning of the pituitary gland and the production of growth hormone.
Arginine is necessary for anyone who seriously cares about beauty and longevity. Good metabolism and rapid tissue repair make people younger and more energetic. By providing the body with a daily and sufficient intake of Arginine, we can prolong our life.
Sources of arginine
L-arginine is not considered an essential amino acid, which must be supplied to the body through food. Like glutamine, it is a conditionally essential amino acid, the need for which increases under conditions of stress or during growth.
Arginine is a conditionally essential amino acid. In an adult and healthy person, arginine is produced by the body in sufficient quantities. At the same time, in children and adolescents, in elderly and sick people, the production of arginine is often either insignificant or absent.
Natural sources of arginine are products such as soy, chocolate, and cocoa. Arginine is rich in watermelon, nuts, seafood, seaweed, oatmeal and wholemeal bread, raisins, sunflower and sesame seeds, brown rice and soy protein concentrate. For comparison, 100 grams of peanuts provide 2.5 g of L-arginine.
Application in sports
Athletes use ornithine for:
- increased lipolysis during drying;
- gaining muscle mass;
- activation of oxidation processes;
- following the Dukan diet.
The substance has gained popularity in nutrition regimens due to its ability to enhance the excretion of metabolic products, which are formed in significant quantities during training, as well as due to stimulation of the production of insulin and somatotropin, which promote muscle growth.
References
- Weast, Robert S., ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
(62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. item S-408. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8. - Weber A.L., Miller S.L. (1981). "The Reasons for the Twenty Encoded Protein Amino Acids" (PDF). Journal of Molecular Evolution
.
17
(5): 273–84. Doi:10.1007/BF01795749. PMID 7277510. - "Biosynthesis of ornithine." Queen Mary School of Biological and Chemical Sciences, University of London. Archived from the original on 2012-04-14. Retrieved 2007-08-17. Magazine citation required | log = (Help)
- Sugino T., Shirai T., Kajimoto Y., Kajimoto O. (November 2008). "L-ornithine supplementation reduces physical fatigue in healthy volunteers by regulating lipid and amino acid metabolism." Nutrition Research
.
28
(11): 738–43. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2008.08.008. PMID 19083482. - Demura S., Yamada T., Yamaji S., Komatsu M., Morishita K. (October 2010). "Effects of oral L-ornithine hydrochloride ingestion on performance during additional exhaustive exercise on a bicycle ergometer and ammonia metabolism during and after exercise." European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
.
64
(10): 1166–71. Doi:10.1038/ejcn.2010.149. PMID 20717126. - Fogelholm GM, Näveri HK, Kiilavuori KT, Härkönen MH (September 1993). "Low-Dose Amino Acid Supplementation: No Effect on Serum Human Growth Hormone and Insulin in Male Weightlifters." International Journal of Sports Nutrition
.
3
(3): 290–7. Doi:10.1123/ijsn.3.3.290. PMID 8220394. - Chromiak J. A., Antonio J. (2002). "Athletes' Use of Amino Acids as Growth Hormone-Releasing Agents." Nutrition
.
18
(7–8): 657–61. Doi:10.1016/s0899-9007(02)00807-9. PMID 12093449. - Sikorska H, Cianciara J, Wiercińska-Drapało A (June 2010). "[Physiological functions of L-ornithine and L-aspartate in the body and the effectiveness of L-ornithine-L-aspartate administration under conditions of relative deficiency]". Polish Mercuriusz Lekarski
.
28
(168): 490–5. PMID 20642112.
Analogs
For pathologies of the liver, analogues can be used:
- Artichoke, characterized by choleretic, antioxidant and diuretic effects.
- Silymarin (milk thistle extract), which enhances the regenerative abilities of the liver.
- Indole-3-Carbinol, exhibiting detoxifying and antiradical effects.
© M.studio – stock.adobe.com